|
Binary Compounds Of Hydrogen
Binary compounds of hydrogen are binary compound, binary chemical compounds containing just hydrogen and one other chemical element. By convention all binary hydrogen compounds are called hydrides even when the hydrogen atom in it is not an anion. These hydrogen compounds can be grouped into several types. Overview Binary hydrogen compounds in group 1 element, group 1 are the ionic hydrides (also called saline hydrides) wherein hydrogen is bound electrostatically. Because hydrogen is located somewhat centrally in an electronegative sense, it is necessary for the counterion to be exceptionally electropositive for the hydride to possibly be accurately described as truly behaving ionic. Therefore, this category of hydrides contains only a few members. Hydrides in group 2 element, group 2 are polymeric covalent hydrides. In these, hydrogen forms bridging covalent bonds, usually possessing mediocre degrees of ionic character, which make them difficult to be accurately described as either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Compound
In materials chemistry, a binary phase or binary compound is a chemical compound containing two different elements. Some binary phase compounds are molecular, e.g. carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). More typically binary phase refers to extended solids. Famous examples zinc sulfide, which contains zinc and sulfur, and tungsten carbide, which contains tungsten and carbon. Phases with higher degrees of complexity feature more elements, e.g. three elements in ternary phases, four elements in quaternary phase In materials chemistry, a quaternary phase is a chemical compound containing four elements. Some compounds can be molecular or ionic, examples being chlorodifluoromethane () sodium bicarbonate (). More typically quaternary phase refers to exten ...s. References Chemical compounds {{chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-block
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. The block names (s, p, d, and f) are derived from the spectroscopic notation for the value of an electron's azimuthal quantum number: sharp (0), principal (1), diffuse (2), or fundamental (3). Succeeding notations proceed in alphabetical order, as g, h, etc., though elements that would belong in such blocks have not yet been found. Characteristics There is an ''approximate'' correspondence between this nomenclature of blocks, based on electronic configuration, and sets of elements based on chemical properties. The s-block and p-block together are usually considered main-group elements, the d-block corresponds to the transition metals, and the f-block corresponds to the inner transiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium Hydride
Thallane (systematically named trihydridothallium) is an inorganic compound with the empirical chemical formula In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbol ... . It has not yet been obtained in bulk, hence its bulk properties remain unknown. However, molecular thallane has been isolated in solid gas matrices. Thallane is mainly produced for academic purposes. It is the simplest thallanes. Thallium is the heaviest member of the Group 13 metals; the stability of group 13 hydrides decreases with increasing periodic number. This is commonly attributed to poor overlap of the metal valence orbitals with that of the 1s orbital of Hydrogen. Despite encouraging early reports, it is unlikely that a thallane species has been isolated. Thallanes have been observed only in matrix isolation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 13 Hydride
Group 13 hydrides are chemical compounds containing group 13-hydrogen bonds (elements of group 13: boron, aluminium, gallium, indium, thallium). Trihydrides The simplest series has the chemical formula XH3, with X representing any of the boron family. The great variety of boranes show a huge covalent cluster chemistry, but the heavier group 13 hydrides do not. Despite their formulae, however, they tend to form polymers. Alane(aluminum trihydride) is a strong reducing agent with octahedrally coordinated aluminium atoms. Gallane is even harder to synthesise and decomposes to gallium and hydrogen at room temperature. Indigane and thallane are too unstable to exist for any significant time when not coordinated. Simple MH3 group 13 hydrides have a trigonal planar molecular geometry. This is due to the sp2 hybridized center and vacant p-orbital, and contrasts with the trigonal pyramidal geometry of the pnictogen hydrides which are sp3 hybridized and contain a non-bonding lone pair o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Hydride
Indium trihydride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (). It has been observed in matrix isolation and laser ablation experiments. Gas phase stability has been predicted. The infrared spectrum was obtained in the gas phase by laser ablation of indium in presence of hydrogen gas InH3 is of no practical importance. Chemical properties Solid InH3 is a three-dimensional network polymeric structure, where In atoms are connected by In-H-In bridging bonds, is suggested to account for the growth of broad infrared bands when samples of InH3 and InD3 produced on a solid hydrogen matrix are warmed. Such a structure is known for solid AlH3. When heated above , indium trihydride decomposes to produce indium–hydrogen alloy and elemental hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tastel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digallane
Digallane (systematically named digallane(6)) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (also written or ). It is the dimer of the monomeric compound gallane. The eventual preparation of the pure compound, reported in 1989, was hailed as a "tour de force." Digallane had been reported as early as 1941 by Wiberg; however, this claim could not be verified by later work by Greenwood and others. This compound is a colorless gas that decomposes above 0 °C. Preparation A two-stage approach proved to be the key to successful synthesis of pure digallane. Firstly the dimeric monochlorogallane, (H2GaCl)2 (containing bridging chlorine atoms and thus formulated as (H2Ga(μ-Cl))2) was prepared via the hydrogenation of gallium trichloride, GaCl3, with Me3SiH. This step was followed by a further reduction with LiGaH4, solvent free, at −23 °C, to produce digallane, Ga2H6 in low yield. :Ga2Cl6 + 4 Me3SiH → (H2GaCl)2 + 4 Me3SiCl :1/2 (H2GaCl)2 + LiGaH4 → Ga2H6 + LiCl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group (aluminium, indium, and thallium). Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal in standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If too much force is applied, the gallium may fracture conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates. The melting point of gallium is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. An even lower melting point of , well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
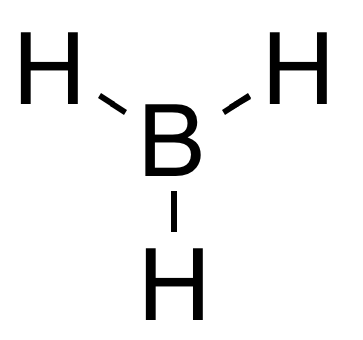
Diborane
Diborane(6), generally known as diborane, is the chemical compound with the formula B2H6. It is a toxic, colorless, and pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odor. Diborane is a key boron compound with a variety of applications. It has attracted wide attention for its electronic structure. Several of its derivatives are useful reagents. Structure and bonding The structure of diborane has D2h symmetry. Four hydrides are terminal, while two bridge between the boron centers. The lengths of the B–Hbridge bonds and the B–Hterminal bonds are 1.33 and 1.19 Å respectively. This difference in bond lengths reflects the difference in their strengths, the B–Hbridge bonds being relatively weaker. The weakness of the B–Hbridge compared to B–Hterminal bonds is indicated by their vibrational signatures in the infrared spectrum, being ≈2100 and 2500 cm−1 respectively. The model determined by molecular orbital theory describes the bonds between boron and the termina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia Borane
Ammonia borane (also systematically named amminetrihydridoboron), also called borazane, is the chemical compound with the formula H3NBH3. The colourless or white solid is the simplest molecular boron-nitrogen-hydride compound. It has attracted attention as a source of hydrogen fuel, but is otherwise primarily of academic interest. Synthesis Reaction of diborane with ammonia mainly gives the diammoniate salt 2B(NH3)2sup>+ (BH4)−. Ammonia borane is the main product when an adduct of borane is employed in place of diborane: :BH3(THF) + NH3 → BH3NH3 + THF Properties and structure The molecule adopts a structure similar to that of ethane, with which it is isoelectronic. The B−N distance is 1.58(2) Å. The B−H and N−H distances are 1.15 and 0.96 Å, respectively. Its similarity to ethane is tenuous since ammonia borane is a solid and ethane is a gas: their melting points differing by 284 °C. This difference is consistent with the highly polar natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral borax, sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Crust (geology), Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury(I) Hydride
Mercury(I) hydride (systematically named mercury hydride) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HgH. It has not yet been obtained in bulk, hence its bulk properties remain unknown. However, molecular mercury(I) hydrides with the formulae HgH and have been isolated in solid gas matrices. The molecular hydrides are very unstable toward thermal decomposition. As such the compound is not well characterised, although many of its properties have been calculated via computational chemistry. Molecular forms History In 1979 and 1985, Swiss chemical physicists, Egger and Gerber, and Soviet chemical physicists, Kolbycheva and Kolbychev, independently, theoretically determined that it is feasible to develop a mercury(I) hydride molecular laser. Chemical properties Mercury(I) hydride is an unstable gas and is the heaviest group 12 monohydride. n mercury(I) hydride, the formal oxidation states of hydrogen and mercury are −1 and +1, respectively, because of the electrone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Hydride
Cadmium hydride (systematically named cadmium dihydride) is an inorganic compound In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemist ... with the chemical formula (also written as or ). It is a solid, known only as a thermally unstable, insoluble white powder. Nomenclature The systematic name ''cadmium dihydride'', a valid IUPAC name, is constructed according to the compositional nomenclature. ''Cadmium dihydride'' is also used to refer to the related molecular compound ''dihydridocadmium'' and its oligomers. Care should be taken to avoid confusing the two compounds. ''Cadmium hydride'' is also used as a compositional IUPAC name for the compound with the chemical formula CdH. History In 1950 a research group led by Glenn D. Barbaras, synthesized cadmium hydride for the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |