|
Amidines
Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2. Examples of amidines include: * DBU * diminazene * benzamidine * Pentamidine * Paranyline Preparation A common route to primary amidines is the Pinner reaction. Reaction of the nitrile with alcohol in the presence of acid gives an iminoether. Treatment of the resulting compound with ammonia then completes the conversion to the amidine. Instead of using a Bronsted acid, Lewis acids such as aluminium trichloride promote the direct amination of nitriles. They are also generated by amination of an imidoyl chloride. They are also prepared by the addition of organolithium reagents to diimines, followed by protonation or alkylation. Dimethylformamide acetal reacts with primary amines to give amidines: :Me2NC(H)(OMe)2 + RNH2 → Me2NC=NHR + 2 MeOH Properties and applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzamidine
Benzamidine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(NH)NH2. It is the simplest aryl amidine. The compound is a white solid that is slightly soluble in water. It is usually handled as the hydrochloride salt, a white, water-soluble solid. In terms of its molecular structure, Benzamidine features one short C=NH bond and one longer C-NH2 bond, respectively 129 and 135 picometers. Applications Benzamidine is a reversible competitive inhibitor of trypsin, trypsin-like enzymes and serine proteases. It is often used as a ligand in protein crystallography to prevent proteases from degrading a protein of interest; the triangular diamine group at the bottom gives it a very obvious 'stick-man' shape which shows up in difference density maps. The benzamidine moiety is also found in some pharmaceuticals, like dabigatran. Condensation with various haloketones provides a synthetic route to 2,4-disubstituted imidazole Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribendimidine
Tribendimidine is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic agent developed in China, at the National Institute of Parasitic Diseases in Shanghai. It is a derivative of amidantel.Free full text In s, it was highly effective in treating , and . It is also effective against |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. Fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amitraz
Amitraz (development code BTS27419) is a non-systemic acaricide and insecticideCorta, E., Bakkali, A., Berrueta, L. A., Gallo, B., & Vicente, F. (1999). Kinetics and mechanism of amitraz hydrolysis in aqueous media by HPLC and GC-MS. Talanta, 48(1), 189-199 and has also been described as a scabicide. It was first synthesized by the Boots Co. in England in 1969.Harrison, I. R., et al. (1973). 1,3,5-Triazapenta-1, 4-dienes: Chemical aspects of a new group of pesticides. Pestic. Sci. 4: 901 Amitraz has been found to have an insect repellent effect, works as an insecticide and also as a pesticide synergist.PubChem Substance. Amitraz – Substance Summary. retrieved from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?sid=24868774#x332 Its effectiveness is traced back on alpha-adrenergic agonist activity, interaction with octopamine receptors of the central nervous system and inhibition of monoamine oxidases and prostaglandin synthesis. Therefore, it leads to overexcitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,8-Diazabicycloundec-7-ene
1,8-Diazabicyclo .4.0ndec-7-ene, or more commonly DBU, is a chemical compound and belongs to the class of amidine compounds. It is used in organic synthesis as a catalyst, a complexing ligand, and a non-nucleophilic base. Occurrence Although all commercially available DBU is produced synthetically, it may also be isolated from the sea sponge '' Niphates digitalis''. The biosynthesis of DBU has been proposed to begin with 1,6-hexanedial and 1,3-diaminopropane. Uses As a reagent in organic chemistry, DBU is used as a catalyst, a complexing ligand, and a non-nucleophilic base. It is also used as a curing agent for epoxy resins. It is used in the separation of fullerenes in conjunction with trimethylbenzene. It reacts with C70 and higher fullerenes, but not with to C60 It is also used as a catalyst in the production of polyurethanes. It also exhibited its dual character (base and nucleophile) in the synthesis of aryl- and styryl-terminal acetylenes. See also * 1,5-Diazabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminazene
Diminazene (INN; also known as diminazen) is an anti-infective medication for animals that is sold under a variety of brand names. It is effective against certain protozoa such as ''Babesia'', ''Trypanosoma'', and '' Cytauxzoon''. The drug may also be effective against certain bacteria including ''Brucella'' and ''Streptococcus''. Chemically it is a di-amidine and it is formulated as its aceturate salt, diminazene aceturate. The mechanism is not well understood; it probably inhibits DNA replication, but also has affinity to RNA. __TOC__ Side effects Acute side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, and hypotension (low blood pressure). Diminazen can harm the liver, kidneys and brain, which is potentially life-threatening; camels are especially susceptible to these effects. Resistance The Gibe River Valley in southwest Ethiopia showed universal resistance between July 1989 and February 1993. This likely indicates a permanent loss of function in this area against the tested target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentamidine
Pentamidine is an antimicrobial medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, ''Balamuthia'' infections, babesiosis, and to prevent and treat pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in people with poor immune function. In African trypanosomiasis it is used for early disease before central nervous system involvement, as a second line option to suramin. It is an option for both visceral leishmaniasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis. Pentamidine can be given by injection into a vein or muscle or by inhalation. Common side effects of the injectable form include low blood sugar, pain at the site of injection, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and kidney problems. Common side effects of the inhaled form include wheezing, cough, and nausea. It is unclear if doses should be changed in those with kidney or liver problems. Pentamidine is not recommended in early pregnancy but may be used in later pregnancy. Its safety during breastfeeding is unclear. Pentamidine is in the aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
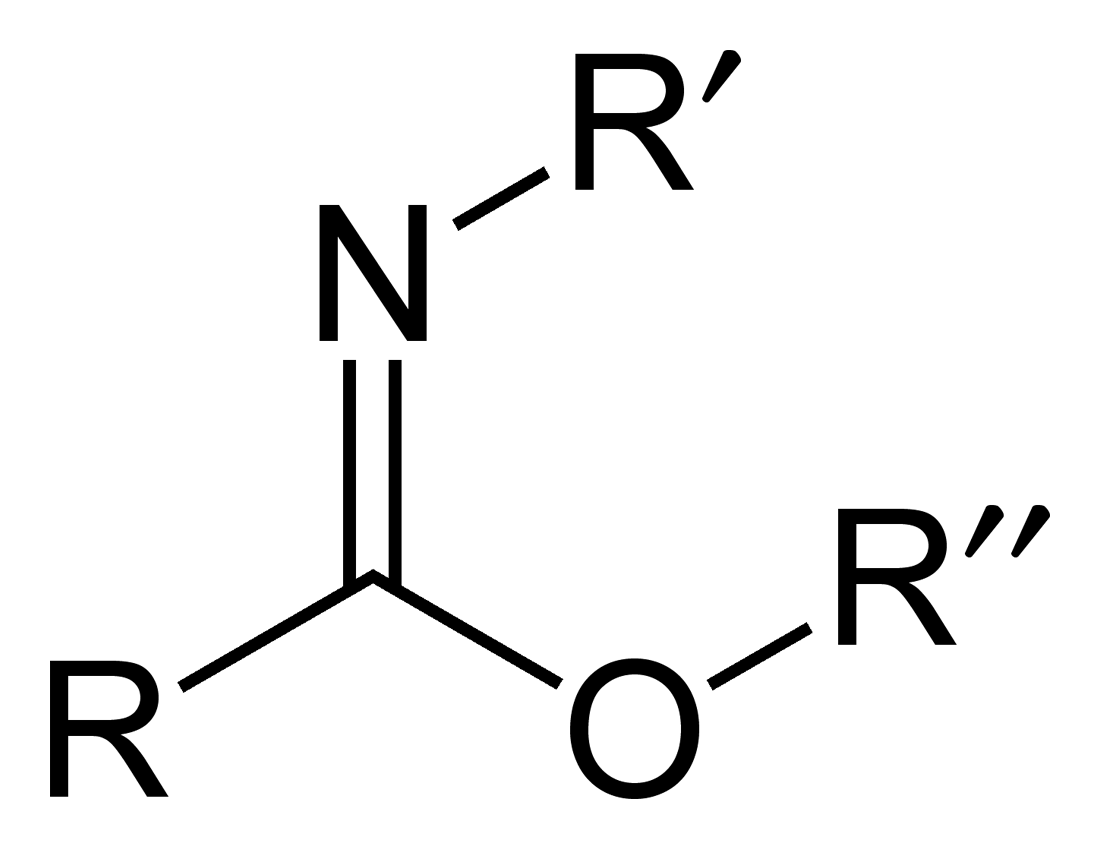
Carboximidate
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as esters formed between a carboximidic acid (R-C(=NR')OH) and an alcohol, with the general formula R-C(=NR')OR". They are also known as imino ethers, since they resemble imines (>C=N-) with an oxygen atom connected to the carbon atom of the C=N double bond. Synthesis Imidates may be generated by a number of synthetic routes, but are in general formed by the Pinner reaction. This proceeds via the acid catalyzed attack of nitriles by alcohols. Imidates produced in this manner are formed as their hydrochloride salts, which are sometimes referred to as Pinner salts. Carboximidates are also formed as intermediates in the Mumm rearrangement and the Overman rearrangement. Imidate/amidate anions An amidate/imidate anion is formed upon deprotonation of an amide or imidic acid. Since amides and imidic acids are tautomers, they form the same anion upon deprotonation. The two names are thus sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delocalized Electron
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref> The term delocalization is general and can have slightly different meanings in different fields: * In organic chemistry, it refers to resonance in conjugated systems and aromatic compounds. * In solid-state physics, it refers to free electrons that facilitate electrical conduction. * In quantum chemistry, it refers to molecular orbital electrons that have extended over several adjacent atoms. Resonance In the simple aromatic ring of benzene, the delocalization of six π electrons over the C6 ring is often graphically indicated by a circle. The fact that the six C-C bonds are equidistant is one indication that the electrons are delocalized; if the structure were to have isolated double bonds alternating with discrete single bonds, the bond would likewise have alternating longer and short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula ( CH3)2NC(O)H. Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such as SN2 reactions. Structure and properties As for most amides, the spectroscopic evidence indicates partial double bond charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetal
In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity . Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other (a "symmetric acetal") or not (a "mixed acetal"). Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry. The term ketal is sometimes used to identify structures associated with ketones (both R groups organic fragments rather than hydrogen) rather than aldehydes and, historically, the term acetal was used specifically for the aldehyde-related cases (having at least one hydrogen in place of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |