|
Breast Hematoma
Breast hematoma is a collection of blood within the breast. It arises from internal bleeding (hemorrhage) and may arise due to trauma (breast injury or surgery) or due to a non-traumatic cause. Symptoms Symptoms may include visible discoloring (ecchymosis), breast pain, and swelling. The symptoms may be similar to those of fibrocystic breast changes. Causes A breast hematoma may appear due to direct trauma to the breast, for example from a sports injury or a road accident, for example a vehicle collision in which a seat belt injury occurs. Hematoma can also be a consequence of breast surgery, usually due to post-operative bleeding. Bleeding may occur shortly after the intervention or a number of days later and can occur for cosmetic surgery (for example breast reduction or breast enhancement) and for non-cosmetic surgery (for example lymph node removal, lumpectomy, or mastectomy). More rarely, hematoma can result from breast biopsy. Rarely, a breast hematoma can also occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissues give the breast its size and shape. At the ends of the ducts are lobules, or clusters of alveoli, where milk is produced and stored in response to hormonal signals. During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin, that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of lactation and breastfeeding. Humans are the only animals with permanent breasts. At puberty, estrogens, in conjunction with growth hormone, cause permanent breast growth in female humans. This happens only to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Implant
A breast implant is a prosthesis used to change the size, shape, and contour of a person's breast. In reconstructive plastic surgery, breast implants can be placed to restore a natural looking breast following a mastectomy, to correct congenital defects and deformities of the chest wall or, cosmetically, to enlarge the appearance of the breast through breast augmentation surgery. Complications of implants may include breast pain, rashes, skin changes, infection, rupture, cosmetic changes to the breasts such as asymmetry and hardness, and a fluid collection around the breast. The most serious complication is a type of lymphoma (cancer of the immune system) known as Breast Implant Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL). There are four general types of breast implants, defined by their filler material: saline solution, silicone gel, structured and composite filler. The saline implant has an elastomer silicone shell filled with sterile saline solution during sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine Needle Aspiration
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, are examined under a microscope (biopsy). The sampling and biopsy considered together are called fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) (the latter to emphasize that any aspiration biopsy involves cytopathology, not histopathology). Fine-needle aspiration biopsies are very safe minor surgical procedures. Often, a major surgical (excisional or open) biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration biopsy instead, eliminating the need for hospitalization. In 1981, the first fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the United States was done at Maimonides Medical Center. Today, this procedure is widely used in the diagnosis of cancer and inflammatory conditions. Aspiration is safer and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical History
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other people who know the person and can give suitable information, with the aim of obtaining information useful in formulating a diagnosis and providing medical care to the patient. The medically relevant complaints reported by the patient or others familiar with the patient are referred to as symptoms, in contrast with clinical signs, which are ascertained by direct examination on the part of medical personnel. Most health encounters will result in some form of history being taken. Medical histories vary in their depth and focus. For example, an ambulance paramedic would typically limit their history to important details, such as name, history of presenting complaint, allergies, etc. In contrast, a psychiatric history is frequently lengthy and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
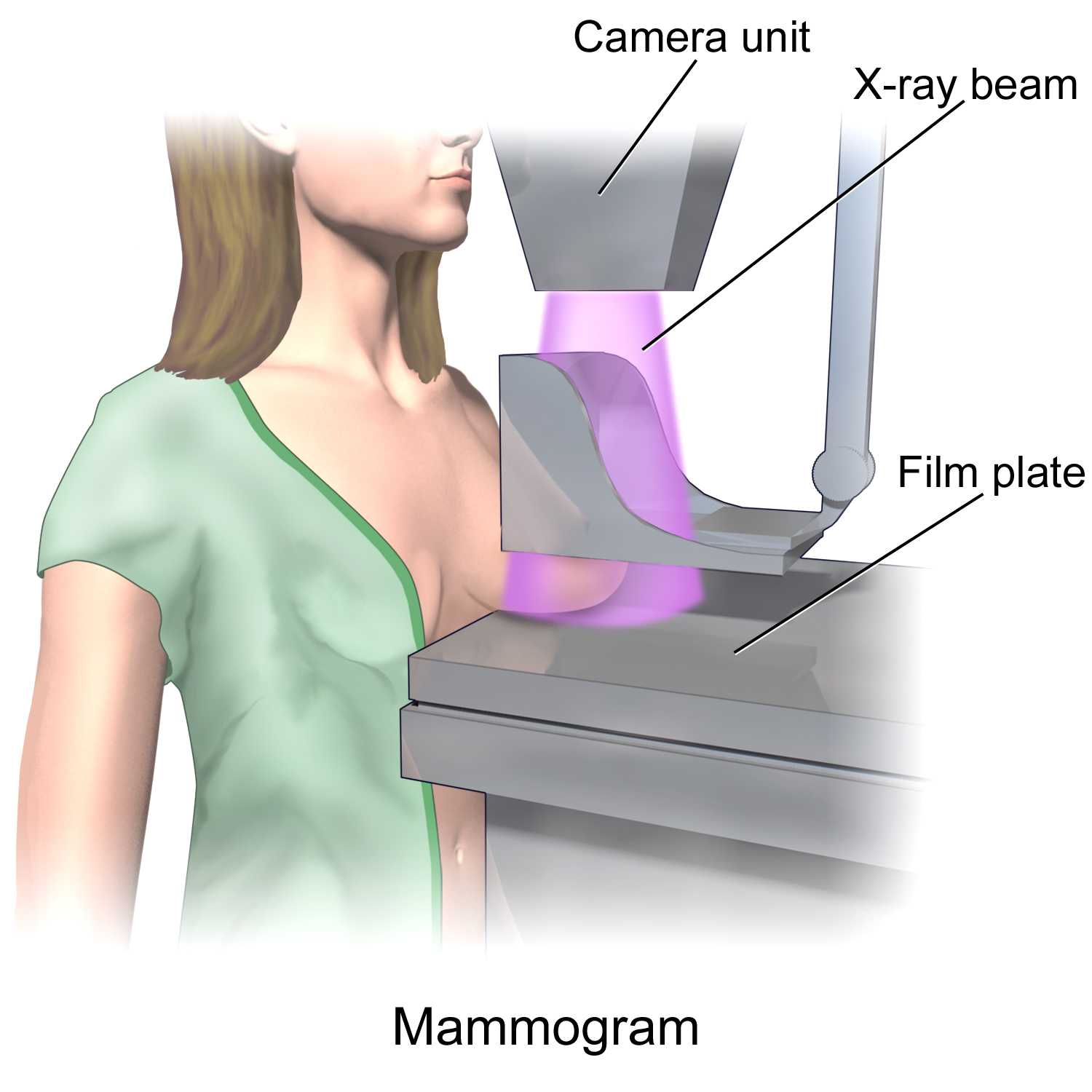
Mammogram
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 Peak kilovoltage, kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D (tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment and/or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable masses that may or may not b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Abscess
Mastitis is inflammation of the breast or udder, usually associated with breastfeeding. Symptoms typically include local pain and redness. There is often an associated fever and general soreness. Onset is typically fairly rapid and usually occurs within the first few months of delivery. Complications can include abscess formation. Risk factors include poor latch, cracked nipples, use of a breast pump, and weaning. The bacteria most commonly involved are ''Staphylococcus'' and ''Streptococci''. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms. Ultrasound may be useful for detecting a potential abscess. Prevention is by proper breastfeeding techniques. When infection is present, antibiotics such as cephalexin may be recommended. Breastfeeding should typically be continued, as emptying the breast is important for healing. Tentative evidence supports benefits from probiotics. About 10% of breastfeeding women are affected. Types When it occurs in breastfeeding mothers, it is known as puer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is the use of medical ultrasonography to perform imaging of the breast. It can be considered either a diagnostic or a screening procedure. It may be used either with or without a mammogram. It may be useful in younger women, where the denser fibrous tissue of the breast may make mammograms more difficult to interpret. Automated whole-breast ultrasound (AWBU) is an ultrasound investigation of the breast that is largely independent of the operator skill and that allows the reconstruction of volumetric images of the breast. Using high-frequency ultrasound, a diagnostic evaluation of the lactiferous ducts by means of ultrasound (duct sonography) can be performed. In this manner, dilated ducts and intraductal masses can be made visible. Another technique for visualizing the system of lactiferous ducts is galactography, which allows a wider area of the lactiferous duct system to be visualized. A type of ultrasound examination to measure tissue stiffness, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Surgery
Breast surgery is a form of surgery performed on the breast. Types Types include: *Breast reduction surgery *Augmentation mammoplasty * Mastectomy *Lumpectomy *Breast-conserving surgery, a less radical cancer surgery than mastectomy *Mastopexy, or breast lift surgery * Surgery for breast abscess, including incision and drainage as well as excision of lactiferous ducts * Surgical breast biopsy * Microdochectomy (removal of a lactiferous duct) Complications After surgical intervention to the breast, complications may arise related to wound healing. As in other types of surgery, hematoma (post-operative bleeding), seroma (fluid accumulation), or incision-site breakdown (wound infection) may occur. Breast hematoma due to an operation will normally resolve with time but should be followed up with more detailed evaluation if it does not. Breast abscess can occur as post-surgical complication, for example after cancer treatment or reduction mammaplasty.Noel Weidner, Chapter ''Inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fat Necrosis
Fat necrosis is a form of necrosis characterized by the action upon fat by digestive enzymes. In fat necrosis the enzyme lipase releases fatty acids from triglycerides. The fatty acids then complex with calcium to form soaps. These soaps appear as white chalky deposits.Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; & Mitchell, Richard N. (2007). ''Robbins Basic Pathology'' (8th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 10-11 It is usually associated with trauma of the pancreas or acute pancreatitis. It can also occur in the breast, the salivary glands and neonates after a traumatic delivery. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of fat necrosis are presented below: * masses that seem to be irregular beneath the skin, by touch these should feel smooth and rounded. * tenderness in areas with masses * skin tethering * dimpling * nipple retraction Causes Fat necrosis occurs primarily in the breast and pancreas. Breast lesions are mostly caused by adipose tissue trauma or post-surgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammography Screening
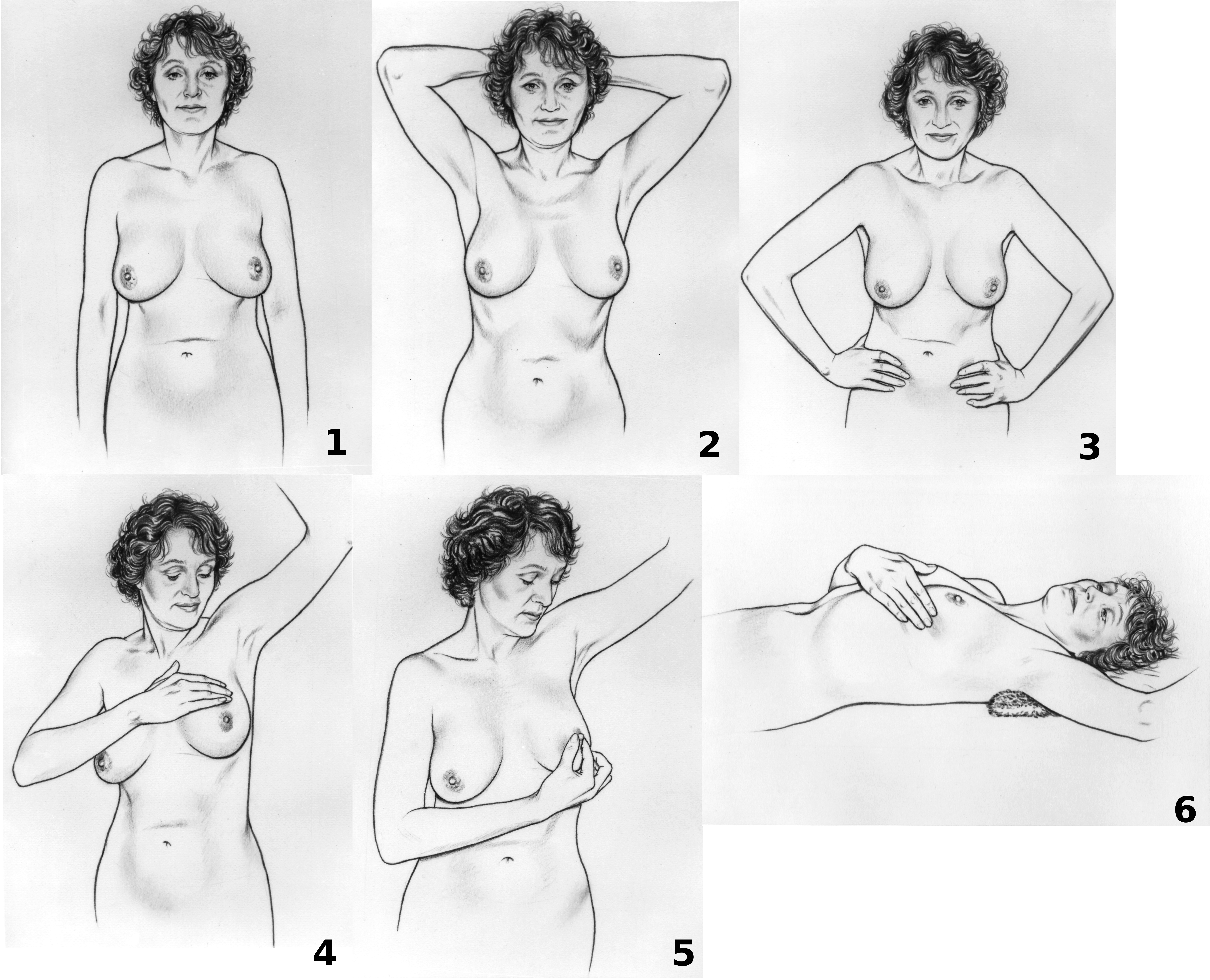
Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. A clinical or self breast exam involves feeling the breast for lumps or other abnormalities. Medical evidence, however, does not support its use in women with a typical risk for breast cancer. Universal screening with mammography is controversial as it may not reduce all-cause mortality and may cause harms through unnecessary treatments and medical procedures. Many national organizations recommend it for most older women. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening mammography in women at normal risk for breast cancer, every two years between the ages of 50 and 74. Other pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |