|
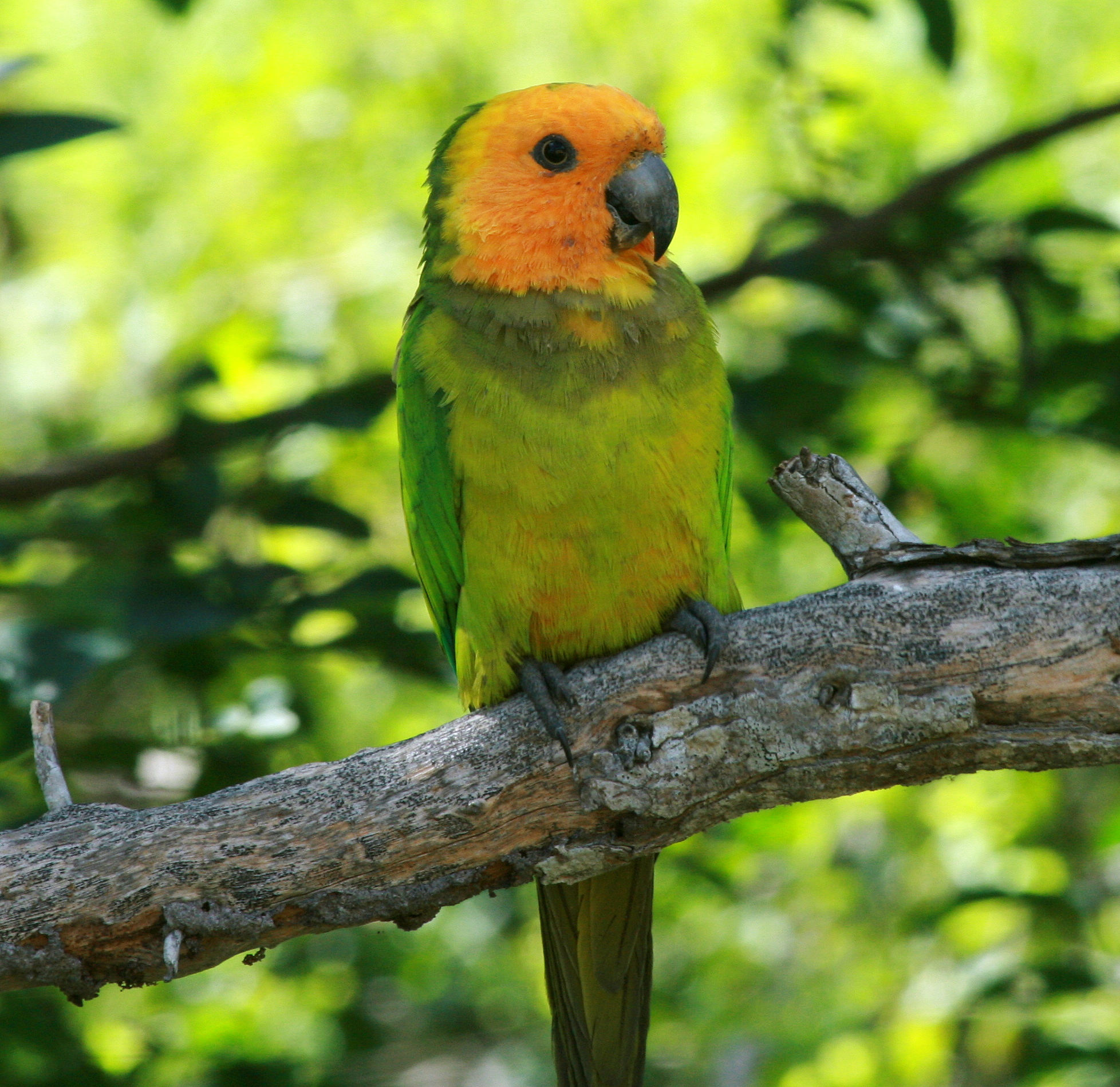
Brown-throated Parakeet (Aratinga Pertinax) -pet
The brown-throated parakeet (''Eupsittula pertinax''), also known as the Prikichi, St. Thomas conure or the brown-throated conure, in aviculture, is a species of parrot in the family Psittacidae. Taxonomy The brown-throated parakeet was formally described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his '' Systema Naturae''. He placed it with all the other parrots in the genus ''Psittacus'' and coined the binomial name ''Psittacus pertinax''. The brown-throated parakeet is now one of five species placed in the genus '' Eupsittula'' that was introduced in 1853 by the French naturalist Charles Lucien Bonaparte. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek ''eu'' meaning "good" with the Modern Latin ''psittula'' meaning "little parrot". The specific epithet ''pertinax'' is Latin meaning "tenacious" or "persistent". Fourteen subspecies are recognised, some of which are island endemics. They have varying colours particularly of the crown, face and underpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of Paraguaná and northwest of Curaçao. It measures long from its northwestern to its southeastern end and across at its widest point. Together with Bonaire and Curaçao, Aruba forms a group referred to as the ABC islands. Collectively, these and the other three Dutch substantial islands in the Caribbean are often called the Dutch Caribbean, of which Aruba has about one-third of the population. In 1986, it became a constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, and acquired the formal name the Country of Aruba. Aruba is one of the four countries that form the Kingdom of the Netherlands, along with the Netherlands, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten; the citizens of these countries are all Dutch nationals. Aruba has no administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
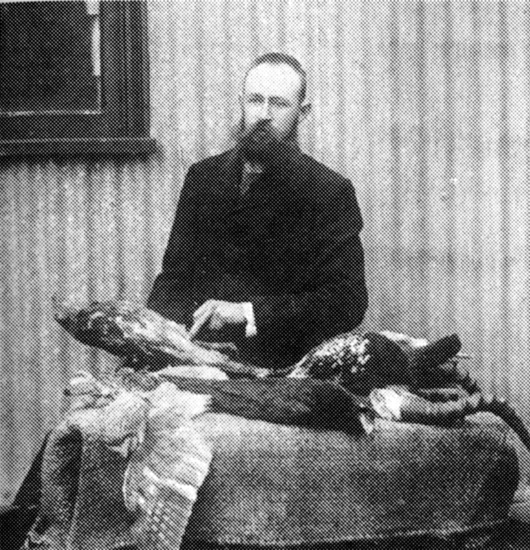
Osbert Salvin
Osbert Salvin FRS (25 February 1835 – 1 June 1898) was an English naturalist, ornithologist, and herpetologist best known for co-authoring ''Biologia Centrali-Americana'' (1879–1915) with Frederick DuCane Godman. This was a 52 volume encyclopedia on the natural history of Central America. Biography Osbert Salvin was born in Finchley, north London, the second son of the architect Anthony Salvin, of Hawksfold, Sussex. He was educated at Westminster and Trinity Hall, Cambridge, taking his degree in 1857. Shortly afterwards he accompanied his second cousin by marriage, Henry Baker Tristram, in a natural history exploration of Tunisia and eastern Algeria. Their account of this trip was published in ''The Ibis'' in 1859 and 1860. In the autumn of 1857, he made the first of several visits to Guatemala, returning there with Frederick DuCane Godman in 1861. It was during this journey that the ''Biologia Centrali-Americana'' was planned. In 1871 Salvin became editor of ''The Ibis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William John Swainson
William John Swainson FLS, FRS (8 October 1789 – 6 December 1855), was an English ornithologist, malacologist, conchologist, entomologist and artist. Life Swainson was born in Dover Place, St Mary Newington, London, the eldest son of John Timothy Swainson the Second (1756–1824), an original fellow of the Linnean Society. He was cousin of the amateur botanist Isaac Swainson.Etymologisches Worterbuch der botanischen Pflanzennamen by H. Genaust. Review by Paul A. Fryxell ''Taxon'', Vol. 38(2), 245–246 (1989). His father's family originated in Lancashire, and both grandfather and father held high posts in Her Majesty's Customs, the father becoming Collector at Liverpool. William, whose formal education was curtailed because of an impediment in his speech, joined the Liverpool Customs as a junior clerk at the age of 14."William Swainson F.R.S, F.L.S., Naturalist and Artist: Diaries 1808–1838: Sicily, Malta, Greece, Italy and Brazil." G .M. Swainson, Palmerston, NZ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William H
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John T
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
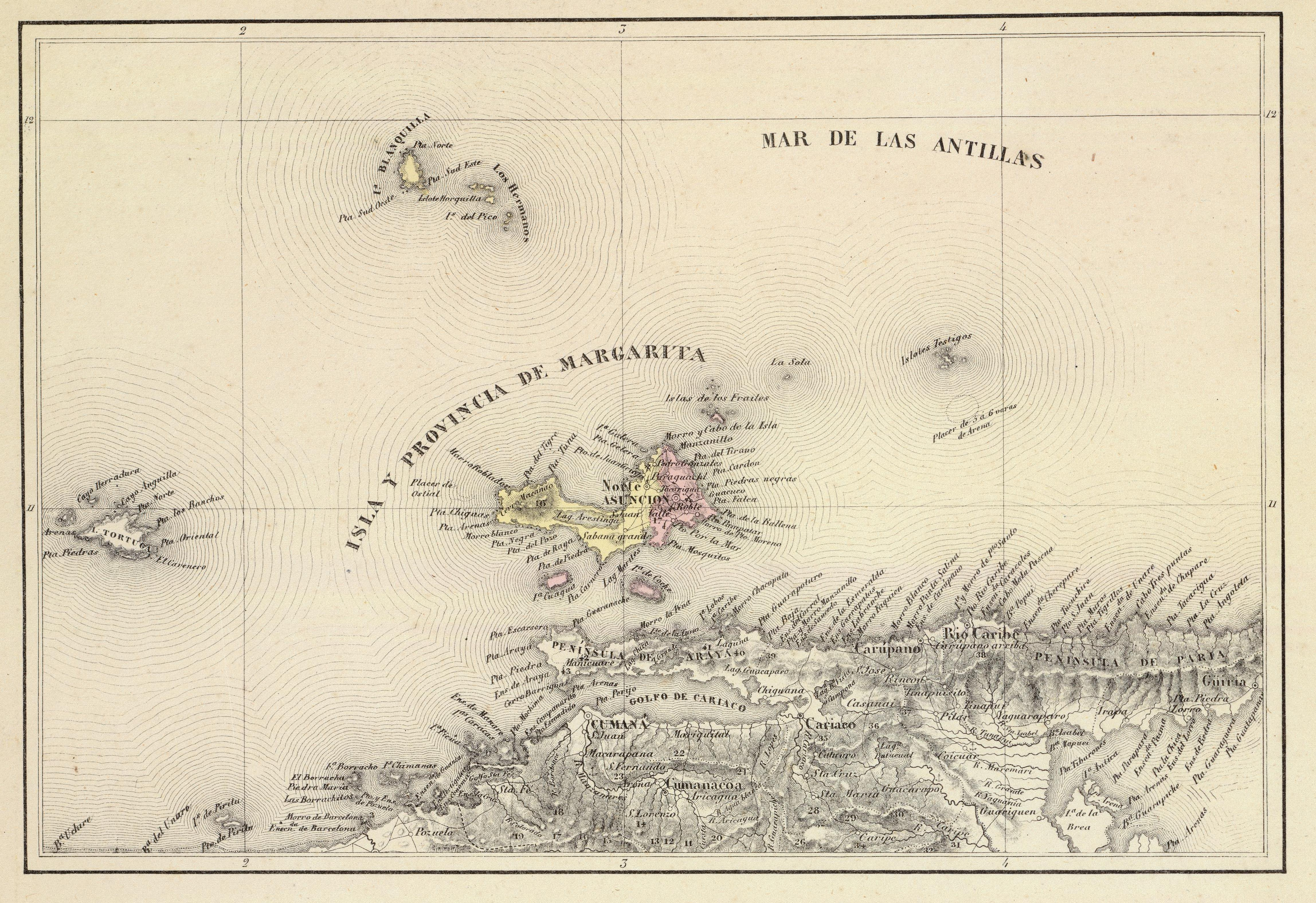
Margarita Island
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the northeastern coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island. History Age of Exploration Christopher Columbus was the first European to arrive on Margarita Island in 1498. The local natives were the Guaiqueries people. The coast of the island was abundant in pearls, which represented almost a third of all New World tribute to the Spanish Crown. Margarita Island was fortified against the increasing threat of pirate attacks, and some fortifications remain today. It was the center of Spanish colonial Margarita Province, established in 1525. In 1561, the island was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador. Around 1675, the island was captured again, this time by Red Legs Greaves, a pirate known for his humanity and morality. He captured a fleet of Spanish ships off por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tortuga Island
La Tortuga Island (; "La Tortuga" means "the turtle") is an uninhabited island of Venezuela, the largest in the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela. It is part of a group of islands that include the Tortuguillos and Cayo Herradura. Isla La Tortuga has an area of . History The island was visited by Amerindians from the coast of present-day Venezuela to exploit its natural resources including salt, fish and turtles, well before Spanish colonization of the New World. It is not known by which European explorer the island was first seen and named, yet the name derives from the large numbers of marine turtles that come to lay eggs on its long sandy beaches every year. The island was seasonally visited by the Dutch who came there to exploit the salt evaporation ponds on the east of the island between 1624 and 1638. They constructed a fort on the island to guard their salt works and repel the Spanish who were eager to keep the Dutch off the island. They were definitively expelled in 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles B
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch and German, have retained the word in two separate senses. In the particular case of Dutch, ''Karel'' refers to the given name, whereas the noun ''kerel'' means "a bloke, fellow, man". Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its depr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC islands, 80 km (50 miles) off the coast of Venezuela. Unlike much of the Caribbean region, the ABC islands lie outside Hurricane Alley. The islands have an arid climate that attracts visitors seeking warm, sunny weather all year round. Bonaire is a popular snorkeling and scuba diving destination because of its multiple shore diving sites and easy access to the island's fringing reefs. As of 1 January 2019, the island's population totaled 20,104 permanent residents, an increase of about 1,200 since 2015. The island's total land area is ; it is long from north to south, and ranges from wide from east to west. A short west of Bonaire across the sea is the uninhabited islet Klein Bonaire with a total land area of . Klein Bonaire has l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curaçao
Curaçao ( ; ; pap, Kòrsou, ), officially the Country of Curaçao ( nl, Land Curaçao; pap, Pais Kòrsou), is a Lesser Antilles island country in the southern Caribbean Sea and the Dutch Caribbean region, about north of the Venezuela coast. It is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Together with Aruba and Bonaire, it forms the ABC islands. Collectively, Curaçao, Aruba, and other Dutch islands in the Caribbean are often called the Dutch Caribbean. Curaçao was formerly part of the Curaçao and Dependencies colony from 1815 to 1954 and later the Netherlands Antilles from 1954 to 2010, as Island Territory of Curaçao ( nl, Eilandgebied Curaçao, links=no, pap, Teritorio Insular di Kòrsou, links=no), and is now formally called the Country of Curaçao. It includes the main island of Curaçao and the much smaller, uninhabited island of Klein Curaçao ("Little Curaçao"). Curaçao has a population of 158,665 (January 2019 est.), with an area of ; its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Hartert
Ernst Johann Otto Hartert (29 October 1859 – 11 November 1933) was a widely published German ornithologist. Life and career Hartert was born in Hamburg, Germany on 29 October 1859. In July 1891, he married the illustrator Claudia Bernadine Elisabeth Hartert in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, with whom he had a son named Joachim Karl (Charles) Hartert, (1893–1916), who was killed as an English soldier on the Somme. Together with his wife, he was the first to describe the blue-tailed Buffon hummingbird subspecies (''Chalybura buffonii intermedia'' Hartert, E & Hartert, C, 1894). The article ''On a collection of Humming Birds from Ecuador and Mexico'' appears to be their only joint publication. Hartert was employed by Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild as ornithological curator of Rothshild's private Natural History Museum at Tring, in England from 1892 to 1929. Hartert published the quarterly museum periodical ''Novitates Zoologicae'' (1894–39) with Rothschild, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armando Dugand
Armando Dugand (July 23, 1906 – 1971) was a Colombian botanist, geobotanist Phytogeography (from Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution o ..., and ornithologist. Dugand's father, François Victor (or Francisco Víctor) Dugand, was a successful French banker; his mother was Reyes Geneco (or Gnecco) Coronado.Borrero, José Ignacio (1975). "Obituaries: Armando Dugand". ''Auk'' 92: 210. Dugand was educated in France and in the United States (at Albany Business College). In 1927 he married Sara Roncallo. In 1940 he co-founded the scientific journal ''Caldasia''. Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . ("Dugand", p. 76). He also founded two other scientific journals: ''Mutisia (Acta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |