|
C-reactive Protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin-6 secretion by macrophages and T cells. Its physiological role is to bind to lysophosphatidylcholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells (and some types of bacteria) in order to activate the complement system via C1q. CRP is synthesized by the liver in response to factors released by macrophages and fat cells (adipocytes). It is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins. It is not related to C-peptide (insulin) or protein C (blood coagulation). C-reactive protein was the first pattern recognition receptor (PRR) to be identified. History Discovered by Tillett and Francis in 1930, it was initially thought that CRP might be a pathogenic secretion since it was elevated in a variety of illnesses, including cancer. The later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentameric Protein
A pentameric protein is a quaternary protein structure that consists of five protein subunits. Examples Ligand-gated ion channels Five sub-units come together to form a channel. Each channel consist of two alpha chain, one beta, one gamma and one delta chain. These five chains assemble together (along with certain receptors like protons or acetylcholine) forming the structure of the channel. A ligand-gated ion channel on the post-synaptic junction of the muscle-end plate is an example of such a channel. They are acetylcholine-operated ion channels, which means that acetylcholine brings about a conformational change. The channel allows the free movement of the cations like Na and K when acetylcholine binds to its receptors. Viral capsids Many viral capsids are formed by hexameric and pentameric proteins. Such capsids are assigned a triangulation number (T-number) which describe relation between the number of pentagons and hexagons. Carboxysomes Protein enclosing bacterial organe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
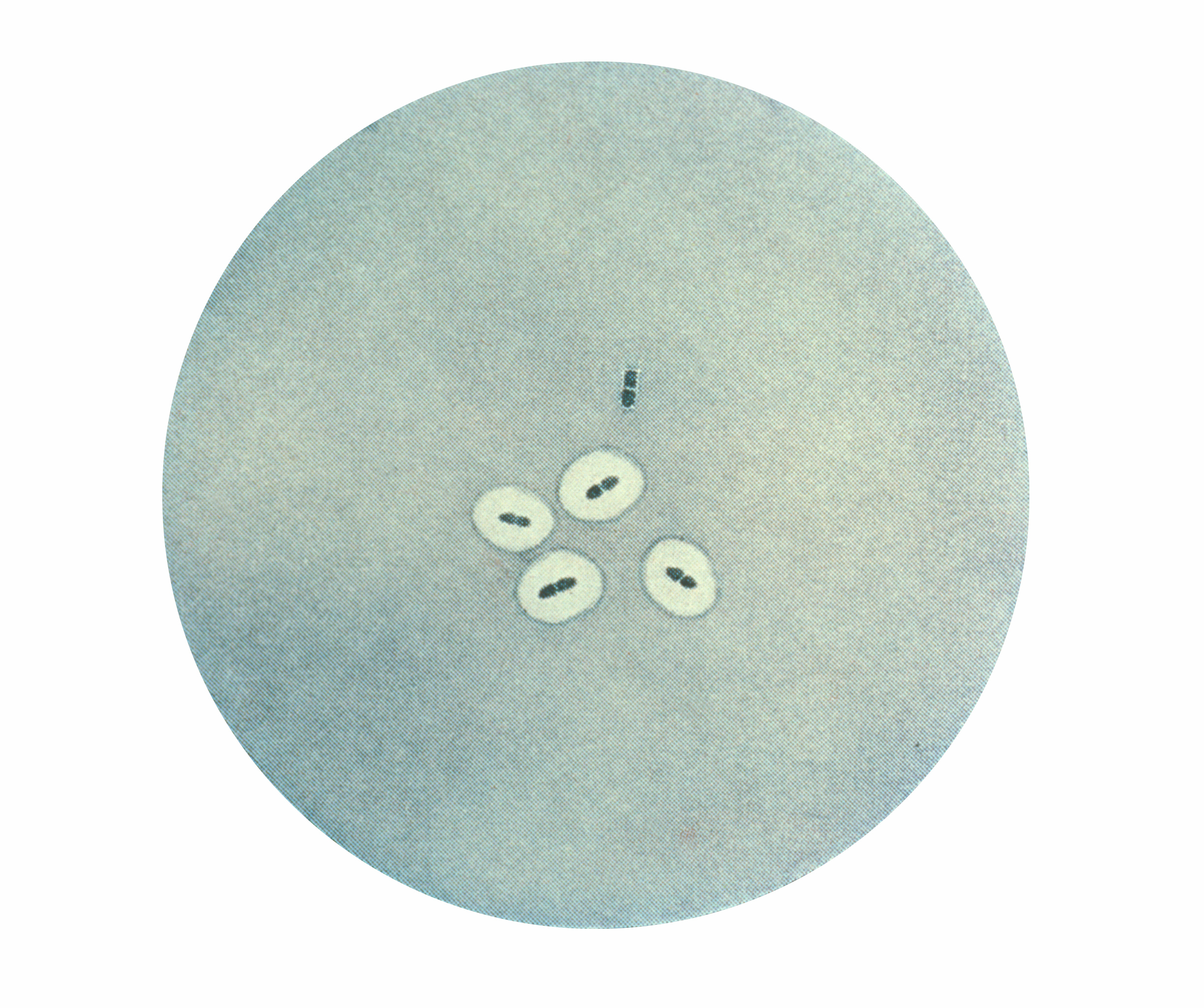
Quellung Reaction
The quellung reaction, also called the Neufeld reaction, is a biochemical reaction in which antibodies bind to the bacterial capsule of ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'', ''Neisseria meningitidis'', ''Bacillus anthracis'', ''Haemophilus influenzae'', ''Escherichia coli'', and ''Salmonella''. The antibody reaction allows these species to be visualized under a microscope. If the reaction is positive, the capsule becomes opaque and appears to enlarge. Quellung is the German word for "swelling" and describes the microscopic appearance of pneumococcal or other bacterial capsules after their polysaccharide antigen has combined with a specific antibody. The antibody usually comes from a bit of serum taken from an immunized laboratory animal. As a result of this combination, and precipitation of the large, complex molecule formed, the capsule appears to swell, because of increased surface tension, and its outlines become clearly demarcated. The pneumococcal quellung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin-6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene. In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth muscle cells in the tunica media of many blood vessels also produce IL-6 as a pro-inflammatory cytokine. IL-6's role as an anti-inflammatory myokine is mediated through its inhibitory effects on TNF-alpha and IL-1 and its activation of IL-1ra and IL-10. There is some early evidence that IL-6 can be used as an inflammatory marker for severe COVID-19 infection with poor prognosis, in the context of the wider coronavirus pandemic. Function Immune system IL-6 is secreted by macrophages in response to specific microbial molecules, referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns ( PAMPs). These PAMPs bind to an important group of detection molecules of the innate immune system, called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Phase Response
Acute-phase proteins (APPs) are a class of proteins whose concentrations in blood plasma either increase (positive acute-phase proteins) or decrease (negative acute-phase proteins) in response to inflammation. This response is called the ''acute-phase reaction'' (also called ''acute-phase response''). The acute-phase reaction characteristically involves fever, acceleration of peripheral leukocytes, circulating neutrophils and their precursors. The terms ''acute-phase protein'' and ''acute-phase reactant'' (APR) are often used synonymously, although some APRs are (strictly speaking) polypeptides rather than proteins. In response to injury, local inflammatory cells (neutrophil granulocytes and macrophages) secrete a number of cytokines into the bloodstream, most notable of which are the interleukins IL1, and IL6, and TNF-α. The liver responds by producing many acute-phase reactants. At the same time, the production of a number of other proteins is reduced; these proteins are, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptotic
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates in the surrounding tissue an inflammatory response, which attracts leukocytes and nearby phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Although mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphocholine
Phosphocholine is an intermediate in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine in tissues. Phosphocholine is made in a reaction, catalyzed by choline kinase, that converts ATP and choline into phosphocholine and ADP. Phosphocholine is a molecule found, for example, in lecithin. In nematodes and human placentas, phosphocholine is selectively attached to other proteins as a posttranslational modification to suppress an immune response by their hosts. It is also one of the binding targets of C-reactive protein (CRP). Thus, when a cell is damaged, CRP binds to phosphocholine, beginning the recognition and phagocytotic immunologic response. Phosphocholine is a natural constituent of hens' eggs (and many other eggs) often used in biomimetic membrane studies. See also * Alkylphosphocholines * Choline * Phosphoethanolamine Phosphorylethanolamine or phosphoethanolamine is an ethanolamine derivative that is used to construct two different categories of phospholipids. One category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u) is a non-SI unit of mass widely used in physics and chemistry. It is defined as of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and at rest. The atomic mass constant, denoted ''m''u, is defined identically, giving . This unit is commonly used in physics and chemistry to express the mass of atomic-scale objects, such as atoms, molecules, and elementary particles, both for discrete instances and multiple types of ensemble averages. For example, an atom of helium-4 has a mass of . This is an intrinsic property of the isotope and all helium-4 atoms have the same mass. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), , has an average mass of approximately . However, there are no acetylsalicylic acid molecules with this mass. The two most common masses of individual acetylsalicylic acid molecules are , having the most common isotopes, and , in which one carbon is carbon-13. The molecular mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentraxins
Pentraxins (PTX), also known as pentaxins, are an evolutionary conserved family of proteins characterised by containing a pentraxin protein domain. Proteins of the pentraxin family are involved in acute immunological responses. They are a class of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). They are a superfamily of multifunctional conserved proteins, some of which are components of the humoral arm of innate immunity and behave as functional ancestors of antibodies (Abs). They are known as classical acute phase proteins (APP), known for over a century. Structure Pentraxins are characterised by calcium dependent ligand binding and a distinctive flattened β-jellyroll structure similar to that of the legume lectins. The name "pentraxin" is derived from the Greek word for five (penta) and axle (axis) relating to the radial symmetry of five monomers forming a ring approximately 95Å across and 35Å deep observed in the first members of this family to be identified. The "short" pentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now called si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |