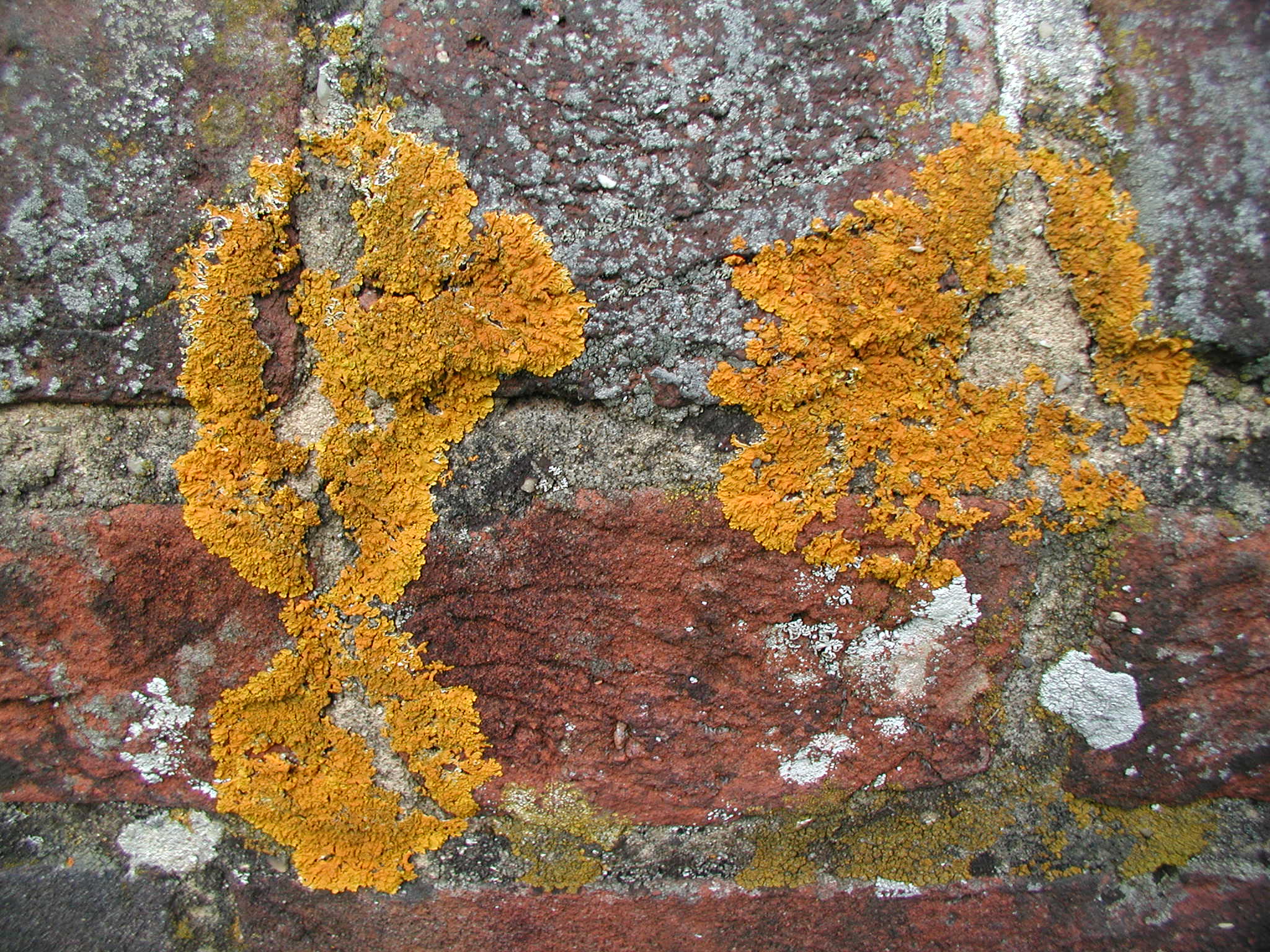|
Brownliella Cinnabarina
''Brownliella'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the subfamily Brownlielloideae of the family Teloschistaceae. It has four species. The genus was circumscribed in 2013 by Sergey Kondratyuk, Ingvar Kärnefelt, John Elix, Arne Thell, and Jae-Seoun Hur, with the widely distributed lichen ''Brownliella aequata'' assigned as the type species. The genus contains species formerly referred to as the ''Caloplaca cinnabarina'' species group. The generic name honours Australian botanist Sue Brownlie. Species *''Brownliella aequata ''Brownliella'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the subfamily Brownlielloideae of the family Teloschistaceae. It has four species. The genus was circumscribed in 2013 by Sergey Kondratyuk, Ingvar Kärnefelt, John Elix, Arne Thell, and Jae-Seou ...'' *'' Brownliella cinnabarina'' *'' Brownliella kobeana'' *'' Brownliella montisfracti'' References Teloschistales Teloschistales genera Taxa described in 2013 Taxa named by John Alan Elix Taxa name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingvar Kärnefelt
Jan Eric Ingvar Kärnefelt (born 1944) is a Swedish lichenologist. Early life and education Kärnefelt was born in Gothenburg, Sweden in 1944. His initial goal in his higher-level studies at University of Cologne in 1966–1967 was to become a dentist. He changed courses in 1968, turning instead to biology at the University of Gothenburg in 1968. Gunnar Degelius, his first teacher during undergraduate studies in botany in 1968, inspired him and others. After Degelius' retirement in 1969, Ingvar continued his studies at Lund University, where Hans Runemark held a position in systematic botany. In 1971 he met Ove Almborn, who became his supervisor. In 1979, he defended his thesis titled "The brown fruticose species of ''Cetraria''". The thesis was later awarded a prize for the best doctoral dissertation in botany at Lund University during a 5-year period by the Royal Physiographic Society in Lund. Career Kärnefelt became associate professor at the Department of Systematic Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscription (taxonomy)
In biological taxonomy, circumscription is the content of a taxon, that is, the delimitation of which subordinate taxa are parts of that taxon. If we determine that species X, Y, and Z belong in Genus A, and species T, U, V, and W belong in Genus B, those are our circumscriptions of those two genera. Another systematist might determine that T, U, V, W, X, Y, and Z all belong in genus A. Agreement on circumscriptions is not governed by the Codes of Zoological or Botanical Nomenclature, and must be reached by scientific consensus. A goal of biological taxonomy is to achieve a stable circumscription for every taxon. This goal conflicts, at times, with the goal of achieving a natural classification that reflects the evolutionary history of divergence of groups of organisms. Balancing these two goals is a work in progress, and the circumscriptions of many taxa that had been regarded as stable for decades are in upheaval in the light of rapid developments in molecular phylogenetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By John Alan Elix
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in '' Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Described In 2013
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teloschistales Genera
The Teloschistales are an order of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. According to one 2008 estimate, the order contains 5 families, 66 genera, and 1954 species. The predominant photobiont partners for the Teloschistales are green algae from the genera ''Trebouxia'' and '' Asterochloris''. Families * Brigantiaeaceae * Letrouitiaceae * Megalosporaceae *Teloschistaceae The Teloschistaceae are a large family of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. The family, estimated to contain over 1800 species, was extensively revised in 2013, including the creati ... References Lichen orders Lecanoromycetes orders Taxa described in 1986 Taxa named by David Leslie Hawksworth {{Teloschistales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teloschistales
The Teloschistales are an order of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. According to one 2008 estimate, the order contains 5 families, 66 genera, and 1954 species. The predominant photobiont partners for the Teloschistales are green algae from the genera ''Trebouxia'' and '' Asterochloris''. Families *Brigantiaeaceae *Letrouitiaceae *Megalosporaceae *Teloschistaceae The Teloschistaceae are a large family of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. The family, estimated to contain over 1800 species, was extensively revised in 2013, including the creati ... References Lichen orders Lecanoromycetes orders Taxa described in 1986 Taxa named by David Leslie Hawksworth {{Teloschistales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Group
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each other, further blurring any distinctions. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two (or more) species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use. Two or more taxa that were once considered conspecific (of the same species) may later be subdivided into infraspecific taxa (taxa within a species, such as bacterial strains or plant varieties), that is complex but it is not a species complex. A species complex is in most cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teloschistaceae
The Teloschistaceae are a large family of mostly lichen-forming fungi belonging to the class Lecanoromycetes in the division Ascomycota. The family, estimated to contain over 1800 species, was extensively revised in 2013, including the creation or resurrection of 31 genera. It contains three subfamilies: Xanthorioideae, Caloplacoideae, and Teloschistoideae. A fourth subfamily, Brownlielloideae, proposed in 2015, has been shown to be part of the Teloschistoideae. Genera This is a list of the genera contained within the Teloschistaceae, based on a 2020 review and summary of ascomycete classification. Following the genus name is the taxonomic authority, year of publication, and the number of species: *'' Amundsenia'' – 2 spp. *'' Andina'' - 1 sp. *'' Apatoplaca'' – 1 sp. *'' Aridoplaca'' - 1 sp. *'' Athallia'' – 17 spp. *'' Austroplaca'' – 10 spp. *'' Blastenia'' – 11 spp. *'' Brownliella'' – 4 spp. *'' Bryoplaca'' – 3 spp. *'' Calogaya'' – 19 spp. *'' Calop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Alan Elix
John Alan (Jack) Elix (born 1941) emeritus professor in chemistry at the Australian National University, is an organic chemist who has contributed in many fields: lichenology, lichen chemotaxonomy, plant physiology and biodiversity and natural product chemistry. He has authored 2282 species names, and 67 genera in the field of mycology. Education His first degree, B.Sc., and his Ph.D were both in organic chemistry from the University of Adelaide. This was followed by post-doctoral years at the University of Cambridge and then a D.Sc. in natural products chemistry from the Australian National University. Career Elix spent a post doctoral year in 1966 at Cambridge, returning to Australia in 1967 to a lectureship in chemistry at the ANU. He retired as professor of chemistry in 2002, becoming professor emeritus. By 1975 he had already published several papers on the organic chemistry of lichens, and ultimately leading to work on the evolution, taxonomy and phylogeny of liche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustose Lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the Substrate (biology), substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cortex (botany), cortex layer, an algal layer, and a medulla. The upper cortex layer is differentiated and is usually pigmented. The algal layer lies beneath the cortex. The medulla fastens the lichen to the substrate and is made up of Fungus, fungal hyphae. The surface of crustose lichens is characterized by branching cracks that periodically close in response to climatic variations such as alternate wetting and drying regimes. Subtypes * Powdery – considered as the simplest subtype due to the absence of an organized thallus. :The thallus appears powdery. :E.g. Genera ''Lepraria'', ''Vezdaea'' * Endolithic – grows inside the rock, usually in interstitial spaces between mineral grains. The :upper cortex is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(2).jpg)