|
390 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 390 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Ambustus, Longus, Ambustus, Fidenas, Ambustus and Cornelius (or, less frequently, year 364 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 390 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Republic * July 18 – Battle of the Allia: Brennus, a chieftain of the Senones of the Adriatic coast of Italy, leads an army of Cisalpine Gauls in their attack on Rome. They capture the entire city of Rome except for the Capitoline Hill, which is successfully held against them. However, seeing their city devastated, the Romans attempt to buy their salvation from Brennus. The Romans agree to pay one thousand pounds weight of gold. Egypt * The Pharaoh of Egypt, Hakor (Akoris), concludes a tripartite alliance with Evagoras, king of Cyprus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the Roman dictator, dictator Julius Caesar and Roman emperor, emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones (calendar), nones, and ides (calendar), ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's Egyptian calendar, former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the Byzantine Empire, later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year. Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andocides
Andocides (; grc-gre, Ἀνδοκίδης, ''Andokides''; c. 440 – c. 390 BC) was a logographer (speech writer) in Ancient Greece. He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian Canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrace in the third century BC. Life Andocides was the son of Leogoras, and was born in Athens around 440 BC. He belonged to the ancient Eupatrid family of the Kerykes, who traced their lineage up to Odysseus and the god Hermes.Pseudo-Plutarch, ''Lives of the Ten Orators''Plutarch, ''Alcibiades'' 21 During his youth, Andocides seems to have been employed on various occasions as ambassador to Thessaly, Macedonia, Molossia, Thesprotia, Italy, and Sicily. And although he was frequently attacked for his political opinions, he maintained his ground until, in 415, he became involved in the charge brought against Alcibiades for having profaned the mysteries and mutilated the Herms on the eve of the departure of the Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
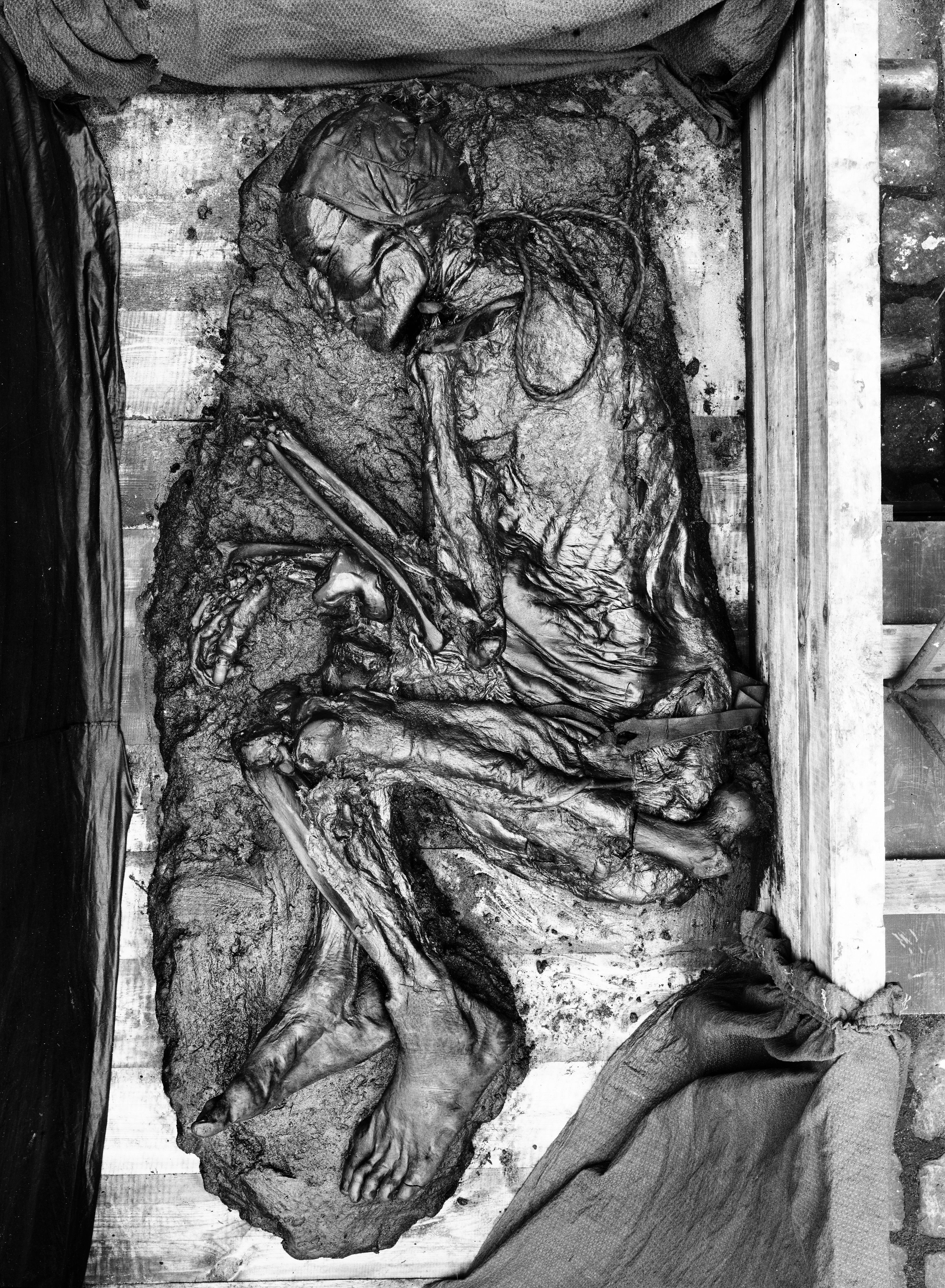
Tollund Man
The Tollund Man (died 405–380 BC) is a naturally mummified corpse of a man who lived during the 5th century BC, during the period characterised in Scandinavia as the Pre-Roman Iron Age. He was found in 1950, preserved as a bog body, near Silkeborg on the Jutland peninsula in Denmark. The man's physical features were so well preserved that he was mistaken for a recent murder victim. Twelve years before his discovery, another bog body, Elling Woman, was found in the same bog. The cause of death has been determined as by hanging. Scholars believe the man was a human sacrifice, rather than an executed criminal, because of the arranged position of his body, and his eyes and mouth being closed.Hart, Edward, dir. "Ghosts of Murdered Kings". NOVA. Prod. Edward Hart and Dan McCabe, PBS, 29 January 2014 Discovery On 8 May 1950, peat cutters Viggo and Emil Hojgaard discovered a corpse in the peat layer of the Bjældskovdal peat bog, west of Silkeborg, Denmark, which was so well pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypereides
Hypereides or Hyperides ( grc-gre, Ὑπερείδης, ''Hypereidēs''; c. 390 – 322 BC; English pronunciation with the stress variably on the penultimate or antepenultimate syllable) was an Athenian logographer (speech writer). He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrace in the third century BC. He was a leader of the Athenian resistance to King Philip II of Macedon and Alexander the Great. He was associated with Lycurgus and Demosthenes in exposing pro-Macedonian sympathizers. He is known for prosecuting Philippides of Paiania for his pro-Macedonian measures and his decree in honoring Alexander the Great. Rise to power Little is known about his early life except that he was the son of Glaucippus, of the deme of Collytus and that he studied logography under Isocrates. In 360 BC, he prosecuted Autocles for treason. During the Social War (358–355 BC) he accused Aristophon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidaurus
Epidaurus ( gr, Ἐπίδαυρος) was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the new municipality of Epidaurus, part of the regional unit of Argolis. The seat of the municipality is the town Lygourio. The nearby sanctuary and ancient theatre were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1988 because of their exemplary architecture and importance in the development and spread of healing sanctuaries and cults across the ancient Greek and Roman worlds. Name and etymology The name “Epidaurus” is of Greek origin. It was named after the hero Epidauros, son of Apollo. According to Strabo, the city was originally named Ἐπίκαρος (Epíkaros) under the Carians, (Aristotle claimed that Caria, as a naval empire, occupied Epidaurus and Hermione) before taking the name Ἐπίταυρος (Epítauros) when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of Apollo), Coronis, or Arsinoe (Greek myth), Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represents the healing aspect of the medical arts; his daughters, the "Asclepiades", are: Hygieia ("Health, Healthiness"), Iaso (from ἴασις "healing, recovering, recuperation", the goddess of recuperation from illness), Aceso (from ἄκεσις "healing", the goddess of the healing process), Aegle (mythology), Aegle (the goddess of good health) and Panacea (the goddess of universal remedy). He has several sons as well. He was associated with the Roman/Etruscan god Vediovis and the Egyptian Imhotep. He shared with Apollo the epithet ''Paean'' ("the Healer"). The rod of Asclepius, a snake-entwined staff, (similar to the caduceus) remains a symbol of medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geographically in Western Asia, its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southern European. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located north of Egypt, east of Greece, south of Turkey, and west of Lebanon and Syria. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. The northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which was established after the 1974 invasion and which is recognised as a country only by Turkey. The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains include the well-preserved ruins from the Hellenistic period such as Salamis and Kourion, and Cypr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evagoras I
Evagoras or Euagoras ( grc, Εὐαγόρας) was the king of Salamis, Cyprus, Salamis (411–374 BC) in Cyprus, known especially from the work of Isocrates, who presents him as a model ruler. History He claimed descent from Teucer, the son of Telamon and half-brother of Ajax the Great, Ajax, and his family had long been rulers of Salamis, although during his childhood Salamis came under Phoenician control, which resulted in his exile. While in Cilicia, Evagoras gathered the support of 50 followers and returned secretly in 410, to gain possession of the throne. Expecting an eventual Achaemenid Empire, Persian response to recapture Cyprus, he cultivated the friendship of the Classical Athens, Athenians, and after Conon's defeat at the Battle of Aegospotami he provided him with a refuge. For a time he also maintained friendly relations with Achaemenid Empire, Persia, and secured the aid of Artaxerxes II for Athens against Sparta. He took part in the Battle of Cnidus of 394 BC which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakor
Hakor or Hagar, also known by the hellenized forms Achoris or Hakoris, was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 29th Dynasty. His reign marks the apex of this feeble and short-lived dynasty, having ruled for 13 years – more than half of its entire duration. Reign Struggle for the accession Hakor's accession and relationships with his predecessor Nepherites I were long debated. After Nepherites' death a dynastic struggle did seem to have occurred, and the throne was claimed by two or maybe three pretenders: Hakor, Psammuthes, and possibly a phantom figure called Muthis who was only mentioned in Eusebius' epitome of Manetho's ''Aegyptiaca''. As a result, Hakor was alternately considered Nepherites' legitimate successor or an unrelated usurper. In 1986, John D. Ray suggested that Hakor was Nepherites' heir, who ruled undisturbed until his Year 2 when he was deposed by Psammuthes. After another year, Hakor managed to retake his legitimate throne by overthrowing the usurper, and cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |