|
Fat Necrosis
Fat necrosis is a form of necrosis characterized by the action upon fat by digestive enzymes. In fat necrosis the enzyme lipase releases fatty acids from triglycerides. The fatty acids then complex with calcium to form soaps. These soaps appear as white chalky deposits.Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; & Mitchell, Richard N. (2007). ''Robbins Basic Pathology'' (8th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 10-11 It is usually associated with trauma of the pancreas or acute pancreatitis. It can also occur in the breast, the salivary glands and neonates after a traumatic delivery. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of fat necrosis are presented below: * masses that seem to be irregular beneath the skin, by touch these should feel smooth and rounded. * tenderness in areas with masses * skin tethering * dimpling * nipple retraction Causes Fat necrosis occurs primarily in the breast and pancreas. Breast lesions are mostly caused by adipose tissue trauma or post-surgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
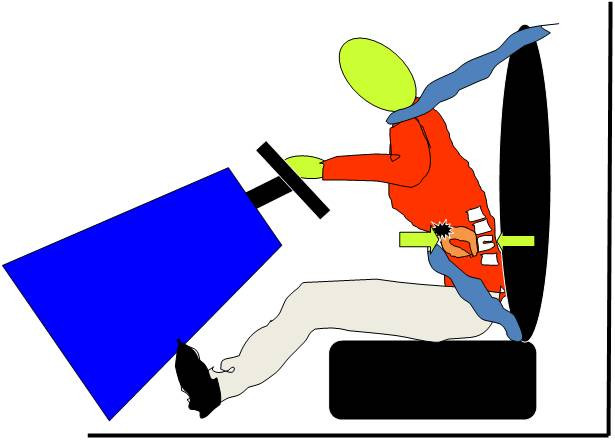
Seat Belt Syndrome
Seat belt syndrome is a collective term that includes all injury profiles associated with the use of seat belts. It is defined classically as a ''seat belt sign'' (seat belt marks on the body) plus an intra-abdominal organ injury (e.g. bowel perforations) and/or thoraco-lumbar vertebral fractures. The seat-belt sign was originally described by Garrett and Braunstein in 1962 as linear ecchymosis of the abdominal wall following a motor vehicle accident. It is indicative of an internal injury in as many as 30% of cases seen in the emergency department. Disruption of the abdominal wall musculature can also occur but is relatively uncommon. Apart from the medical aspects of injury, there are some legal issues associated with seat belt injuries. If your seat belt fails and this can be proved, then you may be entitled to compensation. On the other hand, it may be argued that you did not wear your seat belt as it was intended or designed. Symptoms The symptoms associated with this syndro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipocyte
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types. There are two types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), which are also known as white and brown fat, respectively, and comprise two types of fat cells. Structure White fat cells White fat cells contain a single large lipid droplet surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm, and are known as unilocular. The nucleus is flattened and pushed to the periphery. A typical fat cell is 0.1 mm in diameter with some being twice that size, and others half that size. However, these numerical estimates of fat cell size depend largely on the measurement method and the location of the adipose tissue. The fat stored i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyarteritis Nodosa
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) affecting medium-sized muscular arteries, typically involving the arteries of the kidneys and other internal organs but generally sparing the lungs' circulation. Small aneurysms are strung like the beads of a rosary, therefore making this "rosary sign" an important diagnostic feature of the vasculitis. PAN is sometimes associated with infection by the hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. The condition may be present in infants. PAN is a rare disease. With treatment, five-year survival is 80%; without treatment, five-year survival is 13%. Death is often a consequence of kidney failure, myocardial infarction, or stroke. Signs and symptoms PAN may affect nearly every organ system and thus can present with a broad array of signs and symptoms. These manifestations result from ischemic damage to affected organs, often the skin, heart, kidneys, and nervous system. Constitutional symptoms are see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weber–Christian Disease
Weber–Christian disease, is a cutaneous condition characterized by recurrent subcutaneous nodules that heal with depression of the overlying skin. It is a type of panniculitis. It is a rare disease seen in females 30–60 years of age. It is a recurring inflammation of fatty layers of tissue present beneath the skin. Clinical course is characterised by exacerbations and remissions. Lesions are bilaterally symmetrical and are usually seen in the lower legs. Eponym It is named after Frederick Parkes Weber and Henry Asbury Christian. See also * Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against t ... References External links Conditions of the subcutaneous fat {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Fat Necrosis Of The Newborn
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is a rare form of lobular panniculitis occurring in newborns that is usually self-remitting and non-recurring. Proposed causes include perinatal stress, local trauma, hypoxia and hypothermia, though the exact cause is unknown. It has been suggested that the brown fat seen in newborns is more sensitive to hypoxic injury than fat seen in adults, and that such hypoxia, usually in the context of a complicated birth, leads to the fat necrosis. Complications can include hypercalcemia, hyperlipidemia, dehydration, hypoglycemia, seizures, vomiting, constipation, and thrombocytopenia, and can present months after the onset of SCFN symptomsMatar, Marla. (2021). A Case Report and Anesthetic Considerations in Subcutaneous Fat Necrosis of the Newborn. ''A&A Practice'', ''15'', e01422. https://doi.org/10.1213/XAA.0000000000001422. See also * Pancreatic panniculitis * Panniculitis Panniculitis is a group of diseases whose hallmark is inflammation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panniculitis
Panniculitis is a group of diseases whose hallmark is inflammation of subcutaneous adipose tissue (the fatty layer under the skin – panniculus adiposus). Symptoms include tender skin nodules, and systemic signs such as weight loss and fatigue. Restated, an inflammatory disorder primarily localized in the subcutaneous fat is termed a "panniculitis", a group of disorders that may be challenging both for the clinician and the dermatopathologist. The general term for inflammation of any adipose tissue is steatitis. Signs and symptoms Panniculitis can also be classified based on the presence or absence of systemic symptoms. Panniculitis without systemic disease can be a result of trauma or cold. Panniculitis with systemic disease can be caused by: * connective tissue disorders such as lupus erythematosus or scleroderma; * lymphoproliferative disease such as lymphoma or histiocytosis; * pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer; * sarcoidosis with cutaneous involvement (seen in up to 20 pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
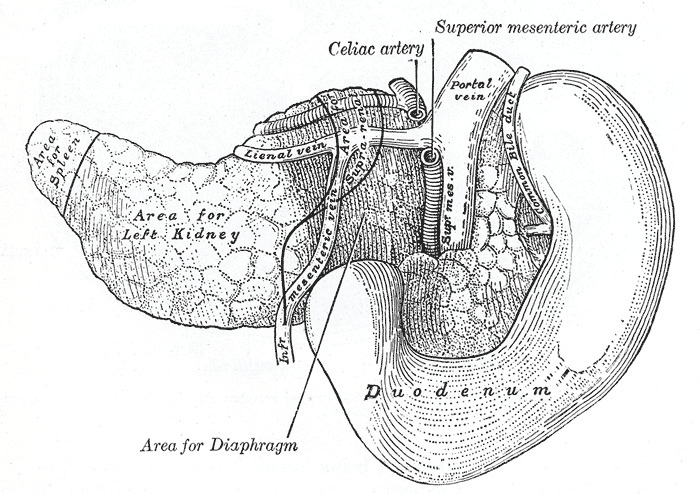
Pancreatic Injury
A pancreatic injury is some form of trauma sustained by the pancreas. The injury can be sustained through either blunt forces, such as a motor vehicle accident, or penetrative forces, such as that of a gunshot wound. The pancreas is one of the least commonly injured organs in abdominal trauma. Management Diagnosis The diagnosis of this form of injury can be challenging because of the pancreas' location inside the abdomen. The use of ultrasound can reveal fluid around the site of injury. Computed tomography (CT) can also be utilized as a non-invasive diagnostic tool, but its reliability is low; one retrospective case review found that computed tomography had either failed to find injuries or had underestimated the severity of injury in more than half of 17 pancreatic injury patients. Serum amylase has also been shown to be of limited diagnostic utility within the first three hours following injury. Management of a pancreatic injury can be difficult because other abdominal o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known. The most common, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, accounts for about 90% of cases, and the term "pancreatic cancer" is sometimes used to refer only to that type. These adenocarcinomas start within the part of the pancreas that makes digestive enzymes. Several other types of cancer, which collectively represent the majority of the non-adenocarcinomas, can also arise from these cells. About 1–2% of cases of pancreatic cancer are neuroendocrine tumors, which arise from the hormone-producing neuroendocrine cell, cells of the pancreas. These are generally less aggressive than pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Signs and symptoms of the most-common form of pancreatic cancer may include jaundice, ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disease; 4) trauma; 5) and, in minors, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis. Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures: hospitalization, pain control, nothing by mouth, intravenous nutritional support, and intravenous fluid rehydration. Severe cases often require admission to an intensive care unit to monitor and manage complications of the disease. Complications are associated with a high mortality, even with optimal management. Signs and symptoms Common *severe epigastric pain (upper abdominal pain) radiating to the back in 50% of cases *nausea *vomiting *loss of appetite *fever * chills (shivering) *hemodynamic instability, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Reconstruction
Breast reconstruction is the surgical process of rebuilding the shape and look of a breast, most commonly in women who have had surgery to treat breast cancer. It involves using autologous tissue, prosthetic implants, or a combination of both with the goal of reconstructing a natural-looking breast. This process often also includes the rebuilding of the nipple and areola, known as nipple-areola complex (NAC) reconstruction, as one of the final stages. Generally, the aesthetic appearance is acceptable to the woman, but the reconstructed area is commonly completely numb afterwards, which results in loss of sexual function as well as the ability to perceive pain caused by burns and other injuries. Timing Breast reconstruction can be performed either immediately following the mastectomy or as a separate procedure at a later date, known as immediate reconstruction and delayed reconstruction, respectively. The decision of when breast reconstruction will take place is patient-specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Reduction
Reduction mammoplasty (also breast reduction and reduction mammaplasty) is the plastic surgery procedure for reducing the size of large breasts. In a breast reduction surgery for re-establishing a functional bust that is proportionate to the woman's body, the critical corrective consideration is the tissue viability of the nipple–areola complex (NAC), to ensure the functional sensitivity and lactational capability of the breasts. The indications for breast reduction surgery are three-fold – physical, aesthetic, and psychological – the restoration of the bust, of the woman's self-image, and of her mental health. In corrective practice, the surgical techniques and praxis for reduction mammoplasty also are applied to mastopexy (breast lift). Presentation The woman with macromastia presents heavy, enlarged breasts that sag and cause her chronic pains to the head, neck, shoulders, and back; an oversized bust also causes her secondary health problems, such as poor blood circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |