|
Bjarmian Languages
Bjarmian languages are a group of extinct Finnic languages once spoken in Bjarmia, or the northern part of the Dvina basin. Vocabulary of the languages in Bjarmia can be reconstructed from toponyms in the Arkhangelsk region, and a few words are documented by Norse travelers. Also some Saamic toponyms can also be found in the Dvina basin. Affinities There were likely many Finnic languages spoken in Bjarmia, the first one was an archaic Finnic language with the diphthong *ai instead of Finnic ei, lack of consonant gradation and the vowel /ɤ/. Later a Karelian-like language started to be spoken in Bjarmia, which did not have the Karelian sound shift of /aa/ into /ua/. Some toponyms in Bjarmia also have the sound /ʃ/ instead of /s/. Janne Saarikivi suggests that some Sámi languages were spoken in Bjarmia alongside Finnic languages. Reconstructions Many toponyms in the Arkhangelsk oblast are of Finno–Ugric origin, together with the Vologda oblast, according to Matvee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finno-Permic Languages
The Finno-Permic (''Fenno-Permic'') or Finno-Permian (''Fenno-Permian'') languages, or sometimes just Finnic (''Fennic'') languages, are a proposed subdivision of the Uralic languages which comprise the Balto-Finnic languages, Sami languages, Mordvinic languages, Mari language, Permic languages and likely a number of extinct languages. In the traditional taxonomy of the Uralic languages, Finno-Permic is estimated to have split from Finno-Ugric around 3000–2500 BC, and branched into Permic languages and Finno-Volgaic languages around 2000 BC. Nowadays the validity of the group as a taxonomical entity is being questioned, and the interrelationships of its five branches are debated with little consensus. The term ''Finnic languages'' has often been used to designate all the Finno-Permic languages, with the term ''Balto-Finnic'' used to disambiguate the Finnic languages proper. In Finnish and Estonian scholarly usage, ''Finnic'' most often refers to the Baltic-Finnic languages alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
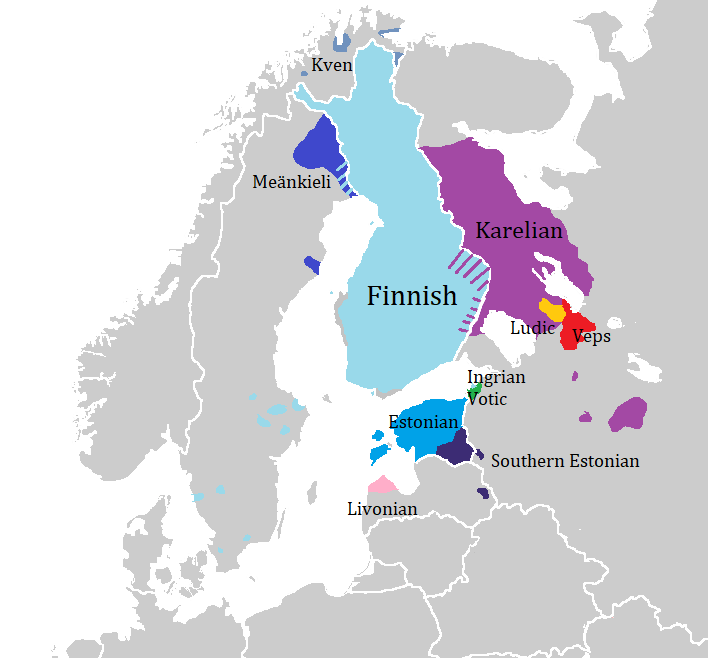
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
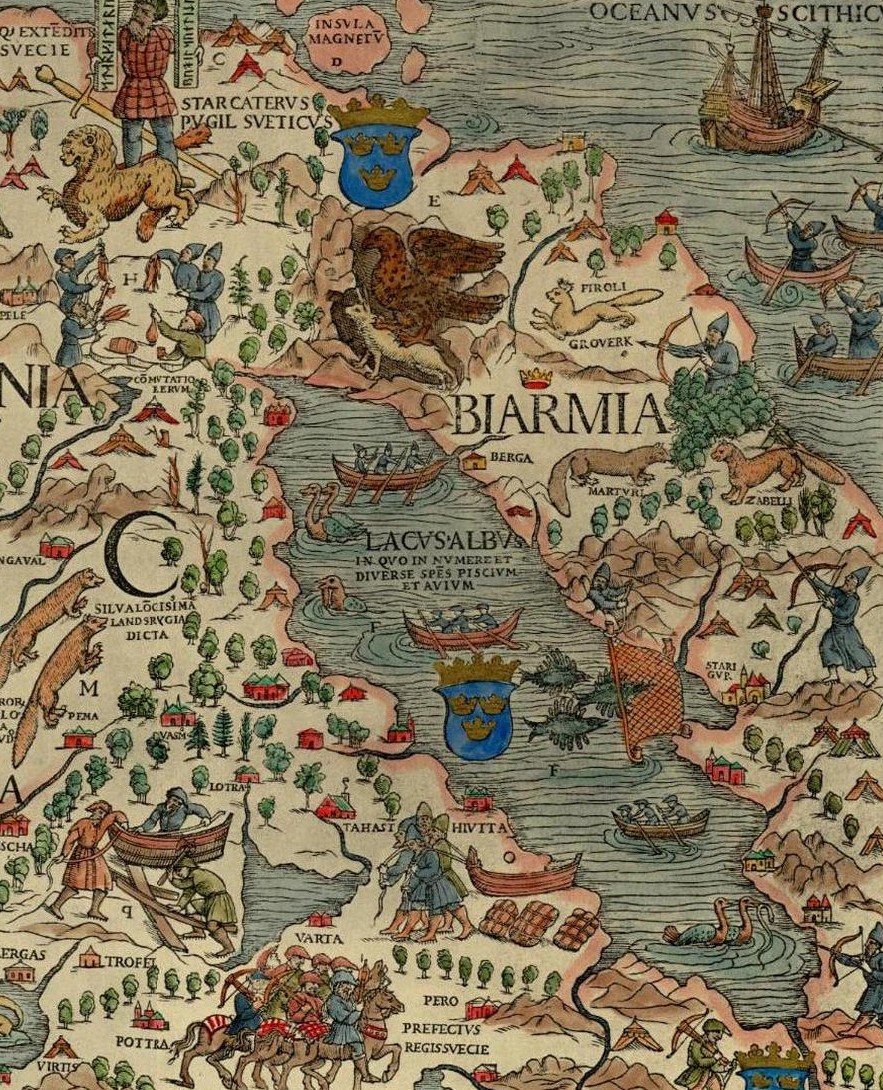
Bjarmaland
Bjarmaland (also spelt ''Bjarmland'' and ''Bjarmia''; Latin: ''Biarmia''; Old English: ''Beormaland,'' Komi: Биармия ''Biarmia,'' Old Permic: 𐍑𐍙𐍐𐍒𐍜𐍙𐍐) was a territory mentioned in Norse sagas since the Viking Age and in geographical accounts until the 16th century. The term is usually seen to have referred to the southern shores of the White Sea and the basin of the Northern Dvina River (''Vienanjoki'' in Finnish) as well as, presumably, some of the surrounding areas. Today, those territories comprise a part of the Arkhangelsk Oblast of Russia, as well as the Kola Peninsula. Norse voyagers in Bjarmaland According to the '' Voyage of Ohthere'' (c. 890 CE), the Norwegian merchant Ottar (Ohthere) reported to king Alfred the Great that he had sailed for 15 days along the northern coast and then southwards, finally arriving at a great river, probably the Northern Dvina. At the estuary of the river dwelt the ''Beormas'', who unlike the nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
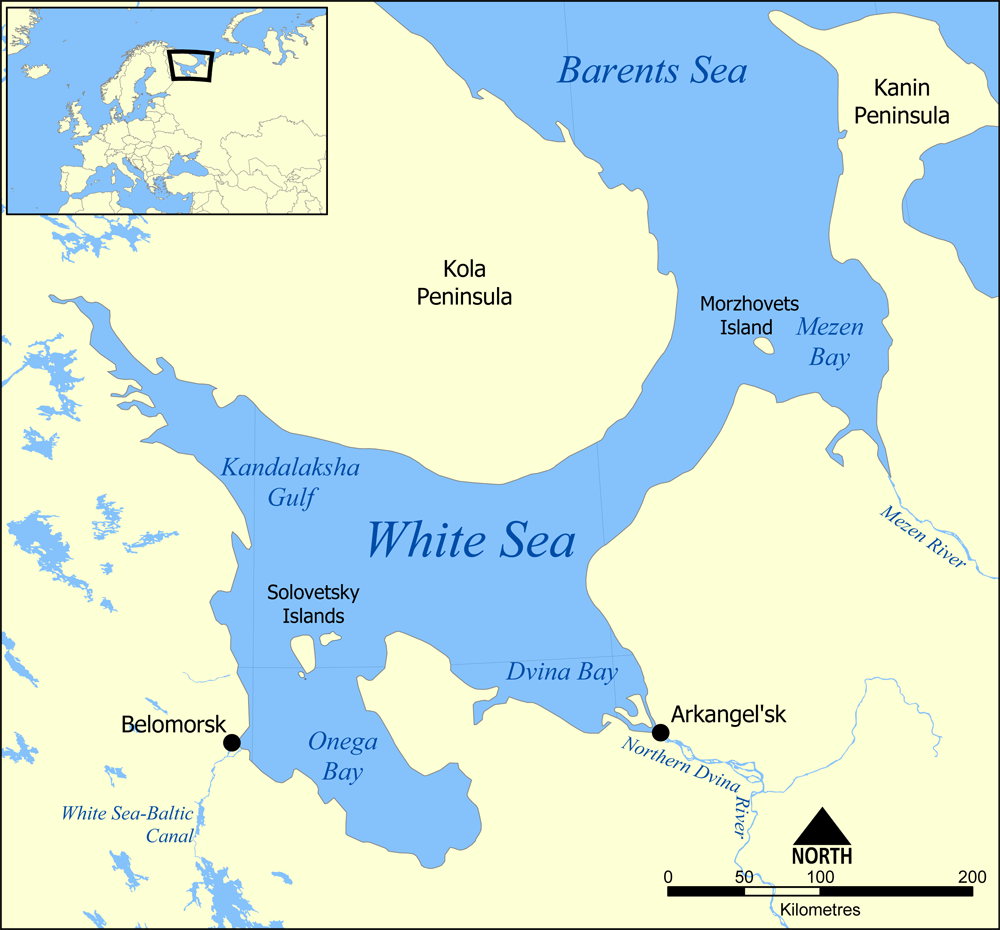
Dvina Bay
The Dvina Bay (russian: Двинская Губа) is located in Arkhangelsk Oblast in Northwestern Russia. It is one of four large bays and gulfs of the White Sea, the others being the Mezen Bay, the Onega Bay, and the Kandalaksha Gulf. The two main river emptying into the Dvina Bay is the Northern Dvina River, while the two cities on the bay are Arkhangelsk and Severodvinsk. The Dvina Bay is long and wide. Administratively, the coast and the islands belong to Primorsky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast. The Northern Dvina forms a delta entering the Dvina Bay, with many islands separating different streams. There are many small islands in the Dvina Bay as well, the biggest being Mudyug Island. A national park, Onezhskoye Pomorye National Park, was open on the Onega Peninsula on 26 February 2013. The Dvina Bay is limited by the Onega Peninsula from the west. At the eastern side, the shore steeply rises to a plateau ( White Sea - Kuloy Plateau) which drains east into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkhangelsk Oblast
Arkhangelsk Oblast (russian: Арха́нгельская о́бласть, ''Arkhangelskaya oblast'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It includes the Arctic Ocean, Arctic archipelagos of Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya, as well as the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea. Arkhangelsk Oblast also has administrative jurisdiction over the Nenets Autonomous Okrug (NAO). Including the NAO, Arkhangelsk Oblast has an area of 587,400 km2. Its population (including the NAO) was 1,227,626 as of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census. The classification of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Arkhangelsk, with a population of 301,199 as of the 2021 Census, is the administrative center of the oblast.Charter, Article 5 The second largest city is the nearby Severodvinsk, home to Sevmash, a major shipyard for the Russian Navy. Among the oldest populated places of the oblast are Kholmogory, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Kholmogory, Kargopol, and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
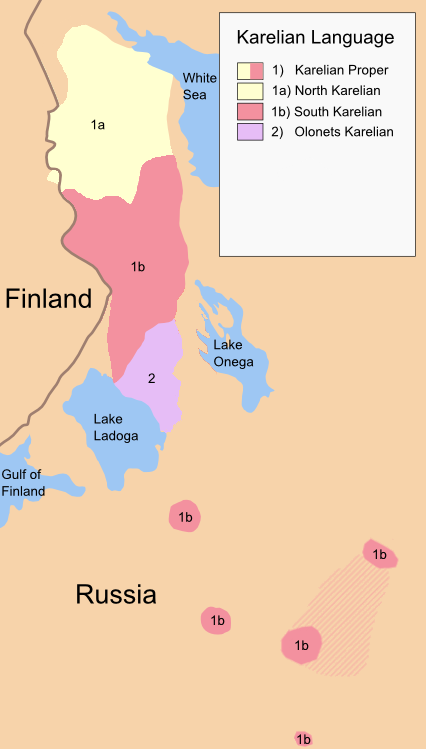
Karelian Language
Karelian (North Karelian and Livvi Karelian: ; Ludic: ; Tver Karelian: ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, though in the modern day it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. There is no single standard Karelian language. Each writer writes in Karelian according to their own dialectal form. Three main written standards have been developed, for North Karelian, Olonets Karelian (also known as Livvi Karelian) and Tver Karelian. Ludic Karelian also appears in writing. All variants are written with the Latin-based Karelian alphabet, though the Cyrillic script has been used in the past. Classification Karelian belongs to the Finnic branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sámi Languages
Sámi languages ( ), in English also rendered as Sami and Saami, are a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sámi people in Northern Europe (in parts of northern Finland, Norway, Sweden, and extreme northwestern Russia). There are, depending on the nature and terms of division, ten or more Sami languages. Several spellings have been used for the Sámi languages, including ''Sámi'', ''Sami'', ''Saami'', ''Saame'', ''Sámic'', ''Samic'' and ''Saamic'', as well as the exonyms Lappish and ''Lappic''. The last two, along with the term ''Lapp'', are now often considered pejorative. Classification The Sámi languages form a branch of the Uralic language family. According to the traditional view, Sámi is within the Uralic family most closely related to the Finnic languages (Sammallahti 1998). However, this view has recently been doubted by some scholars who argue that the traditional view of a common Finno-Sami protolanguage is not as strongly supported as had been earlier assu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
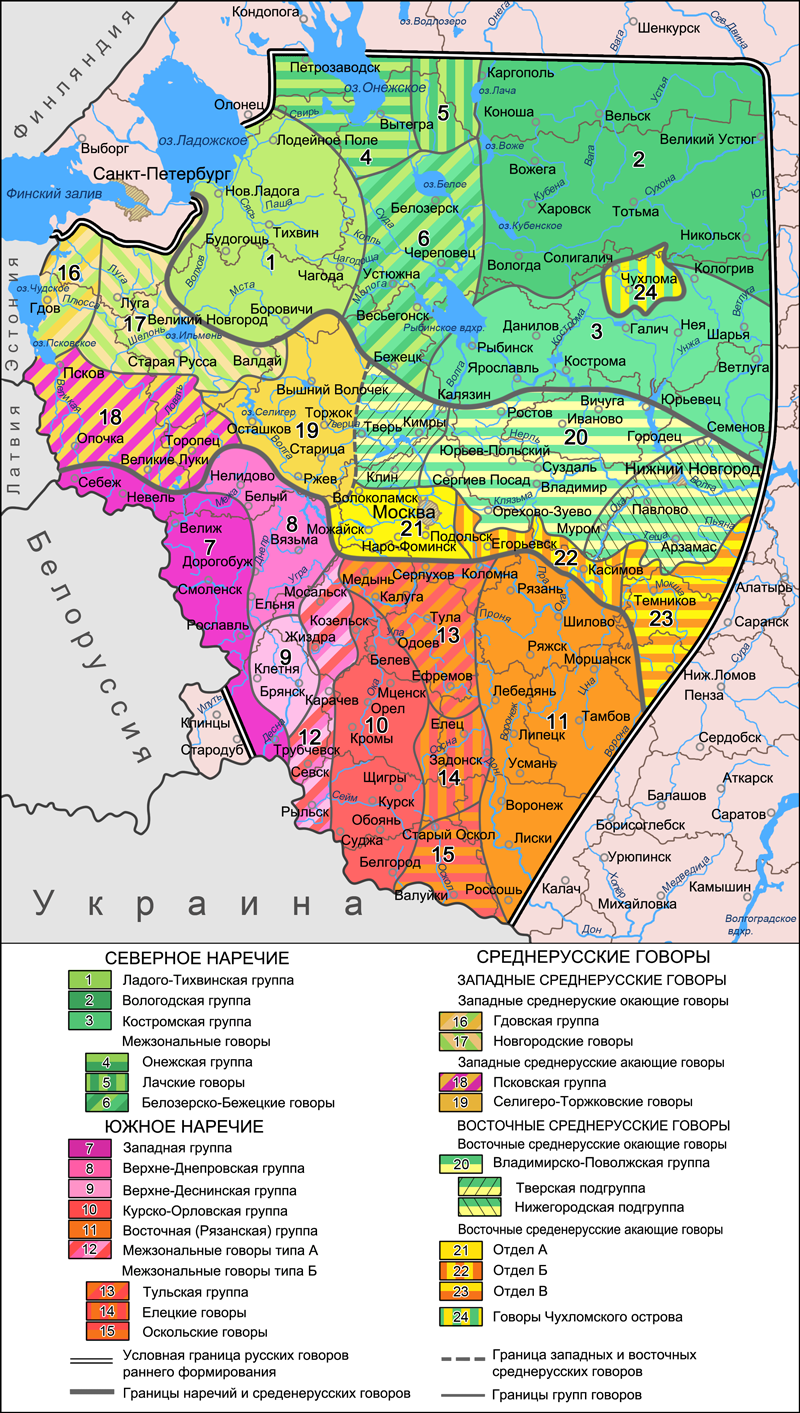
Northern Russian Dialects
The northern Russian dialects make up one of the main groups of the Russian dialects. Territory * The territory of the ''primary formation'' (e.g. that consist of "Old" Russia of the 16th century before Eastern conquests by Ivan IV) is fully or partially modern regions (''oblasts''): Vologda, Kostroma, Yaroslavl, Novgorod, Leningrad, Nizhny Novgorod, Arkhangelsk. * The territory of the ''second formation'' (e.g. where Russians settled after the 16th century) consist of most of the land to the North and North-East of Central Russia, that is Karelia, Murmansk, Vyatka, Perm, Komi, Udmurtia, and as well as Siberia and Far East. List of sub-dialects * Pomor dialects * Olonets group * Novgorod group * Vologda- Kirov group * Vladimir-Volga group Phonology * Lack of vowel reduction: unstressed does not merge with (okanye). Unstressed , and after soft consonants also do not typically merge. * Some dialects have high or diphthongal (in the Novgorod subgroup even ) as a reflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Dialects
Russian dialects are spoken variants of the Russian language. Russian dialects and territorial varieties are divided in two conceptual chronological and geographic categories: Kamusella, Tomasz. (2018). Russian: A Monocentric or Pluricentric Language?. Colloquia Humanistica. 2018. 153–196. 10.11649/ch.2018.010. # The dialects of the territory of the ''primary formation'', which consist of "Old" Russia of the 16th century (before the Eastern conquests by Ivan the Terrible) and roughly correlate with the modern Central and Northwestern Federal districts. These "historical dialects" are claimed as ethnically Russian (Russkii). # The dialects of the territory of the ''second formation'', where Russians settled after the 16th century. These new territorial varieties were produced by the Russian and Soviet imperial expansions during the last centuries and are mainly spoken by non- Slavic, non- Slavophone, and non-Orthodox populations in post-Soviet states. In Russia Depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinega
Pinega (russian: Пинега) is a rural locality (a settlement), formerly a town, in Pinezhsky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Pinega River (hence the name). It serves as the administrative center of Pinezhsky Selsoviet, one of the seventeen selsoviets into which the district is administratively divided. Municipally, it is the administrative center of Pinezhskoye Rural Settlement, one of the fifteen rural settlements in the district. Population: . History Pinega was known from 17th century as the pogost of Pinezhsky Volok. In the course of the administrative reform performed in 1708 by Peter the Great the area was included into Archangelgorod Governorate, with the creation of Kevrolsky Uyezd. The center of the uyezd was located in Kevrola, now a village. In 1780, the Governorate was abolished and transformed into Vologda Viceroyalty, with the creation of Pinezhsky Uyezd in place of the Kevrolsky Uyezd. The center of the uyezd was Pin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Sagas
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to the PlayStation 2. The series is notable for its emphasis on open world exploration, non-linear branching plots, and occasionally unconventional gameplay. This distinguishes the games from most of Square's other franchises. Development The ''SaGa'' series was created by game designer Akitoshi Kawazu, whose contributions prior to the franchise's introduction include ''Final Fantasy'' and ''Final Fantasy II''. At a time when Nintendo's Game Boy was becoming popular worldwide due to the puzzle game ''Tetris'', then-Square president Masashi Miyamoto requested that a development team create a game for the handheld console. Kawazu and fellow designer Koichi Ishii suggested that the company develop a role-playing video game, thus making ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the northeast. The whole of the White Sea is under Russian sovereignty and considered to be part of the internal waters of Russia.A. D. Dobrovolskyi and B. S. Zalogi"Seas of USSR. White Sea" Moscow University (1982) (in Russian) Administratively, it is divided between Arkhangelsk and Murmansk oblasts and the Republic of Karelia. The major port of Arkhangelsk is located on the White Sea. For much of Russia's history this was Russia's main centre of international maritime trade, conducted by the Pomors ("seaside settlers") from Kholmogory. In the modern era it became an important Soviet naval and submarine base. The White Sea–Baltic Canal connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |