|
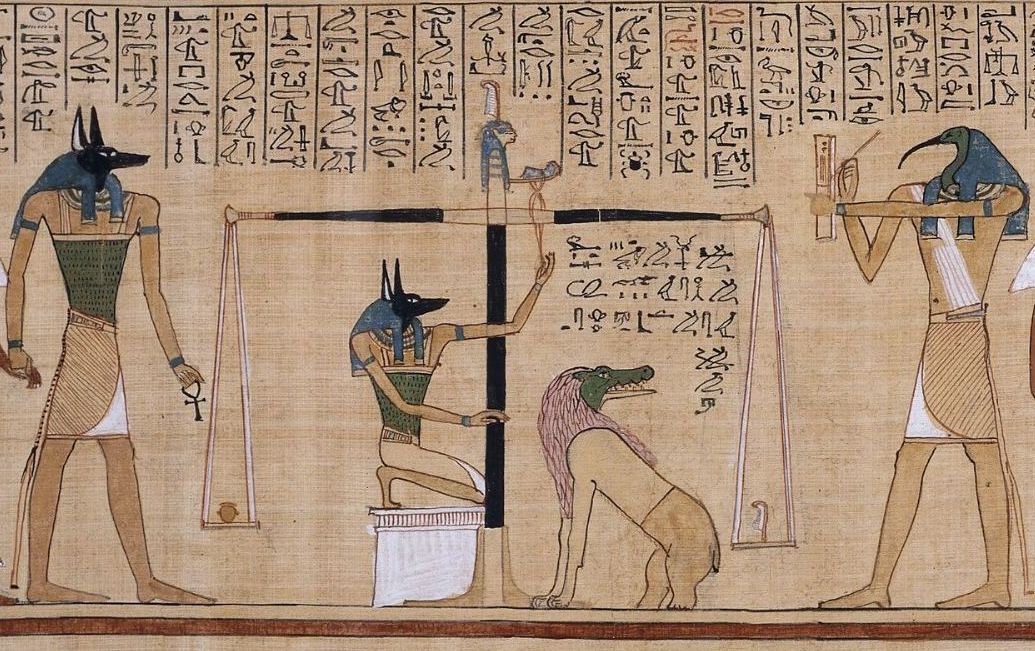
Book Of The Dead (Art Institute Of Chicago)
The Art Institute of Chicago contains a Book of the Dead scroll, an Ancient Egyptian papyrus depicting funerary spells. This scroll of funerary spells serves as a protection from "Second Death". In ancient Egyptian spiritual practice, the term "Second Death" refers to the phenomenon of the body permanently separating from the soul. The Book of the Dead scroll is made of papyrus, a material made of reed plants cultivated on marshy plantations, which is then cut into strips and left to dry in horizontal and vertical rows. The scroll also contains pigments used to inscribe the funerary spells.Meskell, L. (2001), "The Egyptian Ways of Death." ''Archeological Papers of the American Anthropological Association'', 10: 27–40. doi:10.1525/ap3a.2001.10.1.27 Mythology In Ancient Egyptian spirituality, one can only completely achieve sanctity when confronted with death itself, meaning that the physical body is only one place where a person exists. Destruction of a person's body after de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Institute Of Chicago
The Art Institute of Chicago in Chicago's Grant Park, founded in 1879, is one of the oldest and largest art museums in the world. Recognized for its curatorial efforts and popularity among visitors, the museum hosts approximately 1.5 million people annually. Its collection, stewarded by 11 curatorial departments, is encyclopedic, and includes iconic works such as Georges Seurat's ''A Sunday on La Grande Jatte'', Pablo Picasso's ''The Old Guitarist'', Edward Hopper's '' Nighthawks'', and Grant Wood's '' American Gothic''. Its permanent collection of nearly 300,000 works of art is augmented by more than 30 special exhibitions mounted yearly that illuminate aspects of the collection and present cutting-edge curatorial and scientific research. As a research institution, the Art Institute also has a conservation and conservation science department, five conservation laboratories, and one of the largest art history and architecture libraries in the country—the Ryerson and B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a document written on sheets of such material, joined side by side and rolled up into a scroll, an early form of a book. Papyrus is first known to have been used in Egypt (at least as far back as the First Dynasty), as the papyrus plant was once abundant across the Nile Delta. It was also used throughout the Mediterranean region. Apart from a writing material, ancient Egyptians employed papyrus in the construction of other artifacts, such as reed boats, mats, rope, sandals, and baskets. History Papyrus was first manufactured in Egypt as far back as the fourth millennium BCE.H. Idris Bell and T.C. Skeat, 1935"Papyrus and its uses"(British Museum pamphlet). The earliest archaeological evidence of papyrus was excavated in 2012 and 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scene From The Book Of The Dead
Scene (from Greek σκηνή ''skēnḗ'') may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * Scene (subculture), a youth subculture from the early 2000s characterized by a distinct music and style. Groups and performers * The Scene who recorded the song "Scenes (from Another World)" * Scene, the stage name used by Japanese Punk guitarist Minoru Kojima * Selena Gomez & the Scene, an American band * The Scene (Canadian band), a late 1960s psychedelic Canadian band * The Scene (Dutch band), a Dutch band formed by Thé Lau Albums * ''Scene'', a 2005 noise album by Merzbow * ''Scenes'' (album), a 1992 music album by Marty Friedman * ''The Scene'' (Eskimo Callboy album), an Eskimo Callboy album * ''The Scene'', the debut album of The Scene Other uses in music * S.C.E.N.E. Music Festival, an annual festival held in downtown St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada * "The Scene" (song), a song by Canadian band Big Sugar from their 1998 album ''Heated'' Periodicals * ''Scene'' (se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opening Of The Mouth Ceremony
The opening of the mouth ceremony (or ritual) was an ancient Egyptian ritual described in funerary texts such as the Pyramid Texts. ''PeseshKaf'' is an instrument used for this ritual, ''psš'' (“an instrument for Opening of the mouth”) + ''kꜣf'' (“obsidian”). This instrument was made of stone and shaped like the tail of a fish. Funerary magic The ceremony involved a symbolic animation of a statue or mummy by magically opening its mouth so that it could breathe and speak. There is evidence of this ritual from the Old Kingdom to the Roman Period. Special tools were used to perform the ceremony, such as a ritual adze, an arm shaped ritual censer, a spooned blade known as a ''peseshkaf'', a serpent-head blade, and a variety of other amulets. A calf's leg was also held up to the lips painted on the coffin. The ancient Egyptians believed that in order for a person's soul to survive in the afterlife it would need to have food and water. The opening of the mouth ritual was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
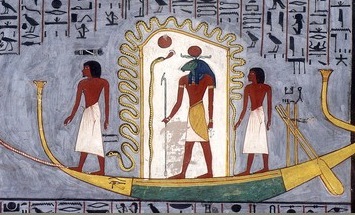
Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother, Set cut him up into pieces after killing him, Osiris' wife Isis found all the pieces and wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was widely worshipped until the decline of ancient Egyptian religion during the rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut, as well as being brother and husband of Isis, and brother of Set, Nephthys, and Horus the Elder, with Horus the Younger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duat
The Duat ( egy, dwꜣt, Egyptological pronunciation "do-aht", cop, ⲧⲏ, also appearing as ''Tuat'', ''Tuaut'' or ''Akert'', ''Amenthes'', ''Amenti'', or ''Neter-khertet'') is the realm of the dead in ancient Egyptian mythology. It has been represented in hieroglyphs as a star-in-circle: 𓇽. The god Osiris was believed to be the lord of the underworld. He was the first mummy as depicted in the Osiris myth and he personified rebirth and life after death. The underworld was also the residence of various other gods along with Osiris. The geography of the ''Duat'' is similar in outline to the world the Egyptians knew: There are realistic features like rivers, islands, fields, lakes, mounds and caverns, but there were also fantastic lakes of fire, walls of iron, and trees of turquoise. In the ''Book of Two Ways'' (a Coffin Text) there is even a map-like image of the ''Duat''. Resident souls, gods, and demons The ''Duat'' was also a residence for various gods, including Osiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriental Institute Of Chicago
The Oriental Institute (OI), established in 1919, is the University of Chicago's interdisciplinary research center for ancient Near Eastern ("Orient") studies and archaeology museum. It was founded for the university by professor James Henry Breasted with funds donated by John D. Rockefeller, Jr. It conducts research on ancient civilizations throughout the Near East, including at its facility, Chicago House, in Luxor, Egypt. The institute publicly exhibits an extensive collection of artifacts related to ancient civilizations at its on-campus building in Hyde Park, Chicago. According to anthropologist William Parkinson of the Field Museum, the OI's highly focused "near Eastern, or southwest Asian and Egyptian" collection is one of the finest in the world. History In the early 20th century, James Henry Breasted built up the collection of the university's Haskell Oriental Museum, which he oversaw along with his field work, and teaching duties. He dreamed, however, of establishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Intermediate Period Of Egypt
The Third Intermediate Period of ancient Egypt began with the death of Pharaoh Ramesses XI in 1077 BC, which ended the New Kingdom, and was eventually followed by the Late Period. Various points are offered as the beginning for the latter era, though it is most often regarded as dating from the foundation of the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty by Psamtik I in 664 BC, following the departure of the Nubian Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty after they were driven out by the Assyrians under King Ashurbanipal. The concept of a "Third Intermediate Period" was coined in 1978 by British Egyptologist Kenneth Kitchen. The period was one of decline and political instability, coinciding with the Late Bronze Age collapse of civilizations in the ancient Near East and Eastern Mediterranean (including the Greek Dark Ages). It was marked by division of the state for much of the period and conquest and rule by non-native Egyptians. History Twenty-first Dynasty The period of the Twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Papyri Containing Images
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt. Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to: Nations and ethnic groups * Egyptians, a national group in North Africa ** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of recorded history ** Egyptian cuisine, the local culinary traditions of Egypt * Egypt, the modern country in northeastern Africa ** Egyptian Arabic, the language spoken in contemporary Egypt ** A citizen of Egypt; see Demographics of Egypt * Ancient Egypt, a civilization from c. 3200 BC to 343 BC ** Ancient Egyptians, ethnic people of ancient Egypt ** Ancient Egyptian architecture, the architectural structure style ** Ancient Egyptian cuisine, the cuisine of ancient Egypt ** Egyptian language, the oldest known language of Egypt and a branch of the Afroasiatic language family * Copts, the ethnic Egyptian Christian minority ** Coptic language or Coptic Egyptian, the latest stage of the Egyptian language, spoken in Egypt until the 17t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |