|
Finno-Permic Languages
The Finno-Permic (''Fenno-Permic'') or Finno-Permian (''Fenno-Permian'') languages, or sometimes just Finnic (''Fennic'') languages, are a proposed subdivision of the Uralic languages which comprise the Balto-Finnic languages, Sami languages, Mordvinic languages, Mari language, Permic languages and likely a number of extinct languages. In the traditional taxonomy of the Uralic languages, Finno-Permic is estimated to have split from Finno-Ugric around 3000–2500 BC, and branched into Permic languages and Finno-Volgaic languages around 2000 BC. Nowadays the validity of the group as a taxonomical entity is being questioned, and the interrelationships of its five branches are debated with little consensus. The term ''Finnic languages'' has often been used to designate all the Finno-Permic languages, with the term ''Balto-Finnic'' used to disambiguate the Finnic languages proper. In Finnish and Estonian scholarly usage, ''Finnic'' most often refers to the Baltic-Finnic languages alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic (now commonly '' Finno-Permic'') language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of the Volga River. The largest Finnic peoples by population are the Finns (or more precisely the Suomi, 6 million), the Estonians (1 million), the Mordvins (800,000), the Mari (570,000), the Udmurts (550,000), the Komis (330,000) and the Sami (100,000). The scope of the name "Finn" and "Finnic" varies by country. Today, Finnish and Estonian scholars restrict the term "Finnic" to the Baltic Finns, who include the Western Finns of Finland and their closest relatives but not the Sami. In Russia, however, where the Eastern Finns live, the word continues to be used in the broad sense, and sometimes implies the Volga Finns who have their own national republics. Three groups of people are covered by the names "Finn" and "Finnic" in the broad se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordvin Languages
The Mordvinic languages, also known as the Mordvin, Mordovian or Mordvinian languages (russian: мордовские языки, ''mordovskiye yazyki''), are a subgroup of the Uralic languages, comprising the closely related Erzya language and Moksha language, both spoken in Mordovia. Previously considered a single "Mordvin language", it is now treated as a small language grouping. Due to differences in phonology, lexicon, and grammar, Erzya and Moksha are not mutually intelligible. The two Mordvinic languages also have separate literary forms. The Erzya literary language was created in 1922 and the Mokshan in 1923. Phonological differences between the two languages include: * Moksha retains a distinction between the vowels while in Erzya, both have merged as . * In unstressed syllables, Erzya features vowel harmony like many other Uralic languages, using in front-vocalic words and in back-vocalic words. Moksha has a simple schwa in their place. * Word-initially, Erzya has a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suomalaisen Kirjallisuuden Seura
The Finnish Literature Society ( fi, Suomalaisen Kirjallisuuden Seura ry or fi, SKS) was founded in 1831 to promote literature written in Finnish. Among its first publications was the ''Kalevala'', the Finnish national epic A national epic is an epic poem or a literary work of epic scope which seeks or is believed to capture and express the essence or spirit of a particular nation—not necessarily a nation state, but at least an ethnic or linguistic group with as .... External links Official website''' Finnish writers' organisations Organisations based in Helsinki {{Europe-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johanna Laakso
Johanna Laakso (born 1962 in Helsinki) is a Finnish linguist and Finno-Ugrist based at the University of Vienna. Biography Laakso studied Finno-Ugric languages, Finnic languages and general linguistics at the University of Helsinki from 1979 to 1990, graduating with a Cand.phil. in 1985, a licentiate in 1988, and a PhD in 1990. Her doctoral thesis was on verbal derivational morphology in the Finnic languages. From 1987 onwards she worked as an assistant at the University of Helsinki, with stints as acting professor of Finnic languages in 1989-90 and acting professor of Finno-Ugric languages in 1991. In 2000 she moved to the University of Vienna to take up her current position as Professor of Finno-Ugric Studies. Laakso has been a member of the Finnish Academy of Science and Letters since 2006, a corresponding member of the Austrian Academy of Sciences since 2008, and an elected member of the Academia Europaea since 2015. Research Laakso is a specialist in Finno-Ugric languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finno-Volgaic Languages
Finno-Volgaic or Fenno-Volgaic is a hypothetical branch of the Uralic languages that tried to group the Finnic languages, Sami languages, Mordvinic languages and the Mari language. It was hypothesized to have branched from the Finno-Permic languages about 2000 BC. The Finnic and Sami languages are sometimes grouped together as Finno-Samic languages, while Mordvinic and Mari were formerly grouped together as the obsolete group of the Volga-Finnic languages. The current stage of research rejects Volga-Finnic, while the validity of Finno-Lappic and Finno-Permic remains disputed.Salminen, Tapani 2002: Problems in the taxonomy of the Uralic languages in the light of modern comparative studies. http://www.helsinki.fi/~tasalmin/kuzn.html In particular the position of Mari within the alleged grouping appears to be marginal, while more evidence can be found uniting specifically Finnic, Samic and Mordvinic. Only a single uniting phonological feature of the Finno-Volgaic languages has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mari Language
The Mari language (Mari: , ''marij jylme''; russian: марийский язык, ''mariyskiy yazyk''), formerly known as the Cheremiss language, spoken by approximately 400,000 people, belongs to the Uralic language family. It is spoken primarily in the Mari Republic (Mari: , ''Marij El'', i.e., 'Mari land') of the Russian Federation as well as in the area along the Vyatka river basin and eastwards to the Urals. Mari speakers, known as the Mari, are found also in the Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, Udmurtia, and Perm regions. Mari is the titular and official language of its republic, alongside Russian. The Mari language today has three standard forms: Hill Mari, Northwestern Mari, and Meadow Mari. The latter is predominant and spans the continuum Meadow Mari to Eastern Mari from the Republic into the Ural dialects of Bashkortostan, Sverdlovsk Oblast and Udmurtia), whereas the former, Hill Mari, shares a stronger affiliation with the Northwestern dialect (spoken in the Nizhny Novgo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordvinic Languages
The Mordvinic languages, also known as the Mordvin, Mordovian or Mordvinian languages (russian: мордовские языки, ''mordovskiye yazyki''), are a subgroup of the Uralic languages, comprising the closely related Erzya language and Moksha language, both spoken in Mordovia. Previously considered a single "Mordvin language", it is now treated as a small language grouping. Due to differences in phonology, lexicon, and grammar, Erzya and Moksha are not mutually intelligible. The two Mordvinic languages also have separate literary forms. The Erzya literary language was created in 1922 and the Mokshan in 1923. Phonological differences between the two languages include: * Moksha retains a distinction between the vowels while in Erzya, both have merged as . * In unstressed syllables, Erzya features vowel harmony like many other Uralic languages, using in front-vocalic words and in back-vocalic words. Moksha has a simple schwa in their place. * Word-initially, Erzya has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
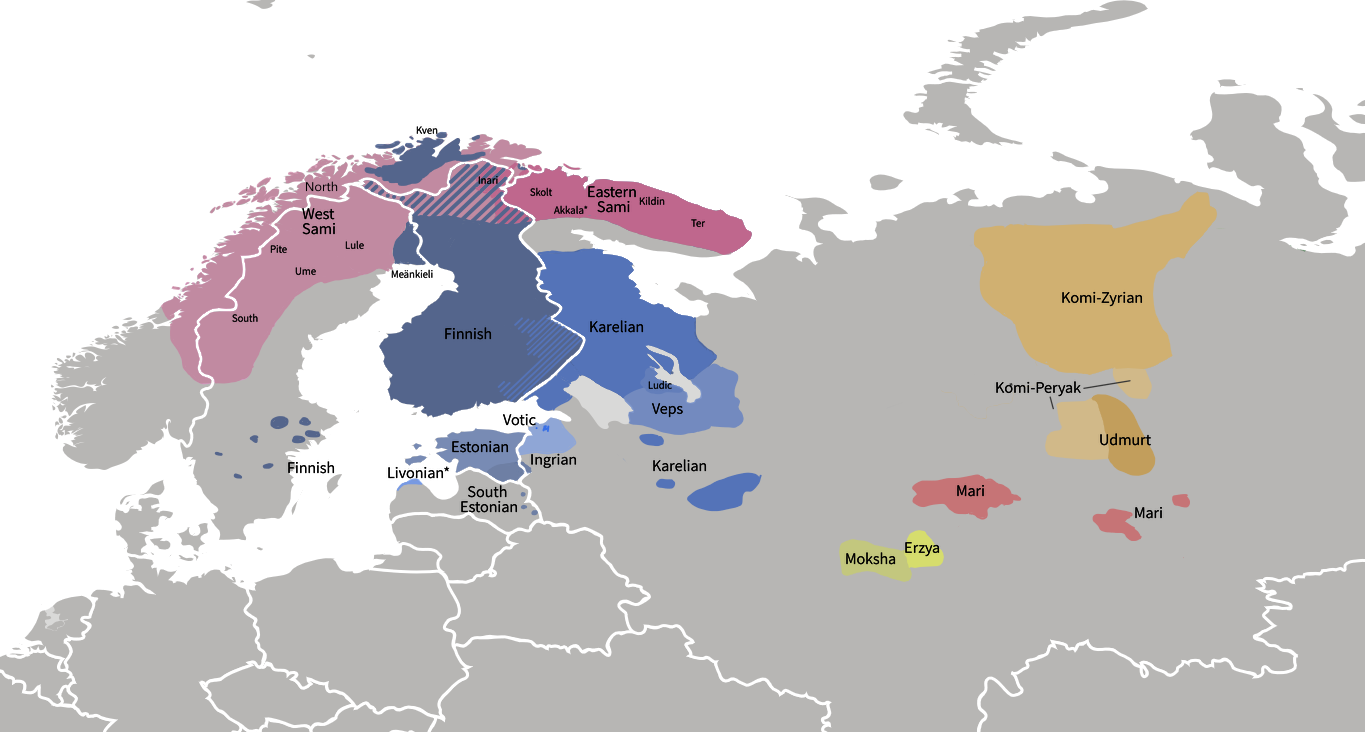
Uralic Languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (which alone accounts for more than half of the family's speakers), Finnish, and Estonian. Other significant languages with fewer speakers are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt, Sami, Komi, and Vepsian, all of which are spoken in northern regions of Scandinavia and the Russian Federation. The name "Uralic" derives from the family's original homeland (''Urheimat'') commonly hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains. Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic, though Finno-Ugric is widely understood to exclude the Samoyedic languages. Scholars who do not accept the traditional notion that Samoyedic split first from the rest of the Uralic family may treat the terms as synonymous. History Homeland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mari Languages
The Mari language (Mari: , ''marij jylme''; russian: марийский язык, ''mariyskiy yazyk''), formerly known as the Cheremiss language, spoken by approximately 400,000 people, belongs to the Uralic language family. It is spoken primarily in the Mari Republic (Mari: , ''Marij El'', i.e., 'Mari land') of the Russian Federation as well as in the area along the Vyatka river basin and eastwards to the Urals. Mari speakers, known as the Mari, are found also in the Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, Udmurtia, and Perm regions. Mari is the titular and official language of its republic, alongside Russian. The Mari language today has three standard forms: Hill Mari, Northwestern Mari, and Meadow Mari. The latter is predominant and spans the continuum Meadow Mari to Eastern Mari from the Republic into the Ural dialects of Bashkortostan, Sverdlovsk Oblast and Udmurtia), whereas the former, Hill Mari, shares a stronger affiliation with the Northwestern dialect (spoken in the Nizhny Novgo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fennoscandia
__NOTOC__ Fennoscandia (Finnish language, Finnish, Swedish language, Swedish and no, Fennoskandia, nocat=1; russian: Фенноскандия, Fennoskandiya) or the Fennoscandian Peninsula is the geographical peninsula in Europe, which includes the Scandinavian Peninsula, Scandinavian and Kola Peninsula, Kola peninsulas, mainland Finland, and Karelia. Administratively this roughly encompasses the mainlands of Finland, Norway and Sweden, as well as Murmansk Oblast, much of the Republic of Karelia, and parts of northern Leningrad Oblast in Russia. Its name comes from the Latin words ''Fennia'' (Finland) and ''Scandia'' (Scandinavian). The term was first used by the Finnish geologist Wilhelm Ramsay in 1898. Geologically, the area is distinct because its bedrock is Archean granite and gneiss with very little limestone, in contrast to adjacent areas in Europe. The similar term Fenno-Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Fennoscandia. Both terms are sometimes used in Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sami Languages
Acronyms * SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft * Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company * South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise network of malaria researchers People * Samee, also spelled Sami, a male given name * Sami (name), including lists of people with the given name or surname * Sámi people, indigenous people of the Scandinavian Peninsula, the Kola Peninsula, Karelia and Finland ** Sámi cuisine ** Sámi languages, of the Sami people ** Sámi shamanism, a faith of the Sami people Places * Sápmi, a cultural region in Northern Europe * Sami (ancient city), in Elis, Greece * Sami Bay, east of Sami, Cephalonia * Sami District, Gambia * Sami, Burkina Faso, a district of the Banwa Province * Sami, Cephalonia, a municipality in Greece * Sami, Gujarat, a town in Patan district of Gujarat, India * Sami, Paletwa, a town in Chin State, Myanmar * Sämi, a village in L� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
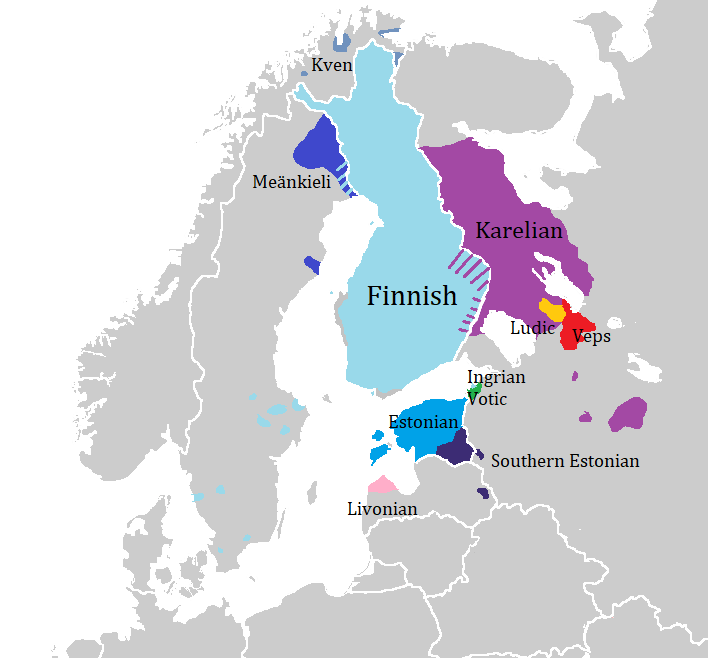
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)