Carboximidate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as
 Imidates produced in this manner are formed as their hydrochloride salts, which are sometimes referred to as Pinner salts. Carboximidates are also formed as intermediates in the Mumm rearrangement and the Overman rearrangement.
Imidates produced in this manner are formed as their hydrochloride salts, which are sometimes referred to as Pinner salts. Carboximidates are also formed as intermediates in the Mumm rearrangement and the Overman rearrangement.

 Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as
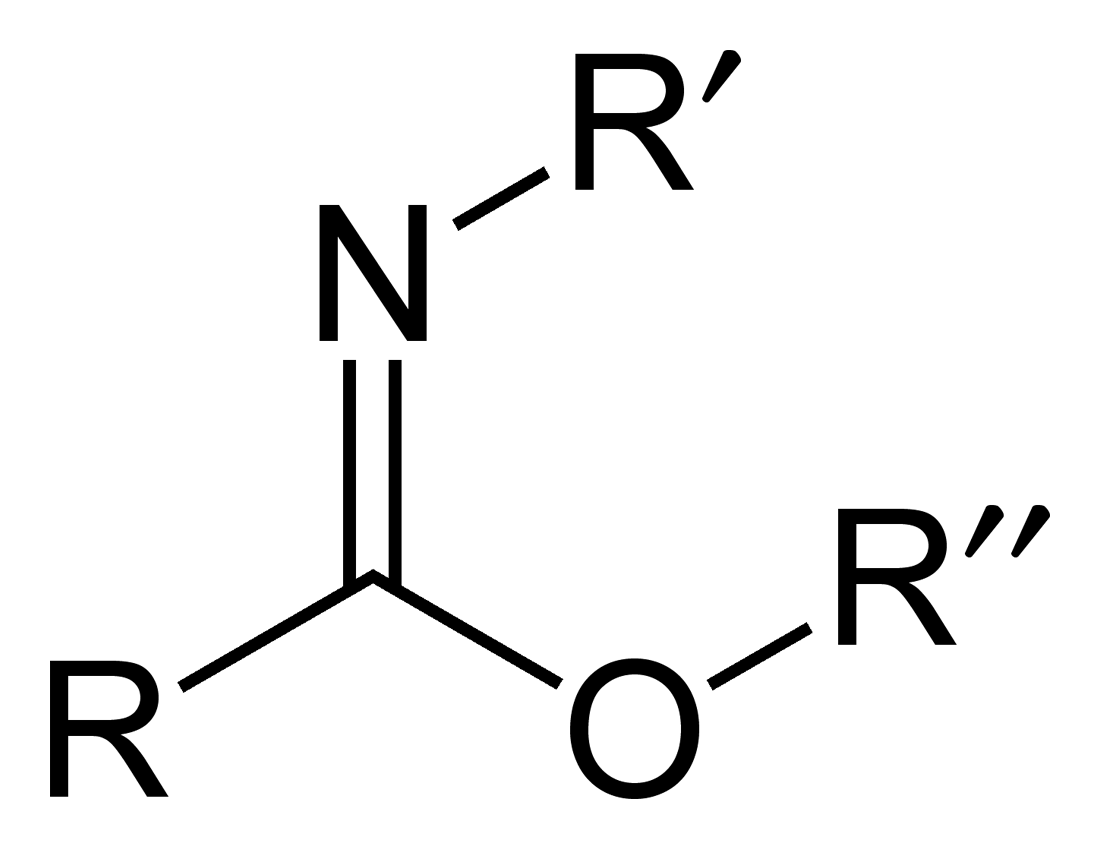
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s formed between a carboximidic acid
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as esters formed between a carboximidic acid (R-C(=NR')OH) and an alcohol, with the general formula R-C(=NR')OR".
They are also known as imino ethers, si ...
(R-C(=NR')OH) and an alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
, with the general formula R-C(=NR')OR".
They are also known as imino ethers, since they resemble imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bo ...
s (>C=N-) with an oxygen atom connected to the carbon atom of the C=N double bond.
Synthesis
Imidates may be generated by a number of synthetic routes, but are in general formed by thePinner reaction
The Pinner reaction refers to the acid catalysed reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol to form an imino ester salt (alkyl imidate salt); this is sometimes referred to as a Pinner salt.
The reaction is named after Adolf Pinner, who first describe ...
. This proceeds via the acid catalyzed attack of nitriles by alcohols.
Imidate/amidate anions
An amidate/imidate anion is formed upondeprotonation
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju. ...
of an amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is ...
or imidic acid. Since amides and imidic acids are tautomers, they form the same anion upon deprotonation. The two names are thus synonyms describing the same anion, although arguably, imidate refers to the resonance contributor on the left, while amidate refers to the resonance contributor on the right. However, they are distinguished when they act as ligands for transition metals, with ''O-''bound species referred to as imidates and ''N''-bound species referred to as amidates. They can be considered aza-substituted analogues of enolate
In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl () compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the synthesis of organic compounds.
Bonding and structure
Enolate anions are electr ...
s with the formula R-N=C(O−)R.
Reactions
Carboximidates are good electrophiles and undergo a range of addition reactions; withaliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane, ...
imidates generally reacting faster than aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic (ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to sat ...
imidates. They can be hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
to give esters
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are ...
and by an analogous process react with amines (including ammonia) to form amidine
Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2.
Examples of amidines inclu ...
s. Aliphatic imidates react with an excess of alcohol under acid catalysis to form orthoester
In organic chemistry, an ortho ester is a functional group containing three alkoxy groups attached to one carbon atom, i.e. with the general formula . Orthoesters may be considered as products of exhaustive alkylation of unstable orthocarboxyli ...
s RC(OR)3, aromatic imidates can also be converted but far less readily.
Chapman rearrangement
The Chapman rearrangement is the thermal conversion of aryl ''N''‐arylbenzimidates to the corresponding amides, via intramolecular migration of an aryl group from oxygen to nitrogen. It is named after Arthur William Chapman, who first described it, and is conceptually similar to the Newman–Kwart rearrangement.As a protecting group
Carboximidates can act asprotecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In man ...
for alcohols. For example, the base catalyzed reaction of benzyl alcohol
Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with the formula C6H5CH2OH. The benzyl group is often abbreviated "Bn" (not to be confused with "Bz" which is used for benzoyl), thus benzyl alcohol is denoted as BnOH. Benzyl alcohol is a colorless liqui ...
upon trichloroacetonitrile yields a trichloroacetimidate. This species has orthogonal stability to acetate and TBS protections and may be cleaved by acid hydrolysis.
See also
*Amidines
Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2.
Examples of amidines includ ...
* Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s
* Oxazoline
Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with the formula . It is the parent of a family of compounds called oxazolines (emphasis on plural), which contain non-hydrogenic substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are the ...
- the corresponding 5-membered heterocycle
References
{{reflist * Functional groups