|
Barry Domvile
Admiral Sir Barry Edward Domvile, (5 September 1878 – 13 August 1971) was a high-ranking Royal Navy officer who was interned during the Second World War for being a Nazi sympathiser. Throughout the 1930s, he had expressed support for Germany's Adolf Hitler as well as pro-Nazi and anti-Semitic sentiments.Hitler's Munich Man: The Fall of Sir Admiral Barry Domvile, Martin Connolly, 2017 Naval career Domvile was the son of Admiral Sir Compton Domvile and followed his father into the Royal Navy in 1892.[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, or fleet admiral. Etymology The word in Middle English comes from Anglo-French , "commander", from Medieval Latin , . These evolved from the Arabic () – (), “king, prince, chief, leader, nobleman, lord, a governor, commander, or person who rules over a number of people,” and (), the Arabic article answering to “the.” In Arabic, admiral is also represented as (), where () means the sea. The 1818 edition of Samuel Johnson's '' A Dictionary of the English Language'', edited and revised by the Rev. Henry John Todd, states that the term “has been traced to the Arab. emir or amir, lord or commander, and the Gr. , the sea, q. d. ''prince of the sea''. The word is written both with and without the d, in other languages, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compton Domvile (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Compton Edward Domvile, (10 October 1842 – 19 November 1924) was a distinguished Royal Navy officer in the Edwardian and Victorian eras. Early life Compton Domvile was born on 10 October 1842 to Henry Barry Domvile (1813–1843) and Frances Domvile (née Winnington-Ingram) (d 1884). He was educated at the Royal Academy, Gosport. Career Early career Compton Domvile joined the Royal Navy in 1856. He served in the Royal Yacht and was promoted to lieutenant on 28 October 1862. He commanded the steam-gunboat HMS ''Algerine'' from 16 April 1866 and was promoted to commander on 2 September 1868 for service against piracy. HMS ''Dryad'' On 3 August 1874 he became captain of the screw sloop HMS ''Dryad'' from commissioning at Devonport. ''Dryad'' served on the North America and West Indies Station until December 1877. Domvile was promoted to captain on 27 March 1876, whilst serving in ''Dryad''. Commander John Edward Stokes replaced him as ''Dryad''s captain some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hythe (UK Parliament Constituency)
Hythe was a United Kingdom constituencies, constituency centred on the town of Hythe, Kent, Hythe in Kent. It returned two Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons until 1832, when its representation was reduced to one member. The constituency was abolished for the 1950 United Kingdom general election, 1950 general election, and replaced with the new Folkestone and Hythe (UK Parliament constituency), Folkestone and Hythe constituency. Boundaries 1918–1950: The Municipal Boroughs of Folkestone and Hythe, the Urban District of Cheriton, and part of the Urban District of Sandgate. Members of Parliament 1366-1640 1640-1832 1832-1950 Election results Elections in the 1830s Townsend-Farquhar's death caused a by-election. * 204 Scot and Lot votes were placed for Fraser and Kelly, but these were rejected Marjoribanks resigned, causing a by-election. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
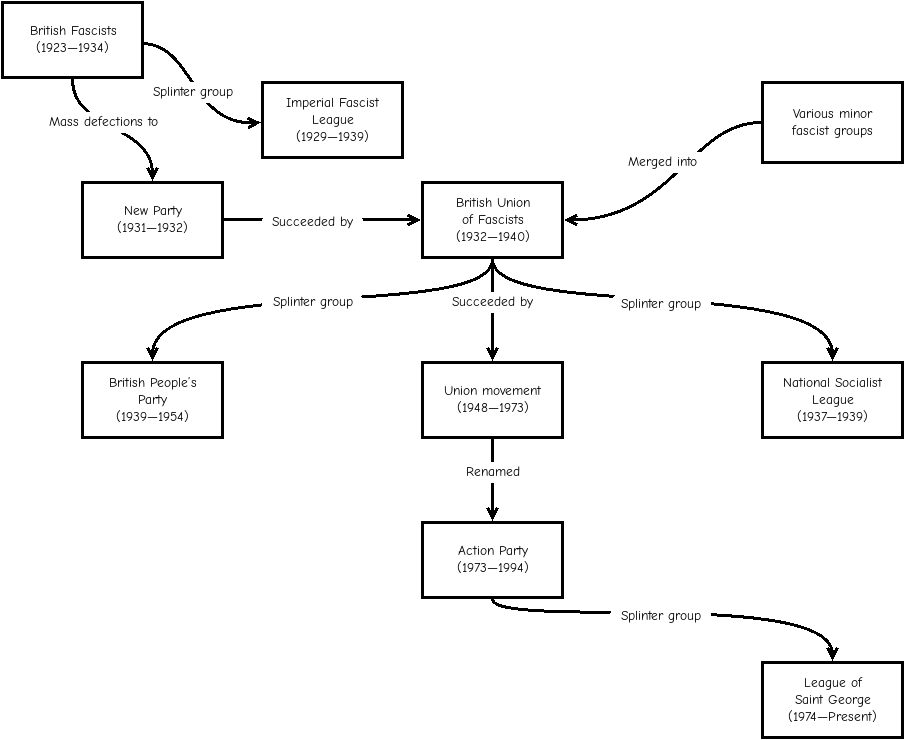
British People's Party (1939)
The British People's Party (BPP) was a British far-right political party founded in 1939 and led by ex-British Union of Fascists (BUF) member and Labour Party Member of Parliament John Beckett. Origins The BPP had its roots in the journal ''New Pioneer'', edited by John Beckett and effectively the mouthpiece of the British Council Against European Commitments, a co-ordinating body involving the National Socialist League (NSL), English Array and League of Loyalists. The main crux of this publication was opposition to war with Nazi Germany, although it also endorsed fascism and anti-Semitism. The proprietor of this journal was Viscount Lymington, a strong opponent of war with Germany.D. Boothroyd, ''The History of British Political Parties'', London: Politico's Publishing, 2001, p. 24 Others involved in its production included A. K. Chesterton and the anthropologist George Henry Lane-Fox Pitt-Rivers, whilst individual members, especially Lymington, were close to ruralist Rolf G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism. Antisemitism has historically been manifested in many ways, ranging from expressions of hatred of or discrimination against individual Jews to organized pogroms by mobs, police forces, or genocide. Although the term did not come into common usage until the 19th century, it is also applied to previous and later anti-Jewish incidents. Notable instances of persecution include the Rhineland massacres preceding the First Crusade in 1096, the Edict of Expulsion from England in 1290, the 1348–1351 persecution of Jews during the Black Death, the massacres of Spanish Jews in 1391, the persecutions of the Spanish Inquisition, the expulsion from Spain in 1492, the Cossack massacres in Ukraine from 1648 to 1657, various anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Link (organisation)
The Link was established in July 1937 as an "independent non-party organisation to promote Anglo-German friendship". It generally operated as a cultural organisation, although its journal, the ''Anglo-German Review'', reflected the pro-Nazi views of Barry Domvile, and particularly in London it attracted a number of anti-semites and pro-Nazis. At its height the membership numbered around 4,300. The Link opposed war between Britain and Germany, and because of this attracted the support of some British pacifists.David C. Lukowitz, "British Pacifists and Appeasement: The Peace Pledge Union", ''Journal of Contemporary History,'' Vol. 9, No. 1 (January 1974), pp. 115–127 When The Link and the ''Anglo-German Review'' were included among peace organisations across the political spectrum in the ''Peace Service Handbook'' (a publication put out by the Peace Pledge Union), ''The Daily Telegraph'' and the ''News Chronicle'' published articles accusing the PPU of supporting Nazism. In respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-German Fellowship
The Anglo-German Fellowship was a membership organisation that existed from 1935 to 1939, and aimed to build up friendship between the United Kingdom and Germany. It was widely perceived as being allied to Nazism. Previous groups in Britain with the same aims had been wound up when Adolf Hitler came to power. Origins In a 1935 speech, the Prince of Wales (later Edward VIII) had called for a closer understanding of Germany in order to safeguard peace in Europe, and in response Sir Thomas Moore, a Conservative Member of Parliament, suggested setting up a study group of pro-German MPs. From that idea emerged the AGF, established in September 1935 with Lord Mount Temple as chairman, and historian Philip Conwell-Evans and merchant banker Ernest Tennant as secretaries.Martin Pugh, ''"Hurrah For the Blackshirts!" Fascists and Fascism in Britain Between the War'', Pimlico, 2006, p. 269 Tennant was a friend of Joachim von Ribbentrop, German Ambassador to Britain. The group's stated aim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945. Ribbentrop first came to Adolf Hitler's notice as a well-travelled businessman with more knowledge of the outside world than most senior Nazis and as a perceived authority on foreign affairs. He offered his house Schloss Fuschl for the secret meetings in January 1933 that resulted in Hitler's appointment as Chancellor of Germany. He became a close confidant of Hitler, to the disgust of some party members, who thought him superficial and lacking in talent. He was appointed ambassador to the Court of St James's, the royal court of the United Kingdom, in 1936 and then Foreign Minister of Germany in February 1938. Before World War II, he played a key role in brokering the Pact of Steel (an alliance with Fascist Italy) and the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact (the Nazi–Soviet non-aggr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
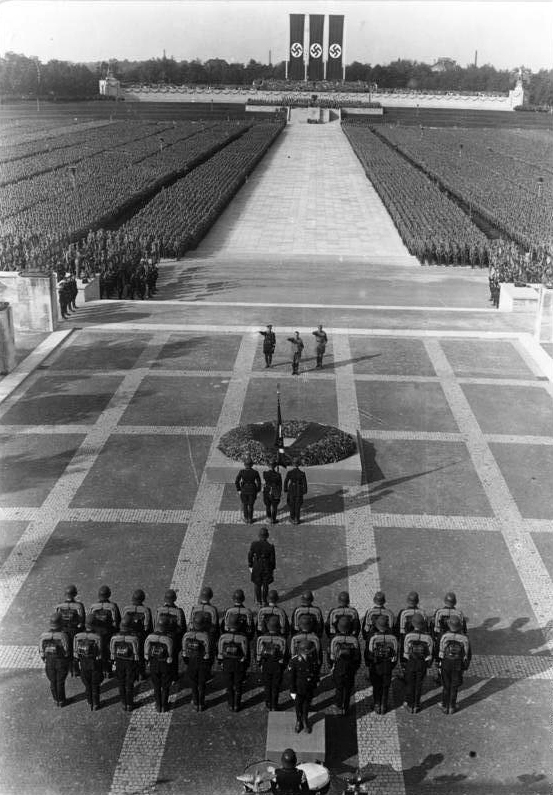
Nuremberg Rallies
The Nuremberg Rallies (officially ', meaning ''Reich Party Congress'') refer to a series of celebratory events coordinated by the Nazi Party in Germany. The first rally held took place in 1923. This rally was not particularly large or impactful; however, as the party grew in size, the rallies became more elaborate and featured larger crowds. They played a seminal role in Nazi propaganda events, conveying a unified and strong Germany under Nazi control. The rallies became a national event once Adolf Hitler rose to power in 1933, when they became annual occurrences. Once the Nazi dictatorship was firmly established, the party's propagandists began filming them for a national and international audience. Nazi filmmaker Leni Riefenstahl produced some of her best known work including ''Triumph of the Will'' (1934) and ''The Victory of Faith'' (1933), both filmed at the Nazi party rally grounds near Nuremberg. The party's 1938 Nuremberg rally celebrated the Anschluss that occurred ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruiser Squadron
The Cruiser Squadron was a naval formation of the British Home Fleet consisting of Armored cruisers of the Royal Navy from 1899 to 1905. History In October 1899 the Royal Navy's Training Squadron consisting mainly of sailing ships was abolished. On the 30 October the Cruiser Squadron was formed using more modern armoured cruisers. Commodore Edmund S. Poë was appointed its first commander. The squadron was assigned to the Home Fleet The Home Fleet was a fleet of the Royal Navy that operated from the United Kingdom's territorial waters from 1902 with intervals until 1967. In 1967, it was merged with the Mediterranean Fleet creating the new Western Fleet. Before the First ... and existed until 1905. . Commodore and Rear-Admirals commanding Post holders included: References {{Cruiser squadrons of the Royal Navy, state=collapsed Cruiser squadrons of the Royal Navy Military units and formations established in 1899 Military units and formations disestablished in 1905< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Intelligence Division (United Kingdom)
The Naval Intelligence Division (NID) was created as a component part of the Admiralty War Staff in 1912. It was the intelligence arm of the British Admiralty before the establishment of a unified Defence Intelligence Staff in 1964. It dealt with matters concerning British naval plans, with the collection of naval intelligence. It was also known as "Room 39", after its room number at the Admiralty. History The Foreign Intelligence Committee was established in 1882 and it evolved into the Naval Intelligence Department in 1887. The NID staff were originally responsible for fleet mobilisation and war plans as well as foreign intelligence collection; thus in the beginning there were originally two divisions: (1) intelligence (Foreign) and (2) Mobilisation. In 1900 another division, War, was added to deal with issues of strategy and defence, and in 1902 a fourth division, Trade, was created for matters related to the protection of merchant shipping. The Trade Division was abolishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Of Staff Mediterranean Fleet
The Chief of Staff, Mediterranean Fleet also formally known as Chief of Staff to the Commander-in-Chief Mediterranean Fleet and originally called Flag Captain, Mediterranean Fleet. was a senior British Royal Navy appointment. He was the commander-in-chiefs primary aide-de-camp providing administrative support from October 1893 to 1967. History The office was created in October 1893 the first incumbent of the office was Captain Francis C. B. Bridgeman. From May, 1905 until July, 1912 the office holder also held the additional title of Flag Captain, Mediterranean Fleet or formally Flag Captain to the Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet. During a period of restructuring and cost cutting from 1954 and 1971 senior fleet commands were either abolished or merged into fewer but larger commands. As part of continuing cost cutting by the Ministry of Defence in 1967 the Mediterranean Fleet was abolished along with this office. The final office holder was Commodore David B. N. Mellis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |