|
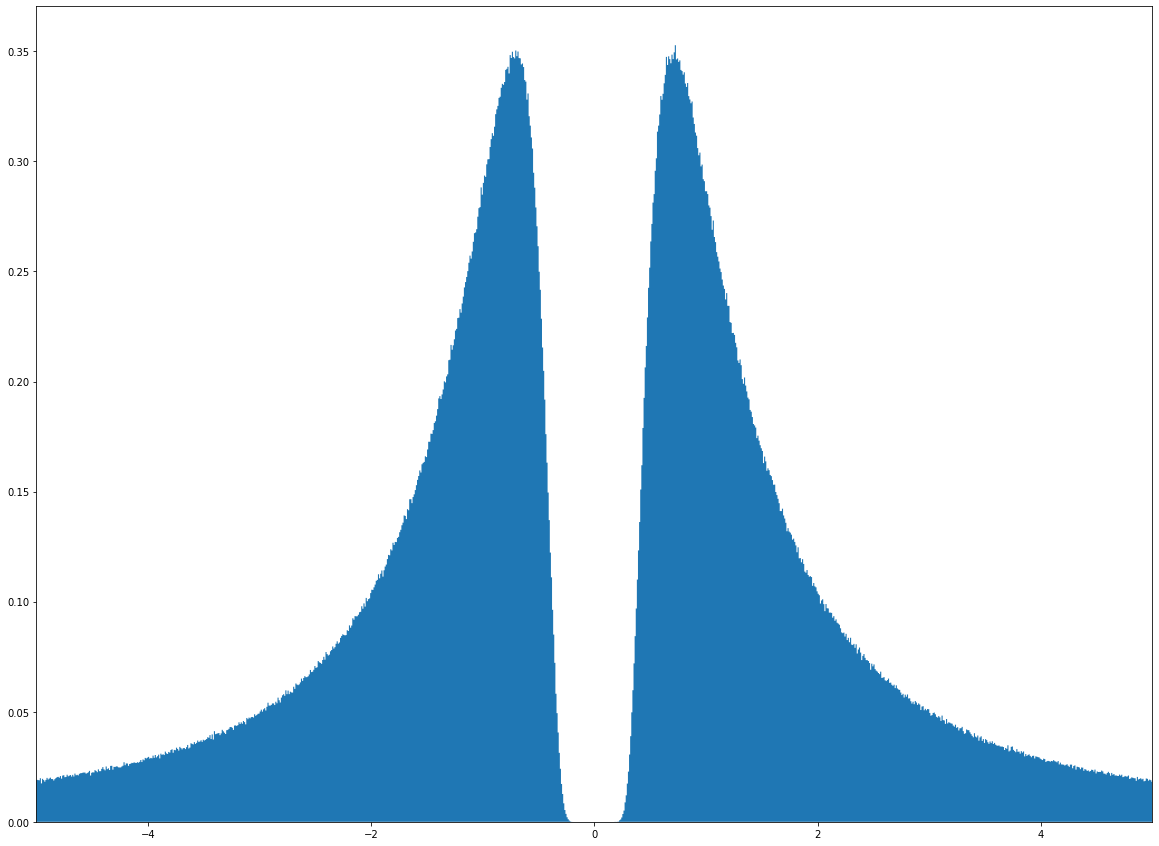
Bimodal
In statistics, a multimodal distribution is a probability distribution with more than one mode (i.e., more than one local peak of the distribution). These appear as distinct peaks (local maxima) in the probability density function, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. Categorical, continuous, and discrete data can all form multimodal distributions. Among univariate analyses, multimodal distributions are commonly bimodal. Terminology When the two modes are unequal the larger mode is known as the major mode and the other as the minor mode. The least frequent value between the modes is known as the antimode. The difference between the major and minor modes is known as the amplitude. In time series the major mode is called the acrophase and the antimode the batiphase. Galtung's classification Galtung introduced a classification system (AJUS) for distributions: *A: unimodal distribution – peak in the middle *J: unimodal – peak at either end *U: bimodal – peaks at both ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimodal Geological
In statistics, a multimodal distribution is a probability distribution with more than one mode (i.e., more than one local peak of the distribution). These appear as distinct peaks (local maxima) in the probability density function, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. Categorical, continuous, and discrete data can all form multimodal distributions. Among univariate analyses, multimodal distributions are commonly bimodal. Terminology When the two modes are unequal the larger mode is known as the major mode and the other as the minor mode. The least frequent value between the modes is known as the antimode. The difference between the major and minor modes is known as the amplitude. In time series the major mode is called the acrophase and the antimode the batiphase. Galtung's classification Galtung introduced a classification system (AJUS) for distributions: *A: unimodal distribution – peak in the middle *J: unimodal – peak at either end *U: bimodal – peaks at both ends * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the beta distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions defined on the interval [0, 1] or (0, 1) in terms of two positive Statistical parameter, parameters, denoted by ''alpha'' (''α'') and ''beta'' (''β''), that appear as exponents of the variable and its complement to 1, respectively, and control the shape parameter, shape of the distribution. The beta distribution has been applied to model the behavior of random variables limited to intervals of finite length in a wide variety of disciplines. The beta distribution is a suitable model for the random behavior of percentages and proportions. In Bayesian inference, the beta distribution is the conjugate prior distribution, conjugate prior probability distribution for the Bernoulli distribution, Bernoulli, binomial distribution, binomial, negative binomial distribution, negative binomial, and geometric distribution, geometric distributions. The formulation of the beta dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unimodal
In mathematics, unimodality means possessing a unique mode. More generally, unimodality means there is only a single highest value, somehow defined, of some mathematical object. Unimodal probability distribution In statistics, a unimodal probability distribution or unimodal distribution is a probability distribution which has a single peak. The term "mode" in this context refers to any peak of the distribution, not just to the strict definition of mode which is usual in statistics. If there is a single mode, the distribution function is called "unimodal". If it has more modes it is "bimodal" (2), "trimodal" (3), etc., or in general, "multimodal". Figure 1 illustrates normal distributions, which are unimodal. Other examples of unimodal distributions include Cauchy distribution, Student's ''t''-distribution, chi-squared distribution and exponential distribution. Among discrete distributions, the binomial distribution and Poisson distribution can be seen as unimodal, thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unimodal Nonmonotonic Distribution
In mathematics, unimodality means possessing a unique mode. More generally, unimodality means there is only a single highest value, somehow defined, of some mathematical object. Unimodal probability distribution In statistics, a unimodal probability distribution or unimodal distribution is a probability distribution which has a single peak. The term "mode" in this context refers to any peak of the distribution, not just to the strict definition of mode which is usual in statistics. If there is a single mode, the distribution function is called "unimodal". If it has more modes it is "bimodal" (2), "trimodal" (3), etc., or in general, "multimodal". Figure 1 illustrates normal distributions, which are unimodal. Other examples of unimodal distributions include Cauchy distribution, Student's ''t''-distribution, chi-squared distribution and exponential distribution. Among discrete distributions, the binomial distribution and Poisson distribution can be seen as unimodal, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems, but causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. This type is usually created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. If the orbital period of the system is a few days or less, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to draw accreted matter onto its surface, creating a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmosphere, mostly consisting of hydrogen, is heated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, an inverse distribution is the distribution of the multiplicative inverse, reciprocal of a random variable. Inverse distributions arise in particular in the Bayesian inference, Bayesian context of prior distributions and posterior distributions for scale parameters. In the algebra of random variables, inverse distributions are special cases of the class of ratio distributions, in which the numerator random variable has a degenerate distribution. Relation to original distribution In general, given the probability distribution of a random variable ''X'' with strictly positive support, it is possible to find the distribution of the reciprocal, ''Y'' = 1 / ''X''. If the distribution of ''X'' is Continuous probability distribution, continuous with Probability density function, density function ''f''(''x'') and cumulative distribution function ''F''(''x''), then the cumulative distribution function, ''G''(''y''), of the reciprocal is found by noting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaver Ant
Weaver ants or green ants are eusocial insects of the Hymenoptera family Formicidae belonging to the tribe Oecophyllini. Weaver ants live in trees (they are obligately arboreal) and are known for their unique nest building behaviour where workers construct nests by weaving together leaves using larval silk. Colonies can be extremely large consisting of more than a hundred nests spanning numerous trees and containing more than half a million workers. Like many other ant species, weaver ants prey on small insects and supplement their diet with carbohydrate-rich honeydew excreted by scale insects (Hemiptera). Weaver ant workers exhibit a clear bimodal size distribution, with almost no overlap between the size of the minor and major workers. The major workers are approximately in length and the minors approximately half the length of the majors. Major workers forage, defend, maintain, and expand the colony whereas minor workers tend to stay within the nests where they care for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, non-painful enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Persons affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying Reed–Sternberg cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-positive cases are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode (statistics)
In statistics, the mode is the value that appears most often in a set of data values. If is a discrete random variable, the mode is the value at which the probability mass function takes its maximum value (i.e., ). In other words, it is the value that is most likely to be sampled. Like the statistical mean and median, the mode is a way of expressing, in a (usually) single number, important information about a random variable or a population (statistics), population. The numerical value of the mode is the same as that of the mean and median in a normal distribution, and it may be very different in highly skewed distributions. The mode is not necessarily unique in a given discrete distribution since the probability mass function may take the same maximum value at several points , , etc. The most extreme case occurs in Uniform distribution (discrete), uniform distributions, where all values occur equally frequently. A mode of a continuous probability distribution is often conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U-quadratic Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the U-quadratic distribution is a continuous probability distribution defined by a unique convex quadratic function with lower limit ''a'' and upper limit ''b''. : f(x, a,b,\alpha, \beta)=\alpha \left ( x - \beta \right )^2, \quad\text x \in , b Parameter relations This distribution has effectively only two parameters ''a'', ''b'', as the other two are explicit functions of the support defined by the former two parameters: : \beta = (gravitational balance center, offset), and : \alpha = (vertical scale). Related distributions One can introduce a vertically inverted (\cap)-quadratic distribution in analogous fashion. That inverted distribution is also closely related to the Epanechnikov distribution. Applications This distribution is a useful model for symmetric bimodal processes. Other continuous distributions allow more flexibility, in terms of relaxing the symmetry and the quadratic shape of the density function, which are enforc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crepuscular
In zoology, a crepuscular animal is one that is active primarily during the twilight period, being matutinal (active during dawn), vespertine (biology), vespertine/vespertinal (active during dusk), or both. This is distinguished from diurnality, diurnal and nocturnality, nocturnal behavior, where an animal is active during the hours of daytime and of night, respectively. Some crepuscular animals may also be active by moonlight or during an overcast day. Matutinal animals are active only after dawn, and vespertine (biology), vespertine only before dusk. A number of factors affect the time of day an animal is active. Predation, Predators hunt when their prey is available, and prey try to avoid the times when their principal predators are at large. The temperature may be too high at midday or too low at night. Some creatures may adjust their activities depending on local competition. Etymology and usage The word ''crepuscular'' derives from the Latin ''wiktionary:crepusculum, cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |