|
Because (The Beatles Song)
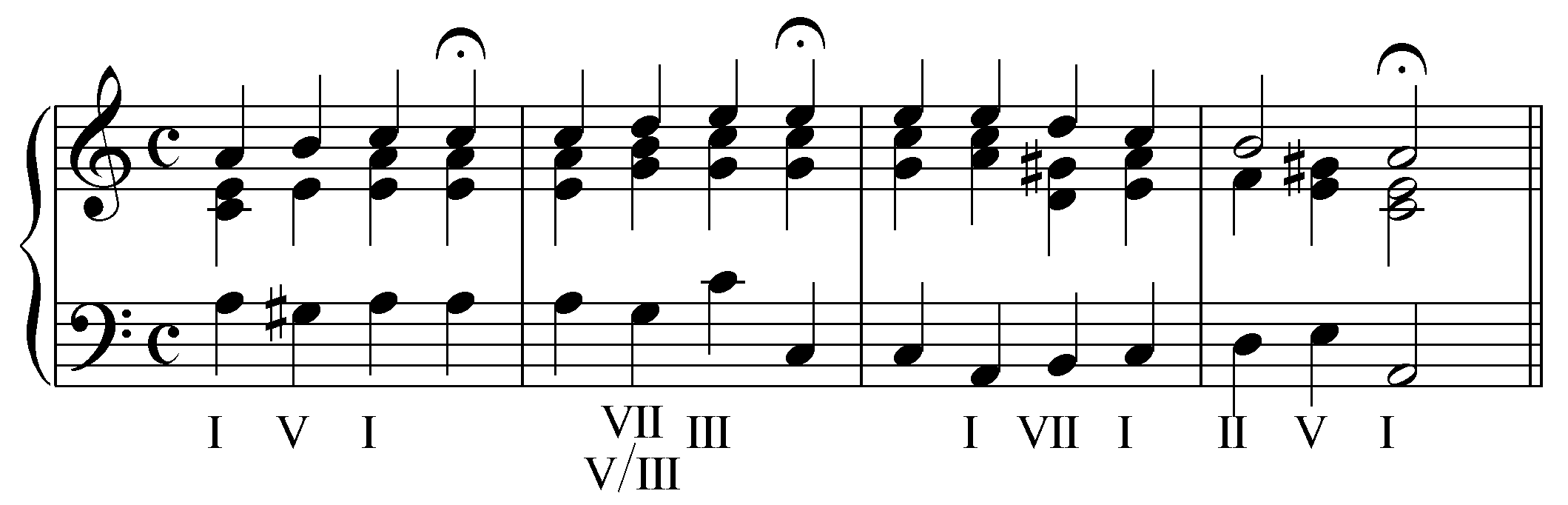
"Because" is a song written by John Lennon (credited to Lennon–McCartney) and recorded by the English rock band the Beatles. It was released on their 1969 album ''Abbey Road'', immediately preceding the extended medley on side two of the record. It features a prominent three-part vocal harmony by Lennon, Paul McCartney and George Harrison, recorded three times to make nine voices in all. Composition The song begins with a distinctive electric harpsichord intro played by producer George Martin. The harpsichord is joined by Lennon's guitar (mimicking the harpsichord line) played through a Leslie speaker. Then vocals and bass guitar enter. "Because" was one of few Beatles recordings to feature a Moog synthesiser, played by George Harrison. It appears in what Alan Pollack refers to as the "mini-bridge", and then again at the end of the song. According to Lennon, the song's close musical resemblance to the first movement of Ludwig van Beethoven's ''Moonlight Sonata'' was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatles, most influential band of all time and were integral to the development of counterculture of the 1960s, 1960s counterculture and popular music's recognition as an art form. Rooted in skiffle, beat music, beat and 1950s rock and roll, rock 'n' roll, their sound incorporated elements of classical music and traditional pop in innovative ways; the band also explored music styles ranging from folk music, folk and Music of India, Indian music to Psychedelic music, psychedelia and hard rock. As Recording practices of the Beatles, pioneers in recording, songwriting and artistic presentation, the Beatles revolutionised many aspects of the music industry and were often publicised as leaders of the era's Baby boomers, youth and sociocultural movements. Led by primary songwriter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classical music repertoire and span the transition from the Classical period to the Romantic era in classical music. His career has conventionally been divided into early, middle, and late periods. His early period, during which he forged his craft, is typically considered to have lasted until 1802. From 1802 to around 1812, his middle period showed an individual development from the styles of Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and is sometimes characterized as heroic. During this time, he began to grow increasingly deaf. In his late period, from 1812 to 1827, he extended his innovations in musical form and expression. Beethoven was born in Bonn. His musical talent was obvious at an early age. He was initially harshly and intensively tau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdub
Overdubbing (also known as layering) is a technique used in audio recording in which audio tracks that have been pre-recorded are then played back and monitored, while simultaneously recording new, doubled, or augmented tracks onto one or more available tracks of a digital audio workstation (DAW) or tape recorder. The overdub process can be repeated multiple times. This technique is often used with singers, as well as with instruments, or ensembles/orchestras. Overdubbing is typically done for the purpose of adding richness and complexity to the original recording. For example, if there are only one or two artists involved in the recording process, overdubbing can give the effect of sounding like many performers. In vocal performances, the performer usually listens to an existing recorded performance (usually through headphones in a recording studio) and simultaneously plays a new performance along with it, which is also recorded. The intention is that the final mix will contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
You Never Give Me Your Money
"You Never Give Me Your Money" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles. It was written by Paul McCartney (and credited to Lennon–McCartney) and documented the financial and personal difficulties facing the band. The song is the first part of the medley on side two of their 1969 album ''Abbey Road'' and was recorded in stages between May and August that year. The song was the first one to be recorded for the medley, which was conceived by McCartney and producer George Martin as a finale for the Beatles' career. The backing track was recorded at Olympic Sound Studios in Barnes, London, but the remainder of overdubs occurred at EMI Studios. Musically, the song is made up of a suite of various segments, ranging from a piano ballad at the beginning through to guitar arpeggios at the end. Background The song was written by McCartney when he was staying with his wife Linda in New York in March 1969 shortly after their wedding. This was a break following the ''Get Back''/''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminished Triad
In music theory, a diminished triad (also known as the minor flatted fifth) is a triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root. It is a minor triad with a lowered ( flattened) fifth. When using chord symbols, it may be indicated by the symbols "dim", "", "m5", or "MI(5)". However, in most popular-music chord books, the symbol "dim" and "" represents a diminished seventh chord (a four-tone chord), which in some modern jazz books and music theory books is represented by the "dim7" or "7" symbols. For example, the diminished triad built on C, written as C, has pitches C–E–G: : The chord can be represented by the integer notation . In the common practice period, the diminished triad is considered dissonant because of the diminished fifth (or tritone). Harmonic function In major scales, a diminished triad occurs only on the seventh scale degree. For instance, in the key of C, this is a B diminished triad (B, D, F). Since the triad is built on the seventh scale de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminished Seventh Chord
The diminished seventh chord is a four-note chord (a seventh chord) composed of a root note, together with a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a diminished seventh above the root: (1, 3, 5, 7). For example, the diminished seventh chord built on C, commonly written as C7, has pitches C–E–G–B (A): : As such, a diminished seventh chord comprises a diminished triad plus a diminished seventh. Because of this, it can also be viewed as four notes all stacked in intervals of a minor third and can be represented by the integer notation . Since a diminished seventh interval is enharmonically equivalent to a major sixth, the chord is enharmonically equivalent to (1, 3, 5, 6). The diminished seventh chord occurs as a leading-tone seventh chord in the harmonic minor scale. It typically has dominant function and contains two diminished fifths, which often resolve inwards. In most sheet music books, the notation Cdim or C denotes a diminished seventh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtonic
In music, the subtonic is the degree of a musical scale which is a whole step below the tonic note. In a major key, it is a lowered, or flattened, seventh scale degree (). It appears as the seventh scale degree in the natural minor and descending melodic minor scales but not in the major scale. In major keys, the subtonic sometimes appears in borrowed chords. In the movable do solfège system, the subtonic note is sung as ''te'' (or ''ta''). The subtonic can be contrasted with the leading note, which is a ''half step'' below the tonic. The distinction between leading note and subtonic has been made by theorists since at least the second quarter of the 20th century. Before that, the term ''subtonic'' often referred to the leading tone triad, for example. The word ''subtonic'' is also used as an English translation of ''subtonium'', the Latin term used in Gregorian chant theory for the similar usage of a tone one whole step below the mode final in the Dorian, Phrygian, and Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neapolitan Chord
In Classical music theory, a Neapolitan chord (or simply a "Neapolitan") is a major chord built on the lowered ( flatted) second (supertonic) scale degree. In Schenkerian analysis, it is known as a Phrygian II, since in minor scales the chord is built on the notes of the corresponding Phrygian mode. Although it is sometimes indicated by an "N" rather than a "II", some analysts prefer the latter because it indicates the relation of this chord to the supertonic. The Neapolitan chord does not fall into the categories of mixture or tonicization. Moreover, even Schenkerians like Carl Schachter do not consider this chord as a sign for a shift to the Phrygian mode. Therefore, like the augmented sixth chords it should be assigned to a separate category of chromatic alteration. In European Classical music, the Neapolitan most commonly occurs in first inversion so that it is notated either as II6 or N6 and normally referred to as a Neapolitan sixth chord. In C major or C minor, for exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submediant
In music, the submediant is the sixth degree () of a diatonic scale. The submediant ("lower mediant") is named thus because it is halfway between tonic and subdominant ("lower dominant") or because its position below the tonic is symmetrical to that of the mediant above. (See the figure in the Degree (music) article.) In the movable do solfège system, the submediant is sung as ''la'' in a major mode and ''fa'' in a minor mode. It is occasionally called superdominant, as the degree above the dominant. This is its normal name (''sus-dominante'') in French. In Roman numeral analysis, the triad formed on the submediant is typically symbolized by "VI" if it is a major triad (the default in a minor mode) and by "vi" if it is a minor triad (the default in a major mode). The term ''submediant'' may also refer to a relationship of musical keys. For example, relative to the key of C major, the key of A minor is the submediant. In a major key, the submediant key is the relative mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone
A baritone is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the bass and the tenor voice-types. The term originates from the Greek (), meaning "heavy sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second F below middle C to the F above middle C (i.e. F2–F4) in choral music, and from the second A below middle C to the A above middle C (A2 to A4) in operatic music, but the range can extend at either end. Subtypes of baritone include the baryton-Martin baritone (light baritone), lyric baritone, ''Kavalierbariton'', Verdi baritone, dramatic baritone, ''baryton-noble'' baritone, and the bass-baritone. History The first use of the term "baritone" emerged as ''baritonans'', late in the 15th century, usually in French sacred polyphonic music. At this early stage it was frequently used as the lowest of the voices (including the bass), but in 17th-century Italy the term was all-encompassing and used to describe the averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-sharp Minor
C-sharp minor is a minor scale based on C, with the pitches C, D, E, F, G, A, and B. Its key signature consists of four sharps. The C-sharp natural minor scale is: : Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The C-sharp harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: : : Its relative major is E major. Its parallel major, C-sharp major, is usually written instead as the enharmonic key of D-flat major, since C-sharp major’s key signature with seven sharps is not normally used. Its enharmonic equivalent, D-flat minor, having eight flats including the B, has a similar problem. Therefore, C-sharp minor is often used as the parallel minor for D-flat major. (The same enharmonic situation occurs with the keys of A-flat major and G-sharp minor.) Classical music in this key There are only two known symphonies in the 18th century written in this key. One of them is by Joseph Martin Kraus, who appears t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Everett (musicologist)
Walter Everett is a music theorist specializing in popular music who teaches at the University of Michigan. His books include ''The Beatles as Musicians: Revolver through the Anthology'' (1999, ), which has been called "the most important work to appear on the Beatles thus far",The 2007/2008 Kjell Meling Award , ''Penn State Altoona''. and its follow-up volume, ''The Beatles as Musicians: The Quarry Men through Rubber Soul'' (2001). He also wrote ''The Foundations of Rock: From 'Blue Suede Shoes' to 'Suite: Judy Blue Eyes (2008, ) and has contributed to titles in the Cambridge Companions to Music series. Gary Burns, editor of the journal ''Popular Music and Society'', describes Everett's ''Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)