|
B–Bbar Oscillation
Neutral B meson oscillations (or – oscillations) are one of the manifestations of the neutral particle oscillation, a fundamental prediction of the Standard Model of particle physics. It is the phenomenon of B mesons changing (or ''oscillating'') between their matter and antimatter forms before their decay. The meson can exist as either a bound state of a strange antiquark and a bottom quark, or a strange quark and bottom antiquark. The oscillations in the neutral B sector are analogous to the phenomena that produce long and short-lived neutral kaons. – mixing was observed by the CDF experiment at Fermilab in 2006 and by LHCb at CERN in 2011 and 2021. Excess of matter over antimatter The Standard Model predicts that regular matter mesons are slightly favored in these oscillations over their antimatter counterpart, making strange B mesons of special interest to particle physicists. The observation of the – mixing phenomena led physicists to propose the constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Particle Oscillation
In particle physics, neutral particle oscillation is the transmutation of a particle with zero electric charge into another neutral particle due to a change of a non-zero internal quantum number, via an interaction that does not conserve that quantum number. Neutral particle oscillations were first investigated in 1954 by Murray Gell-mann and Abraham Pais. For example, a neutron cannot transmute into an antineutron as that would violate the conservation of baryon number. But in those hypothetical extensions of the Standard Model which include interactions that do not strictly conserve baryon number, neutron–antineutron oscillations are predicted to occur. Such oscillations can be classified into two types: * Particle–antiparticle oscillation (for example, oscillation). * Flavor oscillation (for example, oscillation). In those cases where the particles decay to some final product, then the system is not purely oscillatory, and an interference between oscillation and decay i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
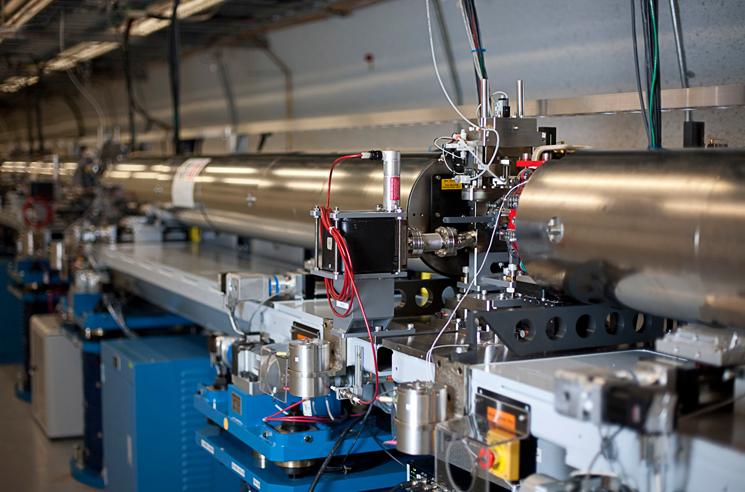
Stanford Linear Accelerator Center
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a United States Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Stanford University under the programmatic direction of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science and located in Menlo Park, California. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 and shut down in the 2000s, that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, the facility is located on of Stanford University-owned land on Sand Hill Road in Menlo Park, Califor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaon
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe. Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of RDF ontologies. Several tools like the graphical ontology editor OIModeler or the KAON Server were based on KAON. There are ontology learning companion tools which take non-annotated natural language text as input: TextToOnto (KAON-based) and Text2Onto (KAON2-based). Text2Onto is based on the Probabilistic Ontology Model (POM). In 2005, the first version of KAON2 was released, offering fast reasoning support for OWL ontologies. KAON2 is not backward-compatible with KAON. KAON2 is developed as a joint effort of the Information Process Engineering (IPE) at the Research Center for Information Technologies (FZI), the Institute of Applied Informatics and Formal Description Methods (AIFB) at the University of Karlsruhe, and the Information Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baryogenesis
In physical cosmology, baryogenesis (also known as baryosynthesis) is the physical process that is hypothesized to have taken place during the early universe to produce baryonic asymmetry, i.e. the imbalance of matter (baryons) and antimatter (antibaryons) in the observed universe. One of the outstanding problems in modern physics is the predominance of matter over antimatter in the universe. The universe, as a whole, seems to have a nonzero positive baryon number density. Since it is assumed in cosmology that the particles we see were created using the same physics we measure today, it would normally be expected that the overall baryon number should be zero, as matter and antimatter should have been created in equal amounts. A number of theoretical mechanisms are proposed to account for this discrepancy, namely identifying conditions that favour symmetry breaking and the creation of normal matter (as opposed to antimatter). This imbalance has to be exceptionally small, on the ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Letters B
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, science, technology policy, and video games. ''Ars Technica'' was privately owned until May 2008, when it was sold to Condé Nast Digital, the online division of Condé Nast Publications. Condé Nast purchased the site, along with two others, for $25 million and added it to the company's ''Wired'' Digital group, which also includes ''Wired'' and, formerly, Reddit. The staff mostly works from home and has offices in Boston, Chicago, London, New York City, and San Francisco. The operations of ''Ars Technica'' are funded primarily by advertising, and it has offered a paid subscription service since 2001. History Ken Fisher, who serves as the website's current editor-in-chief, and Jon Stokes created ''Ars Technica'' in 1998. Its purpose was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP Violation
In particle physics, CP violation is a violation of CP-symmetry (or charge conjugation parity symmetry): the combination of C-symmetry (charge symmetry) and P-symmetry ( parity symmetry). CP-symmetry states that the laws of physics should be the same if a particle is interchanged with its antiparticle (C-symmetry) while its spatial coordinates are inverted ("mirror" or P-symmetry). The discovery of CP violation in 1964 in the decays of neutral kaons resulted in the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1980 for its discoverers James Cronin and Val Fitch. It plays an important role both in the attempts of cosmology to explain the dominance of matter over antimatter in the present universe, and in the study of weak interactions in particle physics. Overview Until the 1950s, parity conservation was believed to be one of the fundamental geometric conservation laws (along with conservation of energy and conservation of momentum). After the discovery of parity violation in 1956, CP-symmetry was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance (particle)
In particle physics, a resonance is the peak located around a certain energy found in differential cross sections of scattering experiments. These peaks are associated with subatomic particles, which include a variety of bosons, quarks and hadrons (such as nucleons, delta baryons or upsilon mesons) and their excitations. In common usage, "resonance" only describes particles with very short lifetimes, mostly high-energy hadrons existing for or less. The width of the resonance (''Γ'') is related to the mean lifetime (''τ'') of the particle (or its excited state) by the relation :\Gamma=\frac where ''h'' is the Planck constant and =\frac. Thus, the lifetime of a particle is the direct inverse of the particle's resonance width. For example, the charged pion has the second-longest lifetime of any meson, at . Therefore, its resonance width is very small, about or about 6.11 MHz. Pions are generally not considered as "resonances". The charged rho meson has a very short lifetim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upsilon Meson
The Upsilon meson () is a quarkonium state (i.e. flavourless meson) formed from a bottom quark and its antiparticle. It was discovered by the E288 experiment team, headed by Leon Lederman, at Fermilab in 1977, and was the first particle containing a bottom quark to be discovered because it is the lightest that can be produced without additional massive particles. It has a lifetime of and a mass about in the ground state. See also * Oops-Leon, an erroneously-claimed discovery of a similar particle at a lower mass in 1976. * The particle is the analogous state made from strange quarks. * The particle is the analogous state made from charm quarks. * List of mesons :''This list is of all known and predicted scalar, pseudoscalar and vector mesons. See list of particles for a more detailed list of particles found in particle physics.'' This article contains a list of mesons, unstable subatomic particles ... References * * * Mesons Onia Subatomic particles wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
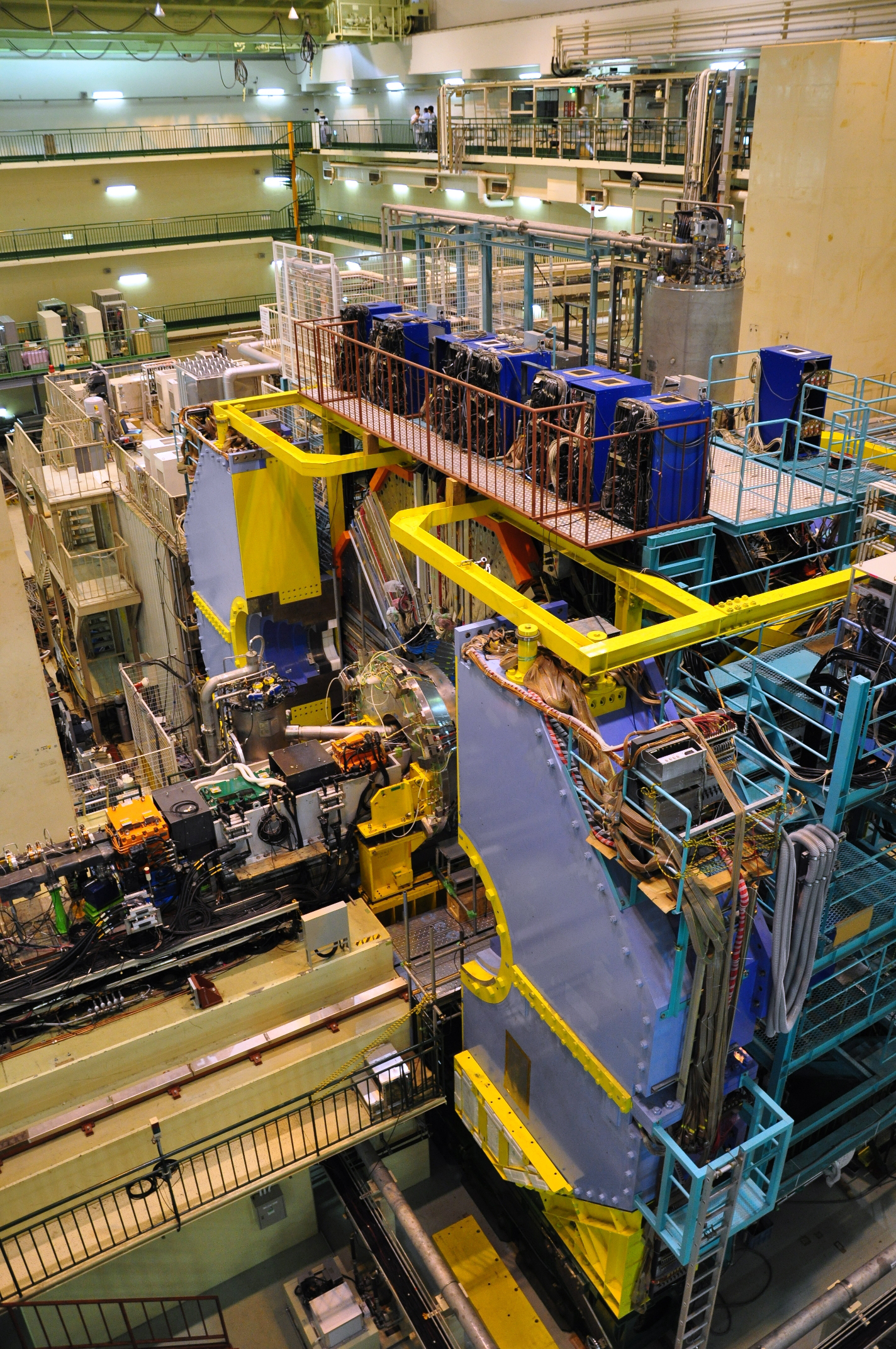
Belle Experiment
The Belle experiment was a particle physics experiment conducted by the Belle Collaboration, an international collaboration of more than 400 physicists and engineers, at the High Energy Accelerator Research Organisation (KEK) in Tsukuba, Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. The experiment ran from 1999 to 2010. The Belle detector was located at the collision point of the asymmetric-energy electron– positron collider, KEKB. Belle at KEKB together with the BaBar experiment at the PEP-II accelerator at SLAC were known as the B-factories as they collided electrons with positrons at the center-of-momentum energy equal to the mass of the (4S) resonance which decays to pairs of B mesons. The Belle detector was a hermetic multilayer particle detector with large solid angle coverage, vertex location with precision on the order of tens of micrometres (provided by a silicon vertex detector), good distinction between pions and kaons in the momenta range from 100 MeV/c to few GeV/c (provided by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BaBar Experiment
The BaBar experiment, or simply BaBar, is an international collaboration of more than 500 physicists and engineers studying the subatomic world at energies of approximately ten times the rest mass of a proton (~10 GeV). Its design was motivated by the investigation of charge-parity violation. BaBar is located at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, which is operated by Stanford University for the Department of Energy in California. Physics BaBar was set up to understand the disparity between the matter and antimatter content of the universe by measuring Charge Parity violation. CP symmetry is a combination of Charge-conjugation symmetry (C symmetry) and Parity symmetry (P symmetry), each of which are conserved separately except in weak interactions. BaBar focuses on the study of CP violation in the B meson system. The name of the experiment is derived from the nomenclature for the B meson (symbol ) and its antiparticle (symbol , pronounced B bar). The experiment's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
