|
Buffer Underflow
In computing, buffer underrun or buffer underflow is a state occurring when a buffer used for communicating between two devices or processes is fed with data at a lower speed than the data is being read from it. The term is distinct from buffer overflow, a condition where a portion of memory forms a buffer of a fixed size yet is filled with more than that amount of data. This requires the program or device reading from the buffer to pause its processing while the buffer refills. This can cause undesired and sometimes serious side effects because the data being buffered is generally not suited to stop-start access of this kind. In terms of concurrent programming, a buffer underrun can be considered a form of resource starvation. The terms buffer underrun and buffer underflow are also used for meaning buffer underwrite, a condition similar to buffer overflow, but where the program is tricked into writing before the beginning of the buffer, overriding potential data there, like p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology and software engineering. The term "computing" is also synonymous with counting and calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by mechanical computing machines, and before that, to human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. Computing is intimately tied to the representation of numbers, though mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rewritable Media
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is what manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast volatile technologies (which lose data when off power) are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage". Even the first computer designs, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Percy Ludgate's Analytical Machine, clearly distinguished between processing and memory (Babbage stored numbers as rotations of gears, while Ludgate stored numbers as displacements of rods in shuttles). This distinction was extended in the Von Neumann ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Headroom (character)
Max Headroom is a fictional artificial intelligence (AI) character portrayed by actor Matt Frewer. Advertised as "the first computer-generated TV presenter", Max was known for his biting commentary on a variety of topical issues, arrogant wit, stuttering, and pitch-shifting voice. The character was created by George Stone, Annabel Jankel, and Rocky Morton. Max was advertised as "computer-generated" and some believed this, but he was actually actor Frewer wearing prosthetic makeup, contact lenses, and a plastic molded suit, and sitting in front of a blue screen. Harsh lighting and other editing and recording effects heighten the illusion of a CGI character. According to his creators, Max's personality was meant to be a satirical exaggeration of the worst tendencies of television hosts in the 1980s who wanted to appeal to youth culture yet weren't a part of it. Frewer proposed that Max reflected an innocence, largely influenced not by mentors and life experience but by inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
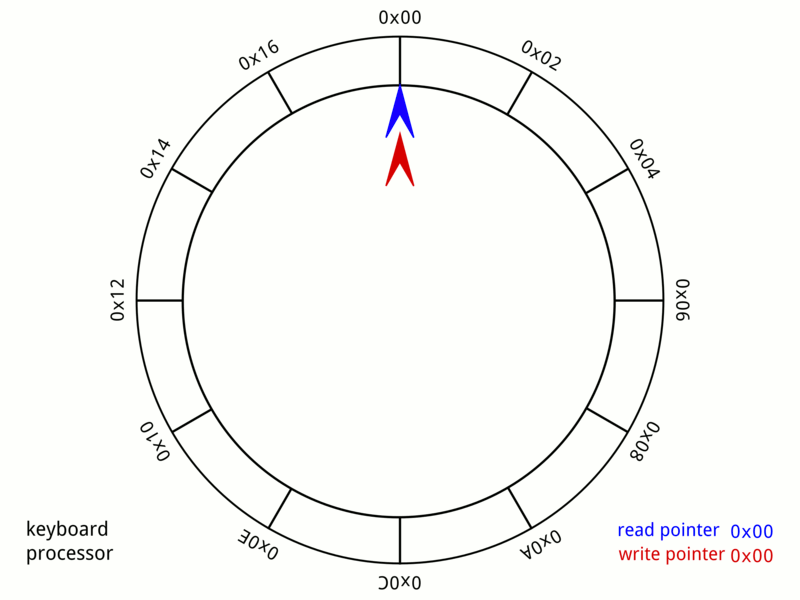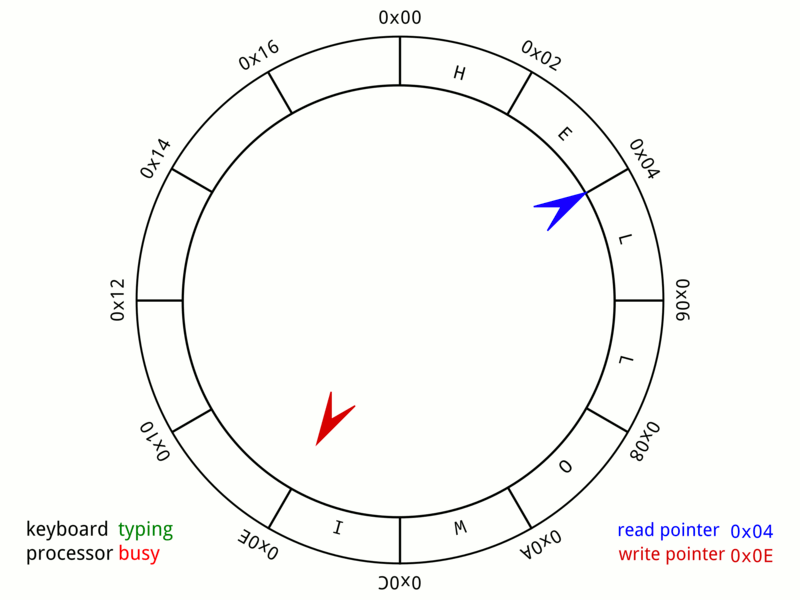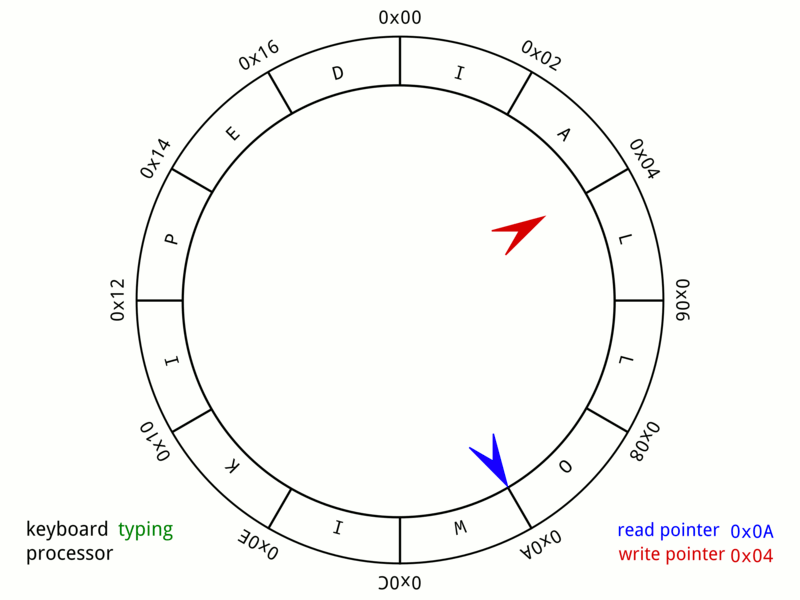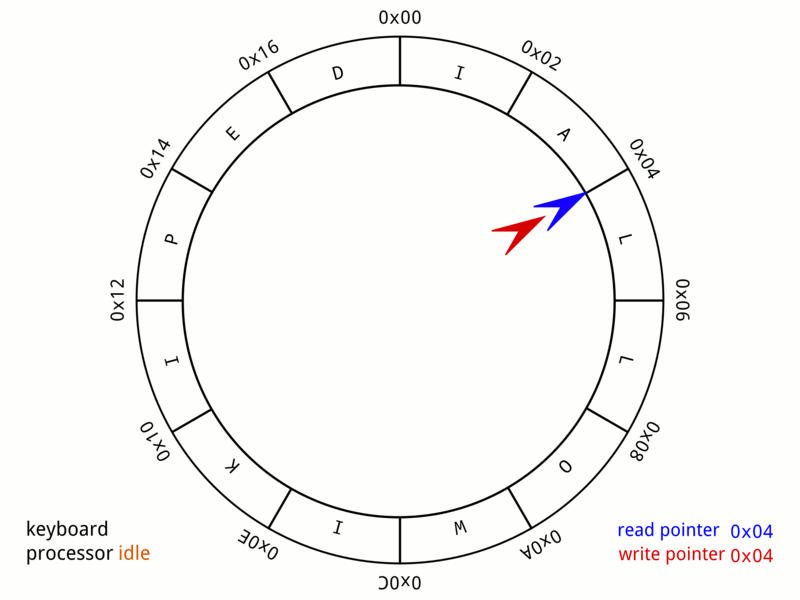
Ring Buffer
In computer science, a circular buffer, circular queue, cyclic buffer or ring buffer is a data structure that uses a single, fixed-size buffer as if it were connected end-to-end. This structure lends itself easily to buffering data streams. There were early circular buffer implementations in hardware. Overview A circular buffer first starts out empty and has a set length. In the diagram below is a 7-element buffer: : Assume that 1 is written in the center of a circular buffer (the exact starting location is not important in a circular buffer): : Then assume that two more elements are added to the circular buffer — 2 & 3 — which get put after 1: : If two elements are removed, the two oldest values inside of the circular buffer would be removed. Circular buffers use FIFO (''first in, first out'') logic. In the example, 1 & 2 were the first to enter the circular buffer, they are the first to be removed, leaving 3 inside of the buffer. : If the buffer has 7 ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Card
A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term ''sound card'' is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications. Sound functionality can also be integrated onto the motherboard, using components similar to those found on plug-in cards. The integrated sound system is often still referred to as a ''sound card''. Sound processing hardware is also present on modern video cards with HDMI to output sound along with the video using that connector; previously they used a S/PDIF connection to the motherboard or sound card. Typical uses of sound cards or sound card functionality include providing the audio component for multimedia applications such as music composition, editing video or audio, presentation, education and entertainment (games) and video projection. Sound cards are also used for comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPlayer
MPlayer is a free and open-source media player software application. It is available for Linux, OS X and Microsoft Windows. Versions for OS/2, Syllable, AmigaOS, MorphOS and AROS Research Operating System are also available. A port for DOS using DJGPP is also available. Versions for the Wii Homebrew Channel and Amazon Kindle have also been developed. History Development of MPlayer began in 2000. The original author, Hungarian Árpád Gereöffy, started the project because he was unable to find any satisfactory video players for Linux after XAnim stopped development in 1999. The first version was titled ''mpg12play v0.1'' and was hacked together in a half-hour using ''libmpeg3'' from . After ''mpg12play v0.95pre5'', the code was merged with an AVI player based on ''avifile''s '' Win32 DLL loader'' to form MPlayer v0.3 in November 2000. Gereöffy was soon joined by many other programmers, in the beginning mostly from Hungary, but later worldwide. Alex Beregszászi h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Controller
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or mistakenly GPU) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display device, such as a computer monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to integrated graphics. A graphics processing unit that performs the necessary computations is the main component of a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole. Most graphics cards are not limited to simple display output. The graphics processing unit can be used for additional processing, which reduces the load from the central processing unit. Additionally, computing platforms such as OpenCL and CUDA allow using graphics cards for general-purpose computing. Applications of general-purpose computing on graphics cards include AI training, cryptocurrency mining, and mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Framebuffer
A framebuffer (frame buffer, or sometimes framestore) is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor. In computing, a screen buffer is a part of computer memory used by a computer application for the representation of the content to be shown on the computer display. The screen buffer may also be called the video buffer, the regeneration buffer, or regen buffer for short. Screen buffers should be distinguished from video memory. To this end, the term off-screen buffer is also used. The information in the buffer typically consists of color values for every pixel to be shown on the display. Color values are commonly stored in 1-bit binary (monochrome), 4-bit palettized, 8-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet (information Technology)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a network packet is a formatted unit of data carried by a packet-switched network. A packet consists of control information and user data; the latter is also known as the ''payload''. Control information provides data for delivering the payload (e.g., source and destination network addresses, error detection codes, or sequencing information). Typically, control information is found in packet headers and trailers. In packet switching, the bandwidth of the transmission medium is shared between multiple communication sessions, in contrast to circuit switching, in which circuits are preallocated for the duration of one session and data is typically transmitted as a continuous bit stream. Terminology In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, ''packet'' strictly refers to a protocol data unit at layer 3, the network layer. A data unit at layer 2, the data link layer, is a '' frame''. In layer 4, the transport layer, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Disk Format
Universal Disk Format (UDF) is an open, vendor-neutral file system for computer data storage for a broad range of media. In practice, it has been most widely used for DVDs and newer optical disc formats, supplanting ISO 9660. Due to its design, it is very well suited to incremental updates on both recordable and (re)writable optical media. UDF was developed and maintained by the Optical Storage Technology Association (OSTA). In engineering terms, Universal Disk Format is a profile of the specification known as ISO/IEC 13346 and ECMA-167. Usage Normally, authoring software will master a UDF file system in a batch process and write it to optical media in a single pass. But when packet writing to rewritable media, such as CD-RW, UDF allows files to be created, deleted and changed on-disc just as a general-purpose filesystem would on removable media like floppy disks and flash drives. This is also possible on write-once media, such as CD-R, but in that case the space occupi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |