|
B Factory
In particle physics, a B-factory, or sometimes a beauty factory, is a particle collider experiment designed to produce and detect a large number of B mesons so that their properties and behavior can be measured with small statistical uncertainty. Tau leptons and D mesons are also copiously produced at B-factories. History and development A sort of "prototype" or "precursor" B-factory was the HERA-B experiment at DESY that was planned to study B-meson physics in the 1990–2000s, before the actual B-factories were constructed/operational. However, usually HERA-B is not considered a B-factory. Two B-factories were designed and built in the 1990s, and they operated from late 1999 onward: the Belle experiment at the KEKB collider in Tsukuba, Japan, and the BaBar experiment at the PEP-II collider at SLAC in California, United States. They were both electron-positron colliders with the center of mass energy tuned to the ϒ(4S) resonance peak, which is just above the threshold f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, most populous U.S. state and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated Administrative division, subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous Statistical area (United States), urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento, California, Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the List of largest California cities by population, most populous city in the state and the List of United States cities by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higgs Factory
A Higgs Factory is a particle accelerator designed to produce Higgs Bosons at a very high rate, allowing precision studies of this particle. A Higgs factory was identified as the highest future priority of particle physics in the 2020 European Strategy Report. This view was reaffirmed in 2022 by the International Committee on Future Accelerators. The Higgs Boson, discovered in 2012, was the final missing particle of the Standard Model of particle physics. However, unexplained phenomena, such as dark matter lead physicists to think that the Standard Model is an incomplete theory and that new particles may exist. Physicists can search for evidence of new particles in two ways. The first is through direct production, which requires sufficient energy, high production rate, and sensitive detector design. Alternatively, the search can focus on careful measurements of properties of known particles, like the Higgs, that may be affected by interactions with the new particles that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Factory
The Neutrino Factory is a proposed particle accelerator complex intended to measure in detail the properties of neutrinos, which are extremely weakly interacting fundamental particles that can travel in straight lines through normal matter for thousands of kilometres. Up until the 1990s, neutrinos were assumed to be massless, but experimental results from searches for solar neutrinos (those produced in the Sun's core) and others are inconsistent with this assumption, and thus indicate that the neutrino does have a very small mass (see Solar neutrino problem). Function The Neutrino Factory will create a fairly focused beam of neutrinos at one site on the Earth and fire it downwards, probably in two beams emitted in different directions from a racetrack shaped underground muon storage ring, until the beams resurface at other points. One example could be a complex in the UK sending beams to Japan (see Super-Kamiokande) and Italy (LNGS). The properties of the neutrinos will be examine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Linear Accelerator
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a United States Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Stanford University under the programmatic direction of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science and located in Menlo Park, California. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 and shut down in the 2000s, that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, the facility is located on of Stanford University-owned land on Sand Hill Road in Menlo Park, Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
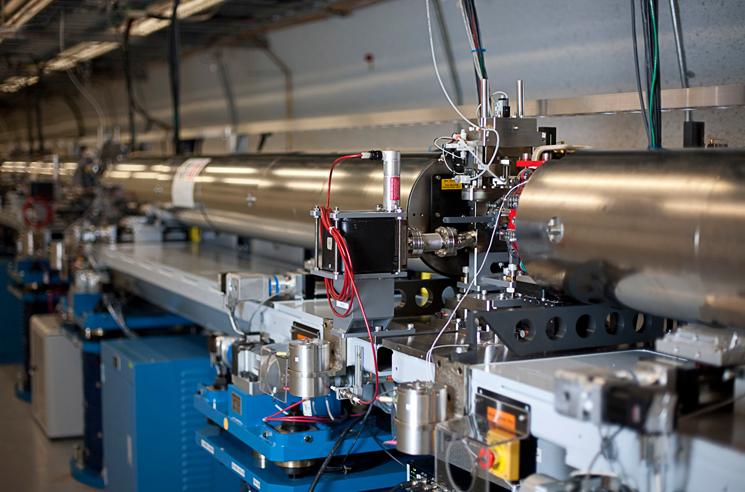
SuperKEKB
SuperKEKB is a particle collider located at KEK (''High Energy Accelerator Research Organisation'') in Tsukuba, Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. SuperKEKB collides electrons with positrons at the centre-of-momentum energy close to the mass of the Υ(4S) resonance making it a second-generation B-factory for the Belle II experiment. The accelerator is an upgrade to the KEKB accelerator, providing approximately 40 times higher luminosity, due mostly to superconducting quadrupole focusing magnets. The accelerator achieved "first turns" (first circulation of electron and positron beams) in February 2016. First collisions occurred on 26 April 2018. At 20:34 on 15 June 2020, SuperKEKB achieved the world’s highest instantaneous luminosity for a colliding-beam accelerator, setting a record of 2.22×1034 cm−2s−1. Description The SuperKEKB design reuses many components from KEKB. Under normal operation, SuperKEKB collides electrons at 7 GeV with positrons at 4 GeV (compared to KEKB at 8 G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-tagging
b-tagging is a method of jet flavor tagging used in modern particle physics experiments. It is the identification (or "tagging") of jets originating from bottom quarks (or b quarks, hence the name). Importance b-tagging is important because: * The physics of bottom quarks is quite interesting; in particular, it sheds light on CP violation. * Some important high-mass particles (both recently discovered and hypothetical) decay into bottom quarks. Top quarks very nearly always do so, and the Higgs boson is expected to decay into bottom quarks more than any other particle given its mass has been observed to be about 125 GeV. Identifying bottom quarks helps to identify the decays of these particles. Methods The methods for b-tagging are based on the unique features of b-jets. These include: *Hadrons containing bottom quarks have sufficient lifetime that they travel some distance before decaying. On the other hand, their lifetimes are not so high as those of light quark hadr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B–Bbar Oscillation
Neutral B meson oscillations (or – oscillations) are one of the manifestations of the neutral particle oscillation, a fundamental prediction of the Standard Model of particle physics. It is the phenomenon of B mesons changing (or ''oscillating'') between their matter and antimatter forms before their decay. The meson can exist as either a bound state of a strange antiquark and a bottom quark, or a strange quark and bottom antiquark. The oscillations in the neutral B sector are analogous to the phenomena that produce long and short-lived neutral kaons. – mixing was observed by the CDF experiment at Fermilab in 2006 and by LHCb at CERN in 2011 and 2021. Excess of matter over antimatter The Standard Model predicts that regular matter mesons are slightly favored in these oscillations over their antimatter counterpart, making strange B mesons of special interest to particle physicists. The observation of the – mixing phenomena led physicists to propose the constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LHCb
The LHCb (Large Hadron Collider beauty) experiment is one of eight particle physics detector experiments collecting data at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. LHCb is a specialized b-physics experiment, designed primarily to measure the parameters of CP violation in the interactions of b-hadrons (heavy particles containing a bottom quark). Such studies can help to explain the matter-antimatter asymmetry of the Universe. The detector is also able to perform measurements of production cross sections, exotic hadron spectroscopy, charm physics and electroweak physics in the forward region. The LHCb collaboration, who built, operate and analyse data from the experiment, is composed of approximately 1260 people from 74 scientific institutes, representing 16 countries. Chris Parkes succeeded on July 1, 2020 as spokesperson for the collaboration to Giovanni Passaleva (spokesperson 2017-2020). The experiment is located at point 8 on the LHC tunnel close to Ferney-Voltaire, France just o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belle II
The BelleII experiment is a particle physics experiment designed to study the properties of B mesons (heavy particles containing a beauty quark) and other particles. BelleII is the successor to the Belle experiment, and commissioned at the SuperKEKB accelerator complex at KEK in Tsukuba, Ibaraki prefecture, Japan. The BelleII detector was "rolled in" (moved into the collision point of SuperKEKB) in April 2017. BelleII started taking data in early 2018. Over its running period, BelleII is expected to collect around 50 times more data than its predecessor mostly due to a 40-fold increase in an instantaneous luminosity provided by SuperKEKB as compared to the previous KEKB accelerator. Physics program Many interesting analyses of the Belle and BaBar experiments were limited by statistical uncertainties, which was the main motivation to build a new generation of B-factory - Belle II. The target dataset is 50 ab−1 at BelleII compared to 988 fb−1 (with 711fb−1 at the Υ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Strong Mayor–Council , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Capitoline Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)