|
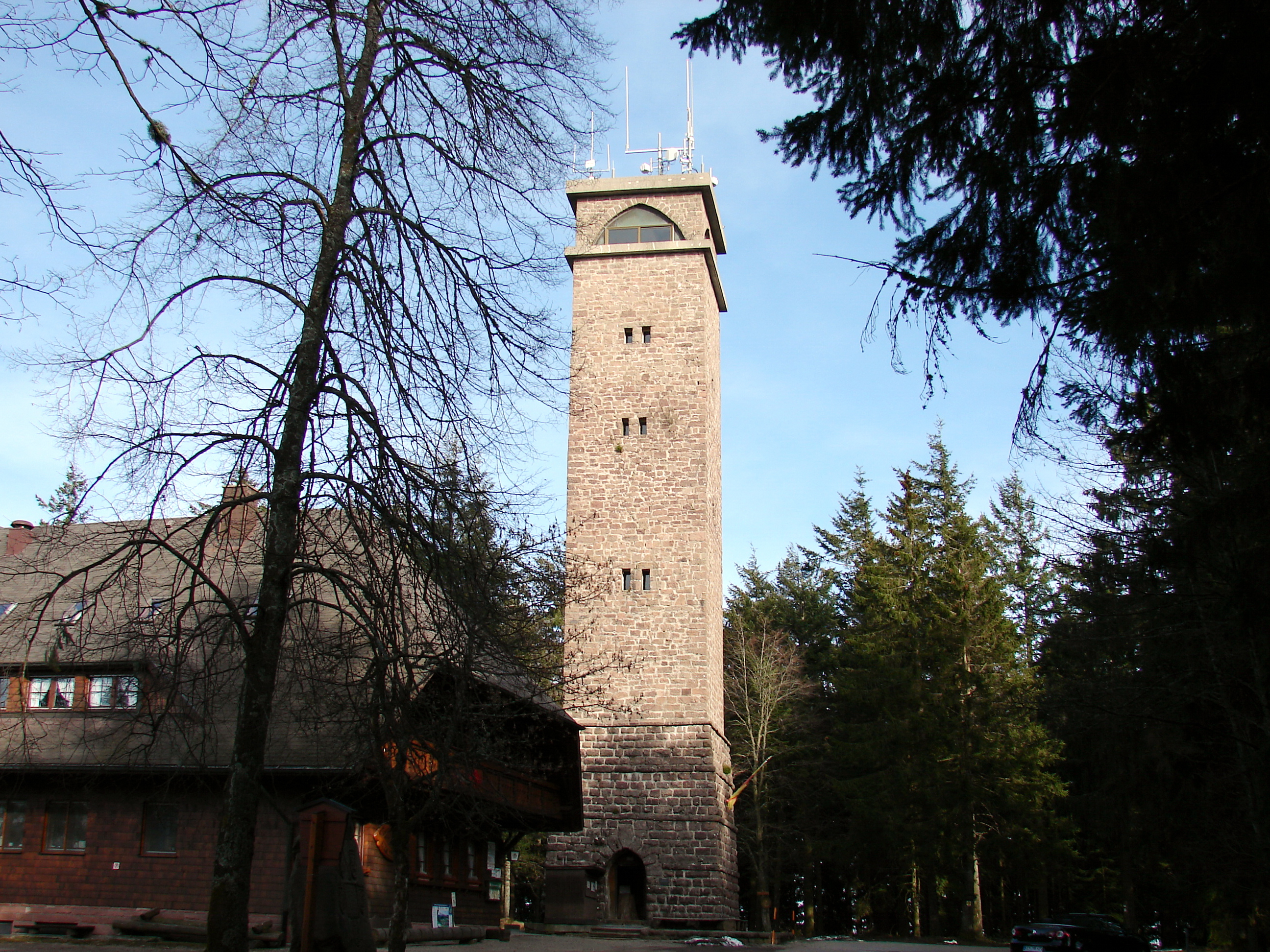
Brandenkopf
The Brandenkopf is and one of the highest mountains in the Central Black Forest in southern Germany. The mountain lies in the county of Ortenaukreis in the state of Baden-Württemberg within the municipalities of Oberharmersbach, Fischerbach and Hausach, its summit is part of Oberharmersbach. The mountain forms the prominent centrepiece between the valleys of the Kinzig, the Wolf and the Harmersbach. The name of the Brandenkopf ("Fire Peak") is derived from a great forest fire in 1730. Before this event it was called the ''Varnlehenskopf''. The Brandenkopf is well developed with roads and footpaths (including the Hansjakobweg II and a link to the West Way, 3.5 km away) from several directions. There is a transmitter, the Sender Brandenkopf, on the mountain. Sights The 32-metre-high Brandenkopf Tower (''Brandenkopfturm'') has stood on the summit since 1929. This is a stone observation tower, which has extensive views over the Black Forest countryside and, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansjakobweg II
The Hansjakob Way II (german: Hansjakobweg II), also called the Great Hansjakob Way ''(Großer Hansjakobweg)'' is a five-day circular walk through the Central Black Forest in Germany, from Haslach im Kinzigtal returning to Haslach. The roughly 92-kilometre-long hiking trail is named after the Baden author and parish priest, Heinrich Hansjakob (1837–1916). The route was opened in 1983 and is sponsored and managed by the Black Forest Club. The waymark is a white diamond with a black Hansjakob hat, the headwear in which Hansjakob is portrayed in many contemporary pictures and photographs. At all the sights along the way, information boards have been erected, that relate mainly to the life and stores of Hansjakob. Day tours/stages First Stage: Haslach – Wolfach Haslach – Sandhaas Hut – Hausach – Gutach/Tower – Wolfach (16.5 km) Second Stage: Wolfach – Brandenkopf Wolfach – Hohenlochen – Burzbühl – Bettelfrau – Brandenkopf (11 km) Third Stag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Way (Black Forest)
The Westweg ("West Way" or "West Trail") is a long-distance hiking trail in Germany, running north–south through the Black Forest from Pforzheim to Basel. The trail is around 285 km long, and was founded in 1900. It is currently maintained under the auspices of the Black Forest Club. The trail symbol is a red lozenge on a white background. The Westweg is a part of the European Long-distance Trail E1 (North Cape, Norway - Sicily) The route passes through or near numerous villages or small towns, so there is no difficulty in finding overnight accommodation and meals along the route. It would actually require more planning to walk it while staying in youth hostel-type accommodation, or camping. There are a number of services that will transport your luggage to the next accommodation by vehicle, leaving the hikers with only their daypacks for the hike. The route can be accessed at several places along its length by road or public transport, so it is easy to walk part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Black Forest
The Central Black Forest (german: Mittlerer Schwarzwald), also called the Middle Black Forest, is a natural or cultural division of the Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It generally refers to a region of deeply incised valleys from the Rench valley and southern foothills of the Kniebis in the north to the area of Freiburg im Breisgau and Donaueschingen in the south. Its highest area, which is southeast of the Elz valley, is also part of the High Black Forest. Geography The dominating valley system of the Kinzig cuts through the Middle Black Forest from east to west. Prominent peaks are the Kandel (), Weißtannenhöhe (), Obereck (), Rohrhardsberg (), Brend (), Stöcklewald () and Mooswaldkopf () south of the Kinzig, and the Brandenkopf () and Lettstädter Höhe () north of the Kinzig. Geology Gneisses and granites predominate. Unlike the Northern Black Forest the Bunter sandstone covering with its plateau-like mountain shapes has only survived in a few pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausach
Hausach (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Huusä) is a town in the Ortenaukreis, in western Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History Hausach was founded in the 13th century, below Husen Castle. In the 14th century, it became a possession of the County of Fürstenberg, who gave the town its charter and maintained a residence in it. In 1806, Hausach was mediatized to the Grand Duchy of Baden. The town was assigned in 1813 to the district of Haslach, but in 1857 was reassigned to the district of Wolfach. In 1939, that district was reorganized as . On 1 Jul 1971, the town of Einbach was incorporated into Hausach. As a result of the , Hausach was assigned to the Ortenau district. Geography The township ('' Stadt'') of Hausach is part of the Ortenau district of Baden-Württemberg, in the Federal Republic of Germany. It is physically located in the Central Black Forest, at the center of the valley of the Kinzig. the elevation above sea level in the municipal area ranges from a high of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas energy sources. Smaller wind turbines are used for applications such as battery charging for auxiliary power for boats or caravans, and to power traffic warning signs. Larger turbines can contribute to a domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility supplier via the electrical grid. Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Forest Club
The Schwarzwaldverein (Black Forest Club or Black Forest Association) was founded in Freiburg im Breisgau (Germany) in 1864, making it the oldest German hiking and mountaineering club. The Schwarzwaldverein has almost 90,000 members in 241 local chapters. Activities of the club include hiking, environmental protection, the promotion of local culture ('' Heimatpflege''), trail maintenance, and family and youth work projects in the Black Forest. Organisation The Schwarzwaldverein consists of the main association and 241 independent local member chapters. The local chapters are organized into 17 regions, and have a membership of almost 90,000 members. The executive committee consists of three members, and the current president is Eugen Dieterle. In addition to the executive committee, there are nine divisional officers, each of whom is responsible for coordinating specific parts of the club's activities. The main offices are in Freiburg. Trail Maintenance The Schwarzwaldvere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
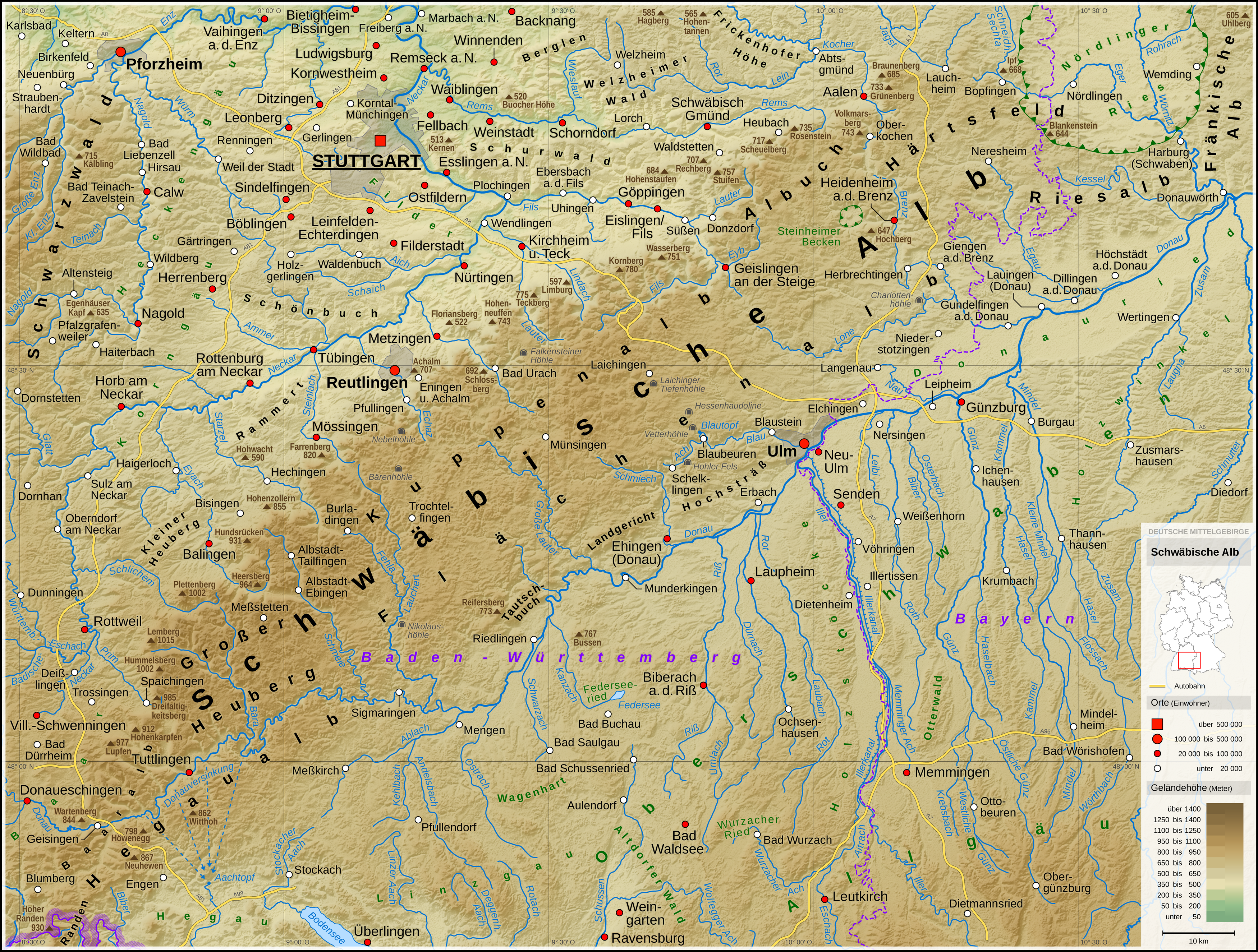
Swabian Jura
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of Swabia. The Swabian Jura occupies the region bounded by the Danube in the southeast and the upper Neckar in the northwest. In the southwest it rises to the higher mountains of the Black Forest. The highest mountain of the region is the Lemberg (). The area's profile resembles a high plateau, which slowly falls away to the southeast. The northwestern edge is a steep escarpment (called the Albtrauf or Albanstieg, rising up , covered with forests), while the top is flat or gently rolling. In economic and cultural terms, the Swabian Jura includes regions just around the mountain range. It is a popular recreation area. Geology The geology of the Swabian Jura is mostly limestone, which formed the seabed during the Jurassic period. The sea r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate (the Belfort–Ronchamp– Lure line) to the Börrstadt Basin (the Winnweiler– Börrstadt–Göllheim line), and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain. The Grand Ballon is the highest peak at , followed by the Storkenkopf (), and the Hohneck ().IGN maps available oGéoportail/ref> Geography Geographically, the Vosges Mountains are wholly in France, far above the Col de Saverne separating them from the Palatinate Forest in Germany. The latter area logically continues the same Vosges geologic structure but traditionally receives this different name for historical and political reasons. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The Alpine arch generally extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 128 peaks higher than . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountains, precipitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is the source of the Danube and Neckar rivers. Its highest peak is the Feldberg with an elevation of above sea level. Roughly oblong in shape, with a length of and breadth of up to , it has an area of about 6,009 km2 (2,320 sq mi). Historically, the area was known for forestry and the mining of ore deposits, but tourism has now become the primary industry, accounting for around 300,000 jobs. There are several ruined military fortifications dating back to the 17th century. History In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity, Abnoba. In Roman times (Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'' = "border"). The Black Forest probably represented the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Tower
An observation tower is a structure used to view events from a long distance and to create a full 360 degree range of vision to conduct long distance observations. Observation towers are usually at least tall and are made from stone, iron, and wood. Many modern towers are also used as TV towers, restaurants, or churches. The towers first appeared in the ancient world, as long ago as the Babylonian Empire. Observation towers that are used as guard posts or observation posts over an extended period to overlook an area are commonly called watchtowers instead. Construction and usage Observation towers are an easily visible sight on the countryside, as they must rise over trees and other obstacles to ensure clear vision. Older control rooms have often been likened to medieval chambers. The heavy use of stone, iron, and wood in their construction helps to create this illusion. Modern towers frequently have observation decks or terraces with restaurants or on the roof of mountain st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberharmersbach Brandenkopfturm
Oberharmersbach ( gsw, label=Low Alemannic Low Alemannic German (german: Niederalemannisch) is a branch of Alemannic German, which is part of Upper German. Its varieties are only partly intelligible to non-Alemannic speakers. Subdivisions * Lake Constance Alemannic ( de) **Northern Vor ..., Haamerschbach) is a town in the district of Ortenau in Baden-Württemberg in Germany References External links * Towns in Baden-Württemberg Ortenaukreis {{Ortenaukreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)