|
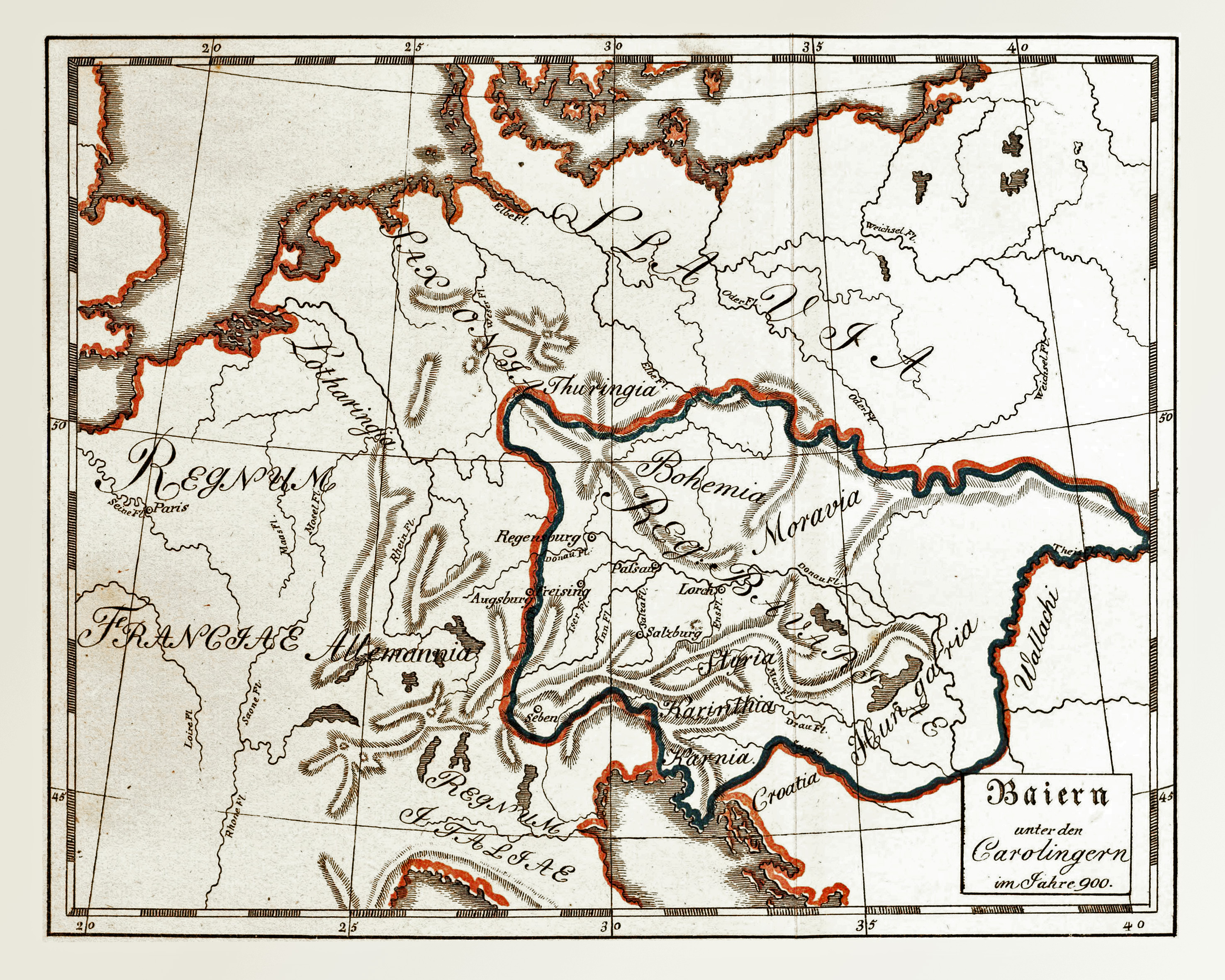
Braslav Of Croatia
Braslav ( 882–896) was a prince who ruled the Slavs in Lower Pannonia, in a territory located mostly in modern-day Croatia, between 884 and 896 as a vassal of Arnulf of Carinthia. He participated in the Frankish–Moravian War (882–84) and the Frankish invasion of Moravia (891–92). He was last mentioned when he was entrusted Pannonia by Arnulf in order to secure the Frankish frontier against the Hungarians (896), who subsequently overran all of Pannonia and continued into Italy. Background In 882–84, a bloody war was fought between Arnulf of Carinthia and Svatopluk I of Moravia, during which Pannonia and the Danube suffered the most. Svatopluk is said to have "slaughtered" and "destroyed much with fire and sword". The two agreed on peace in 884. Life A Slavic prince and ardent Frankish loyalist, according to the ''Frankish Annals'', Braslav was the "Duke of Lower Pannonia" (). He ruled a province from the Drava to the Sava (modern-day Slavonia). He took part in the 88 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs In Lower Pannonia
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, Spodnja Panonija) was used to designate those areas of the Pannonian plain that lie to the east and south of the river Rába, with the division into ''Upper'' and ''Lower'' inherited from the Roman terminology. From the middle of the 6th to the end of the 8th century, the region was under the domination of the Avars, while the Slavic inhabitants lived under Avar rule. By the beginning of the 9th century, that state was destroyed and replaced by the supreme rule of the Frankish Empire, which lasted until the Magyar conquest (c. 900). During the Frankish period, the region of Lower Pannonia was governed by local Slavic rulers, who were under the suzerainty of Frankish kings. Within the Frankish administrative system, the March of Pannonia w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarians
Bavarians ( Bavarian: ''Boarn'', Standard German: ''Baiern'') are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern ("Old Bavaria"), roughly the territory of the Electorate of Bavaria in the 17th century. Like the neighboring Austrians, Bavarians are traditionally Catholic. In much of ''Altbayern'', membership in the Catholic Church remains above 70%, and the center-right Christian Social Union in Bavaria (successor of the Bavarian People's Party of 1919–1933) has traditionally been the strongest party in the Landtag, and also the party of all Ministers-President of Bavaria since 1946, with the single exception of Wilhelm Hoegner, 1954–1957. Areal and dialectal subdivision There is no ethno-linguistic distinction between Bavarians and Austrians. The territory of Bavaria has changed significantly over German history; in the 19th century the Kingdom of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th Century In Croatia
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the character usually has a descender, as, for example, in . The mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century People From East Francia
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, and a northward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Slavs
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rad Jugoslavenske Akademije Znanosti I Umjetnosti
''Rad'' ( Croatian for ''proceedings'', ''work'') is an academic journal An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and ... published by the Yugoslav, now Croatian, Academy of Sciences and Arts. It was their only publication from 1867 until 1882, when each of the individual scientific sections of the academy started printing their own journals. , over five hundred issues have been published. External links * * * Croatian-language journals Publications established in 1867 Multidisciplinary academic journals Academic journals of Croatia Academic journals published by learned and professional societies {{academic-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslav Academy Of Sciences And Arts
The Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts ( la, Academia Scientiarum et Artium Croatica, hr, Hrvatska akademija znanosti i umjetnosti, abbrev. HAZU) is the national academy of Croatia. HAZU was founded under patronage of the Croatian bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer under the name ''Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts'' (, abbrev. JAZU) since its founder wanted to make it the central scientific and artistic institution of all South Slavs. Today, its main goals are encouraging and organizing scientific work, applying the achieved results, development of artistic and cultural activities, carrying about the Croatian cultural heritage and its affirmation in the world, publishing the results of scientific research and artistic creativity and giving suggestions and opinions for the advancement of science and art in areas of particular importance to Croatia. The academy is divided into nine classes; social sciences, mathematical, physical and chemical sciences, natural sciences, medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pressburg
The Battle of Pressburg (german: Schlacht von Pressburg) or Battle of Pozsony ( hu, Pozsonyi csata), or Battle of Bratislava ( sk, Bitka pri Bratislave) was a three-day-long battle, fought between 4–6 July 907, during which the East Francian army, consisting mainly of Bavarian troops led by Margrave Luitpold, was annihilated by Hungarian forces. The exact location of the battle is not known. Contemporary sources say it took place at "Brezalauspurc", but where exactly Brezalauspurc was is unclear. Some specialists place it in the vicinity of Zalavár (Mosapurc); others in a location close to Bratislava (Pressburg), the traditional assumption. An important result of the Battle of Pressburg was the Kingdom of East Francia could not regain control over the Carolingian March of Pannonia, including the territory of the later '' marchia orientalis'' (March of Austria), lost in 900. The most significant result of the Battle of Pressburg is that the Hungarians secured the lands they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the fifth and sixth centuries. In the seventh century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the ninth century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which then became the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approximately 140% of the official figures. Bratislava is in southwestern Slovakia at the foot of the Little Carpathians, occupying both banks of the River Danube and the left bank of the Morava (river), River Morava. Bordering Austria and Hungary, it is the only national capital that borders two sovereign states. The city's history has been influenced by people of many nations and religions, including Austrians, Bulgarians, Croats, Czechs, Germans, Hungarian people, Hungarians, Jews, Romani people, Romani, Serbs and Slovaks. It was the coronation site and legislative center and capital of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1536 to 1783; eleven King of Hungary, Hungarian kings and eight queens were crowned in St Martin's Cathedral, Bratislava, St Martin' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zalavár
Zalavár is a village in Hungary, located in Zala County. It is located around southwest of Lake Balaton. Name According to written sources the settlement was called 'Mosapurc' in the 9th century, "''Mosapurc regia civitate''". It was also known as ''Moosburg'', ''Urbs Paludarum'', ''Braslavespurch'' and ''Blatengrad'' in medieval records. The medieval settlement is known in modern sources as ''Blatnohrad'' ( Slovak), ''Blatnograd'', Блатноград (Serbo-Croatian and Bulgarian). Ján Kollár called it ''Salavár'' in his travel book and described the state of the ruins in 1841. History In the 9th century, ''Mosapurc'' or ''Moosburg'' was a fortified settlement built at the Zala river and was the capital of the Frankish vassal Lower Pannonian Principality ruled by a Slavic prince Pribina (''"Privinae civitas, munimen, castrum in nemore et palude Salae"'' in a Salzburg chronicle). During the reign of Pribina's son, prince Kocel (861-876), in the summer of 867, it provided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders. The Tisza begins near Rakhiv in Ukraine, at the confluence of the White Tisa and Black Tisa, which is at coordinates 48.07465560782065, 24.24443465360461 (the former springs in the Chornohora mountains; the latter in the Gorgany range). From there, the Tisza flows west, roughly following Ukraine's borders with Romania and Hungary, then shortly as border between Slovakia and Hungary, later into Hungary, and finally into Serbia. It enters Hungary at Tiszabecs. It traverses Hungary from north to south. A few kilometers south of the Hungarian city of Szeged, it enters Serbia. Finally, it joins the Danube near the village of Stari Slankamen in Vojvodina, Serbia. The Tisza drains an area of about and has a length of Its mean annual discharge is seas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |