classical complement pathway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the
The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the
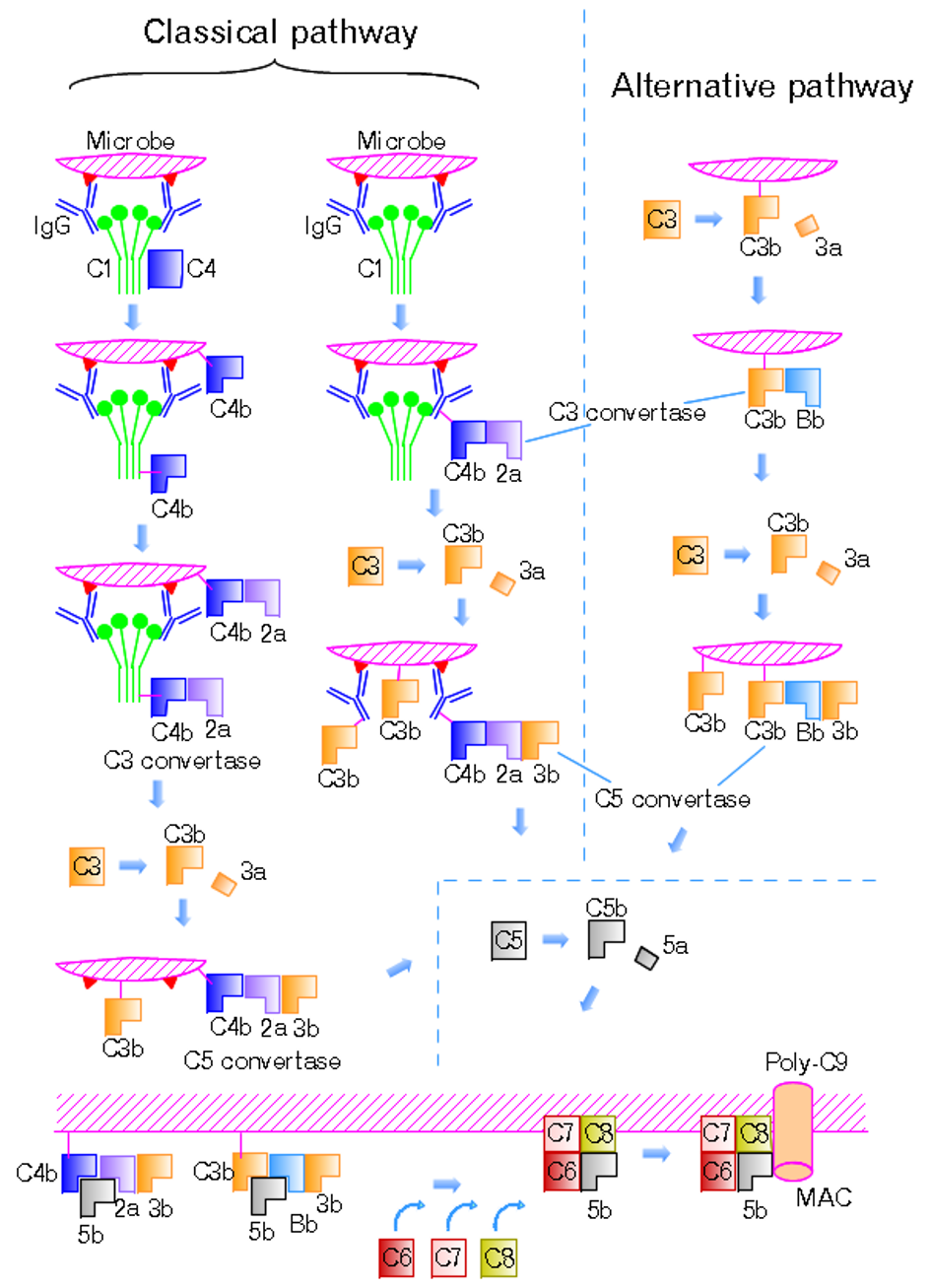
 The classical pathway is distinct from the other complement pathways in its unique activation triggers and cascade sequence. Activation of the complement pathway through the classical,
The classical pathway is distinct from the other complement pathways in its unique activation triggers and cascade sequence. Activation of the complement pathway through the classical,
 The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the
The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at ...
, which is part of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
. The classical complement pathway is initiated by antigen-antibody complex
An immune complex, sometimes called an antigen-antibody complex or antigen-bound antibody, is a molecule formed from the binding of multiple antigens to antibodies. The bound antigen and antibody act as a unitary object, effectively an antigen o ...
es with the antibody isotypes IgG
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG ...
and IgM
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is one of several isotypes of antibody (also known as immunoglobulin) that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the largest antibody, and it is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antig ...
.
Following activation, a series of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s are recruited to generate C3 convertase (C4b2b, historically
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
referred C4b2a), which cleaves the C3 protein. The C3b
C3b is the larger of two elements formed by the cleavage of complement component 3, and is considered an important part of the innate immune system. C3b is potent in opsonization: tagging pathogens, immune complexes (antigen-antibody), and apopto ...
component of the cleaved C3 binds to C3 convertase (C4b2b) to generate C5 convertase
C5 convertase is an enzyme belonging to a family of serine proteases that play key role in the innate immunity. It participates in the complement system ending with cell death.
There are four different C5 convertases able to specifically con ...
(C4b2b3b), which cleaves the C5 protein. The cleaved products attract phagocytes to the site of infection and tags target cells for elimination by phagocytosis. In addition, the C5 convertase initiates the terminal phase of the complement system, leading to the assembly of the membrane attack complex ( MAC). The membrane attack complex creates a pore on the target cell's membrane, inducing cell lysis and death.
The classical complement pathway can also be activated by apoptotic
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes includ ...
cells, necrotic cells, and acute phase protein
Acute-phase proteins (APPs) are a class of proteins whose concentrations in blood plasma either increase (positive acute-phase proteins) or decrease (negative acute-phase proteins) in response to inflammation. This response is called the ''acute-p ...
s.
Complement cascade
lectin
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in rec ...
or alternative complement pathway
The alternative pathway is a type of cascade reaction of the complement system and is a component of the innate immune system, a natural defense against infections.
The alternative pathway is one of three complement pathways that opsonize and k ...
is followed by a cascade of reactions eventually leading to the membrane attack complex.
Initiation
The classical complement pathway can be initiated by the binding of antigen-antibody complexes to theC1q
The complement component 1q (or simply C1q) is a protein complex involved in the complement system, which is part of the innate immune system. C1q together with C1r and C1s form the C1 complex.
Antibodies of the adaptive immune system can bi ...
protein. The globular regions of C1q recognize and bind to the Fc region of antibody isotypes IgG or IgM. These globular regions of C1q can also bind to bacterial and viral surface proteins, apoptotic cells, and acute phase proteins. In the absence of these activation factors, C1q is part of the inactive C1 complex which consists of six molecules of C1q, two molecules of C1r
Complement C1r subcomponent (, ''activated complement C1r'', ''C overbar 1r esterase'', ''C1r'') is a protein involved in the complement system of the innate immune system. In humans, C1r is encoded by the ''C1R'' gene.
C1r along with C1q and C1 ...
, and two molecules of C1s
Complement component 1s (, '' C1 esterase'', ''activated complement C1s'', ''complement C overbar 1r'', ''C1s'') is a protein involved in the complement system. C1s is part of the C1 complex. In humans, it is encoded by the ''C1S'' gene.
C1s cle ...
.
Formation of C4b convertase
The binding of C1q with pathogen surface or antigen-antibody immune complex leads to conformational changes and the activation of the serine protease C1r. The activated C1r then cleaves and activates the serine protease C1s. Activated C1s cleaves C4 into C4a and C4b.Regulation of C4b
The newly formed C4b cannot stay activated as a highly reactive thioester bond is revealed once C4 has been cleaved. The thioester bond is cleaved by water resulting in its cleavage permanently deactivating the C4b molecule. As a result of this C4b is restricted to only bind to pathogen surfaces. They would undergo rapid deactivation in the time it took to travel from the origin of activation where C1q is complexed with an antigen-antibody immune complex(IC) or where C1q is directly attached to the pathogens surface. the pathogen.Formation of C-3 convertase.
Surface bound C4b acts as a receptor for the binding of C2. The binding of C2 and C4b results in C2 being cleaved by C1s into C2a and C2b. C2a diffuses into the plasma as a protein inflammatory mediator while C2b remains attached with C4b forming C4bC2b what is known as C3-convertase, The function of the membrane-bound C3-convertase is the cleavage of many many molecules of C3 into C3a and C3b. C3a is a smaller fragment of C3 is a potent inflammatory mediator.C3b function and structure.
C3b can act as an opsonin . C3b is very similar to C4 in both structure and function also has a thioester bond that forces it to attach to surface nucleophile of the activator(namely the pathogen or IC). Phagocytes have receptors for C3b and as a result of receptor-ligand binding are able to more easily recognize and engulf pathogen molecules. While theanaphylatoxin
Anaphylatoxins, or complement peptides, are fragments ( C3a, C4a and C5a) that are produced as part of the activation of the complement system. Complement components C3, C4 and C5 are large glycoproteins that have important functions in the imm ...
C3a interacts with its C3a receptor
The C3a receptor also known as complement component 3a receptor 1 (C3AR1) is a G protein-coupled receptor protein involved in the complement system.
The receptor binds to complement component C3a, although there is limited evidence that this rec ...
(C3aR) to recruit leukocytes, C3b contributes to further downstream complement activation.
Formation of C5 convertase and MAC
C3b binds to the C3 convertase (C4b2b), to form C5 convertase (C4b2b3b). C5 convertase then cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b. Like C3a, C5a is also an anaphylatoxin that interacts with its cognate C5a receptor (C5aR) to attract leukocytes. Subsequent interactions between C5b and other terminal components C6, C7, C8, and C9 form the membrane attack complex or the C5b-9 complex which forms pores on the target cell membranes to lysing.Clinical significance
Because of its role in the innate immune system classical complement has been implicated in a number of pathogen related disorders. Complement is responsible for immune inflammatory response in adipose tissues which has been implicated in the development ofobesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
. Obesity in turn results in an abnormally high level of complement activation via production of the C1 component of the classical pathway, which can lead to tissue inflammation and eventually insulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cell (biology), cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood gluco ...
, however the exact mechanisms that causes this is yet unknown.
Immunotherapies have been developed to detect and destroy cells infected by the HIV virus via classical complement activation. This process involves creating synthetic peptides that target conserved regions in HIV specific proteins and induce an antibody specific immune response through IgG antibodies. This is important for targeting the virus in its intracellular phase because the antibodies specific to the synthetic peptides can trigger the classical complement pathway and induce the death of HIV infected cells.
Classical complement activation has also been shown to combat Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Certain variants of the IgM antibody were found to bind the Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive ...
'' these IgM were found to be critical in complement activation through the classical pathway and subsequent destruction of the bacteria. Therapies that utilize classical complement activation have been shown to be effective in targeting and killing cancer cells and destroying tumors. Tachyplesin Tachyplesin I and Tachyplesin II
Tachyplesin is an antimicrobial peptide isolated from the horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despi ...
, a small peptide, has been shown to exhibit these effects. When injected into target tissue encourages recruitment of C1q and activates downstream events, eventually leading to the formation of the C5b-9 complex which damages tumor cells, killing them.
Lack of regulation of the classical complement pathway through the deficiency in C1-inhibitor
C1-inhibitor (C1-inh, C1 esterase inhibitor) is a protease inhibitor belonging to the serpin superfamily. Its main function is the inhibition of the complement system to prevent spontaneous activation but also as the major regulator of the cont ...
results in episodic angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling ( edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which ...
. C1-inhibitor defiency can be hereditary or acquired, resulting in hereditary or acquired angioedema. C1-inhibitor plays the role of inactivating C1r and C1s to prevent further downstream classical complement activity. C1-inhibitor controls the processes involved in maintaining vascular permeability. As a result, C1-inhibitor levels of less than 50% of the standard lead to increased vascular permeability, characteristic of angioedema. Cinryze, a human plasma derived C1-esterase inhibitor, has been approved for use in 2008 for the prevention of hereditary angioedema attacks.
Deficiency in the C1q
The complement component 1q (or simply C1q) is a protein complex involved in the complement system, which is part of the innate immune system. C1q together with C1r and C1s form the C1 complex.
Antibodies of the adaptive immune system can bi ...
protein of the classical complement pathway can lead to development of systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
. Among the many functions of C1q, C1q triggers clearance of immune complexes and apoptotic cells by activating the classical pathway and binding directly onto phagocytes. Consequently, systemic lupus erythematosus from insufficient amounts of C1q is characterized by the accumulation of autoantibodies and apoptotic cells. Studies are being done to look into antibodies against C1q as a diagnostic marker for systemic lupus erythematosus.
See also
*Alternative complement pathway
The alternative pathway is a type of cascade reaction of the complement system and is a component of the innate immune system, a natural defense against infections.
The alternative pathway is one of three complement pathways that opsonize and k ...
– another complement system pathway
* Lectin pathway
The lectin pathway or lectin complement pathway is a type of cascade reaction in the complement system, similar in structure to the classical complement pathway, in that, after activation, it proceeds through the action of C4 and C2 to produce act ...
– another complement system pathway
References
{{Complement system Complement system