|
CDK5R1
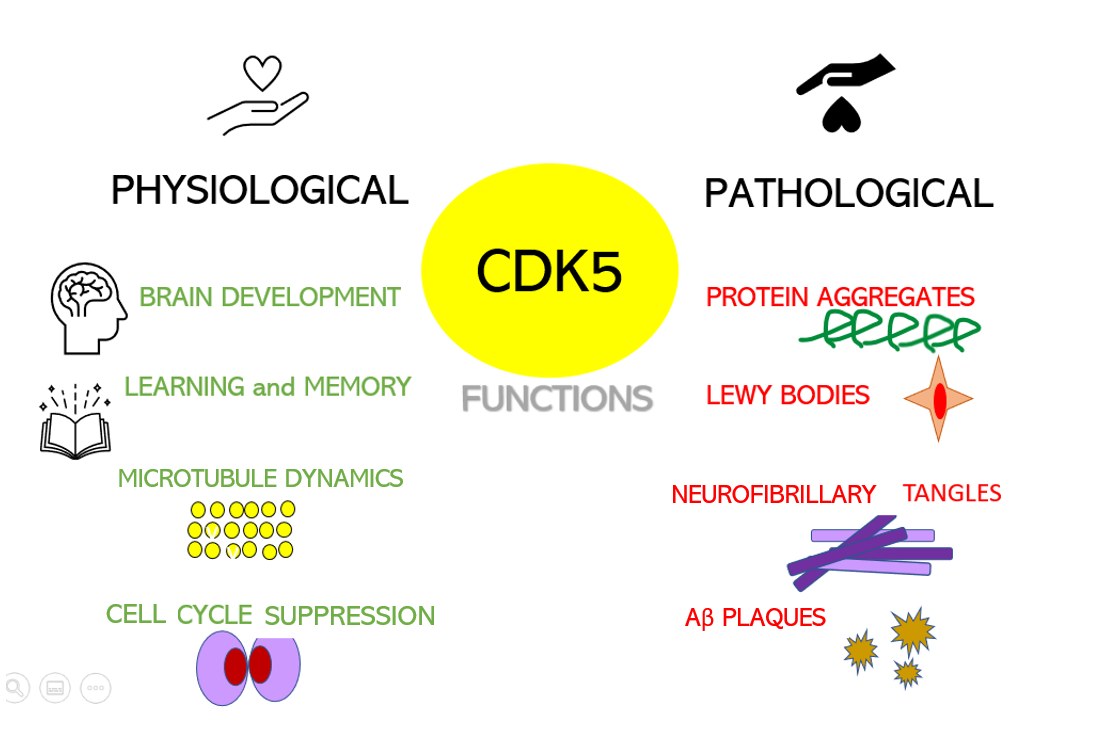
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK5R1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene (p35) is a neuron-specific activator of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5); the activation of CDK5 is required for proper development of the central nervous system. The p35 form of this protein is proteolytically cleaved by calpain, generating a p25 form. The cleavage of p35 into p25 results in relocalization of the protein from the cell periphery to nuclear and perinuclear regions. P25 deregulates CDK5 activity by prolonging its activation and changing its cellular location. The p25 form accumulates in the brain neurons of patients with Alzheimer's disease. This accumulation correlates with an increase in CDK5 kinase activity, and may lead to aberrantly phosphorylated forms of the microtubule-associated protein tau, which contributes to Alzheimer's disease. In melanocytic cells CDK5R1 gene expression may be regulated by MITF. Intera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 5
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a protein, and more specifically an enzyme, that is encoded by the Cdk5 gene. It was discovered 15 years ago, and it is saliently expressed in post-mitotic central nervous system neurons (CNS). The molecule belongs to the cyclin-dependent kinase family. Kinases are enzymes that catalyze reactions of phosphorylation. This process allows the substrate to gain a phosphate group donated by an organic compound known as ATP. Phosphorylations are of vital importance during glycolysis, therefore, making kinases an essential part of the cell due to their role in the metabolism, cell signaling, and many other processes. Structure Cdk5 is a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase, which was first identified as a CDK family member due to its similar structure to CDC2/CDK1 in humans, a protein that plays a crucial role in the regulation of the cell cycle. The gene Cdk5 contains 12 exons in a region that contains around 5000 nucleotides (5kb), as it was deter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDK5RAP2
CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK5RAP2'' gene. It has necessary roles in the formation and stability of microtubules from the centrosome and has been found to be linked to human brain size variation in males. Multiple transcript variants exist for this gene, but the full-length nature of only two has been determined. CDK5RAP2 is homologous to the ''Drosophila'' protein centrosomin (cnn) and paralogous to myomegalin, which in mammals contains an Olduvai domain, a domain implicated in human brain size evolution. Function CDK5RAP2 is necessary for the proper formation, anchoring and orientation of microtubules from the centrosome. It binds with the γ-tubulin ring complex (γTuRC), and this is required for the γTuRC to attach to the centrosome. CDK5RAP2 also binds to p25, a form of CDK5R1 that serves as the activating subunit of CDK5, which is involved in the regulation of neuronal differentiation. CDK5RAP2 th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinin, Alpha 1
Alpha-actinin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ACTN1'' gene. Function Alpha actinins belong to the spectrin gene superfamily which represents a diverse group of cytoskeletal proteins, including the alpha and beta spectrins and dystrophins. Alpha-actinin-1 is an F-actin cross-linking protein – a bundling protein that is thought to anchor actin to a number of intracellular structures. Alpha-actinin-1 is a non-muscle cytoskeletal isoform found along microfilament bundles and adherens-type junctions, where it is involved in binding actin to the membrane. In contrast, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle isoforms are localized to the Z-disc and analogous dense bodies, where they help anchor the myofibrillar actin filaments. Interactions Alpha-actinin-1 has been shown to interact with: * CDK5R1, * CDK5R2, * Collagen, type XVII, alpha 1, * GIPC1, * PDLIM1, * Protein kinase N1, * SSX2IP, and * Zyxin. *PTPRT (PTPrho) See also * Actinin Actinin is a microfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphiphysin
Amphiphysin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AMPH'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein associated with the cytoplasmic surface of synaptic vesicles. A subset of patients with stiff person syndrome who were also affected by breast cancer are positive for autoantibodies against this protein. Alternate splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Additional splice variants have been described, but their full length sequences have not been determined. Amphiphysin is a brain-enriched protein with an N-terminal lipid interaction, dimerisation and cell membrane, membrane bending BAR domain, a middle clathrin and adaptor binding domain and a C-terminal SH3 domain. In the brain, its primary function is thought to be the recruitment of dynamin to sites of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. There are 2 mammalian amphiphysins with similar overall structure. A ubiquitous splice form of amphiphysin-2 (BIN1) that does not contain cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcription. In humans, the CTNNB1 protein is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. In ''Drosophila'', the homologous protein is called ''armadillo''. β-catenin is a subunit of the cadherin protein complex and acts as an intracellular signal transducer in the Wnt signaling pathway. It is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to Plakoglobin, γ-catenin, also known as plakoglobin. β-Catenin is widely expressed in many tissues. In cardiac muscle, β-catenin localizes to adherens junctions in intercalated disc structures, which are critical for electrical and mechanical coupling between adjacent cardiomyocytes. Mutations and overexpression of β-catenin are associated with many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAMK2A
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit alpha (CAMKIIα), protein kinase , is one subunit of CamKII, a protein kinase (i.e., an enzyme which phosphorylates proteins) that in humans is encoded by the ''CAMK2A'' gene. Function The product of the CAMK2A gene is an enzyme that belongs to the serine/threonine-specific protein kinase family, as well as the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II subfamily. Ca2+ signaling is crucial for several aspects of synaptic plasticity at glutamatergic synapses. This enzyme is composed of four different chains: alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. The alpha chain encoded by this gene is required for hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) and spatial learning. In addition to its calcium-calmodulin (CaM)-dependent activity, this protein can undergo autophosphorylation, resulting in CaM-independent activity. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. According to a 2018 study by Bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein SET
Protein SET, also known as Protein SET 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SET'' gene. Interactions Protein SET has been shown to interact with: * Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A, * CDK5R1, * KLF5, * NME1, and * TAF1A TATA box-binding protein-associated factor RNA polymerase I subunit A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''TAF1A'' gene. Function Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I requires the formation of a complex composed of the TA .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Histone Acetyltransferase Inhibitor {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calpain
A calpain (; , ) is a protein belonging to the family of calcium-dependent, non-lysosomal cysteine proteases ( proteolytic enzymes) expressed ubiquitously in mammals and many other organisms. Calpains constitute the C2 family of protease clan CA in the MEROPS database. The calpain proteolytic system includes the calpain proteases, the small regulatory subunit CAPNS1, also known as CAPN4, and the endogenous calpain-specific inhibitor, calpastatin. Discovery The history of calpain's discovery originates in 1964, when calcium-dependent proteolytic activities caused by a "calcium-activated neutral protease" (CANP) were detected in brain, lens of the eye and other tissues. In the late 1960s the enzymes were isolated and characterised independently in both rat brain and skeletal muscle. These activities were caused by an intracellular cysteine protease not associated with the lysosome and having an optimum activity at neutral pH, which clearly distinguished it from the cathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years. The causes of Alzheimer's disease remain poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progression of the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |