|
C3b
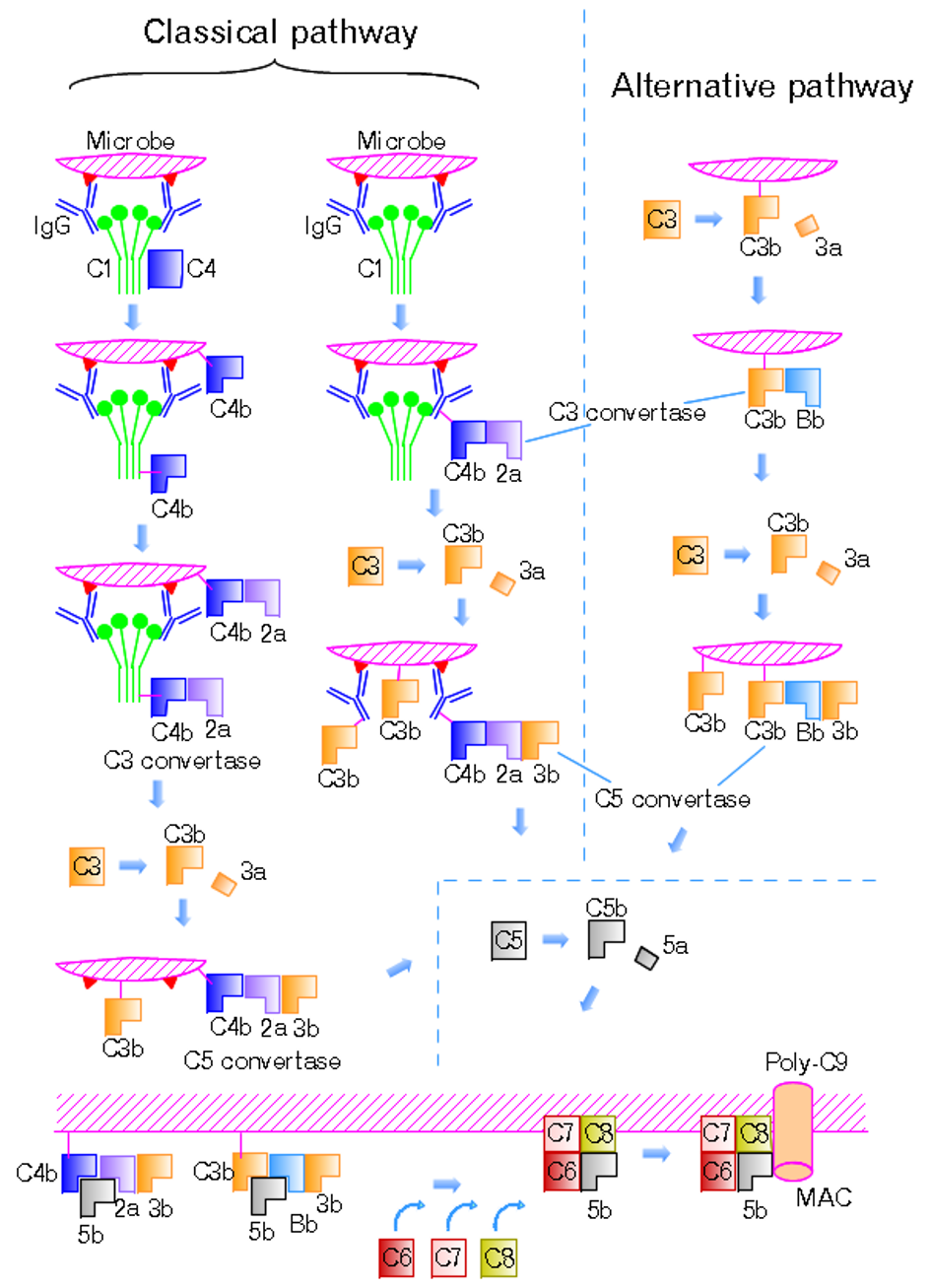
C3b is the larger of two elements formed by the cleavage of complement component 3, and is considered an important part of the innate immune system. C3b is potent in opsonization: tagging pathogens, immune complexes (antigen-antibody), and apoptotic cells for phagocytosis. Additionally, C3b plays a role in forming a C3 convertase when bound to Factor B (C3bBb complex), or a C5 convertase when bound to C4b and C2b (C4b2b3b complex) or when an additional C3b molecule binds to the C3bBb complex (C3bBb3b complex). C3b's ability to perform these important functions derives from its ability to covalently bind to the surface of invading pathogens within an organism's body. The cleavage of C3 leaves C3b with an exposed thioester bond, allowing C3b to effectively coat and tag foreign cells by covalently binding to hydroxyl (-OH) and amine (-NH2) groups on foreign cell surfaces. This cleavage can occur via three mechanisms (classical pathway, alternative pathway and lectin pathway) that ult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C3-convertase
C3 convertase (''C4bC2b'', formerly ''C4b2a'') belongs to family of serine proteases and is necessary in innate immunity as a part of the complement system which eventuate in opsonisation of particles, release of inflammatory peptides, C5 convertase formation and cell lysis. C3 convertase can be used to refer to the form produced in the alternative pathway (C3bBb) or the classical and lectin pathways (C4bC2b, formerly C4b2a). Once formed, both C3 convertases will catalyze the proteolytic cleavage of C3 into C3a and C3b (hence the name "C3-convertase"). The smaller fragment called C3a serves to increase vascular permeability and promote extravasation of phagocytes, while the larger C3b fragment can be used as an opsonin or bind to either type of C3 convertase to form the trimolecular C5 convertase to activate C5 for the membrane attack complex. Formation C3 convertase formation can occur in three different pathways: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. Alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C5-convertase
C5 convertase is an enzyme belonging to a family of serine proteases that play key role in the innate immunity. It participates in the complement system ending with cell death. There are four different C5 convertases able to specifically convert the protein C5 to C5a and C5b fragments. Two of the convertases are physiological complement enzymes, associate to the cell-surface and mediate the classical pathway (C4b2b3b, or ''C4b2a3b'' depending on source) or the alternative pathway (C3bBbC3b) of complement system. Two fluid phase C5 convertases have been described: the classical pathway enzyme, C4b2boxy3b and the cobra venom factor-dependent C5 convertase, CVFBb. Structure Cell-bound C3 and C5 convertase differ in their C3b requirement. C3-convertase (C3bBb) need only one molecule of C3b to form, whereas two or more C3b are required for generation of C5 convertase (C3bBb). It means, when C3b is randomly distributed on the surface of a cell, only C3 convertase activity appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Complement Pathway
The alternative pathway is a type of cascade reaction of the complement system and is a component of the innate immune system, a natural defense against infections. The alternative pathway is one of three complement pathways that opsonize and kill pathogens. The pathway is triggered when the C3b protein directly binds a microbe. It can also be triggered by foreign materials and damaged tissues. Cascade This change in shape allows the binding of plasma protein Factor B, which allows Factor D to cleave Factor B into Ba and Bb. Bb remains bound to C3(H2O) to form C3(H2O)Bb. This complex is also known as a fluid-phase C3-convertase. This convertase, the alternative pathway C3-convertase, although only produced in small amounts, can cleave multiple C3 proteins into C3a and C3b. The complex is believed to be unstable until it binds properdin, a serum protein. The addition of properdin forms the complex C3bBbP, a stable compound which can bind an additional C3b to form alternativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 3
Complement component 3, often simply called C3, is a protein of the immune system. It plays a central role in the complement system and contributes to innate immunity. In humans it is encoded on chromosome 19 by a gene called ''C3''. Function C3 plays a central role in the activation of the complement system. Its activation is required for both classical and alternative complement activation pathways. People with C3 deficiency are susceptible to bacterial infection. One form of C3-convertase, also known as C4b2a, is formed by a heterodimer of activated forms of C4 and C2. It catalyzes the proteolytic cleavage of C3 into C3a and C3b, generated during activation through the classical pathway as well as the lectin pathway. C3a is an anaphylotoxin and the precursor of some cytokines such as ASP, and C3b serves as an opsonizing agent. Factor I can cleave C3b into C3c and C3d, the latter of which plays a role in enhancing B cell responses. In the alternative complement pathway, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Receptor 1
Complement receptor type 1 (CR1) also known as C3b/C4b receptor or CD35 (cluster of differentiation 35) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CR1'' gene. This gene is a member of the regulators of complement activation (RCA) family and is located in the 'cluster RCA' region of chromosome 1. The gene encodes a monomeric single-pass type I membrane glycoprotein found on erythrocytes, leukocytes, glomerular podocytes, hyalocytes, and splenic follicular dendritic cells. The Knops blood group system is a system of antigens located on this protein. The protein mediates cellular binding to particles and immune complexes that have activated complement. Decreases in expression of this protein and/or mutations in its gene have been associated with gallbladder carcinomas, mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and sarcoidosis. Mutations in this gene have also been associated with a reduction in ''Plasmodium falciparum'' rosetting, conferring protectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opsonin
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed (i.e. eaten) by phagocytes (cells that specialise in phagocytosis, i.e. cellular eating). Different types of things ("targets") can be tagged by opsonins for phagocytosis, including: pathogens (such as bacteria), cancer cells, aged cells, dead or dying cells (such as apoptotic cells), excess synapses, or protein aggregates (such as amyloid plaques). Opsonins help clear pathogens, as well as dead, dying and diseased cells. Opsonins were discovered and named "opsonins" in 1904 by Wright and Douglas, who found that incubating bacteria with blood plasma enabled phagocytes to phagocytose (and thereby destroy) the bacteria. They concluded that: “We have here conclusive proof that the blood fluids modify the bacteria in a manner which renders them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Complement Pathway
The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the complement system, which is part of the immune system. The classical complement pathway is initiated by antigen-antibody complexes with the antibody isotypes IgG and IgM. Following activation, a series of proteins are recruited to generate C3 convertase (C4b2b, historically referred C4b2a), which cleaves the C3 protein. The C3b component of the cleaved C3 binds to C3 convertase (C4b2b) to generate C5 convertase (C4b2b3b), which cleaves the C5 protein. The cleaved products attract phagocytes to the site of infection and tags target cells for elimination by phagocytosis. In addition, the C5 convertase initiates the terminal phase of the complement system, leading to the assembly of the membrane attack complex ( MAC). The membrane attack complex creates a pore on the target cell's membrane, inducing cell lysis and death. The classical complement pathway can also be activated by apoptotic cells, necrotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor D
Factor D (, ''C3 proactivator convertase'', ''properdin factor D esterase'', ''factor D (complement)'', ''complement factor D'', ''CFD'', ''adipsin'') is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CFD'' gene. Factor D is involved in the alternative complement pathway of the complement system where it cleaves factor B. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the trypsin family of serine proteases secreted by adipocytes into the bloodstream. The encoded protein is a component of the alternative complement pathway best known for its role in humoral suppression of infectious agents. Finally, the encoded protein has a high level of expression in fat, suggesting a role for adipose tissue in immune system biology. Factor D is a serine protease that stimulates glucose transport for triglyceride accumulation in fats cells and inhibits lipolysis. Clinical significance The level of Factor D is decreased in obese patients. This reduction may be due to high activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Properdin
Properdin is protein that in humans is encoded by the CFP (complement factor properdin) gene. Properdin is plasma glycoprotein that activates the complement system of the innate immune system. This protein binds to bacterial cell walls and dying human cells to stabilize the C3 and C5-convertase enzyme complexes to form an attack complex that lead to the lysis of the cell. Structure Properdin is a gamma globulin protein composed of multiple identical protein subunits with a separate ligand-binding site. Native properdin occurs in head-to-tail dimers, trimers and tetramers in the fixed ratio 22:52:28. Function It is known that it participates in some specific immune responses. It plays a part in tissue inflammation as well as the engulfing of pathogens by phagocytes. In addition it is known to help to neutralize some viruses. The properdin promotes the association of C3b with Factor B and provides a focal point for the assembly of C3bBb on a surface. It binds to preformed alte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Although mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectin Pathway
The lectin pathway or lectin complement pathway is a type of cascade reaction in the complement system, similar in structure to the classical complement pathway, in that, after activation, it proceeds through the action of C4 and C2 to produce activated complement proteins further down the cascade. In contrast to the classical complement pathway, the lectin pathway does not recognize an antibody bound to its target. The lectin pathway starts with mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolin binding to certain sugars. In this pathway, mannose-binding lectin binds to mannose, glucose, or other sugars with 3- and 4-OH groups placed in the equatorial plane, in terminal positions on carbohydrate or glycoprotein components of microorganisms including bacteria such as ''Salmonella'', ''Listeria'', and ''Neisseria'' strains. Fungal pathogens such as ''Candida albicans'' and ''Cryptococcus neoformans'' as well as some viruses such as HIV-1 and Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are bound by MBL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 4
Complement component 4 (C4), in humans, is a protein involved in the intricate complement system, originating from the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system. It serves a number of critical functions in immunity, tolerance, and autoimmunity with the other numerous components. Furthermore, it is a crucial factor in connecting the recognition pathways of the overall system instigated by antibody-antigen (Ab-Ag) complexes to the other effector proteins of the innate immune response. For example, the severity of a dysfunctional complement system can lead to fatal diseases and infections. Complex variations of it can also lead to schizophrenia. The C4 protein was thought to derive from a simple two-locus allelic model, which however has been replaced by a much more sophisticated multimodular RCCX gene complex model which contain long and short forms of the C4A or C4B genes usually in tandem RCCX cassettes with copy number variation, that somewhat parallels variation in the levels of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |