|
Bicoid 3′-UTR Regulatory Element
The bicoid 3′-UTR regulatory element is an mRNA regulatory element that controls the gene expression of the bicoid protein in fruitfly ''Drosophila melanogaster''. The structured RNA element consists of four domains (denoted as II, III, IV and V) in the 3′UTR of the mRNA. It is essential for the correct transport and localisation of bicoid mRNA during oocyte and embryo differentiation, which has been studied most thoroughly in the development of ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (fruitfly) larva A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. ...e. References External links * {{Rfam, id=RF00551, name=Bicoid 3′-UTR regulatory element Cis-regulatory RNA elements Animal developmental biology Drosophila melanogaster genetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem-loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The resulting structure is a key building block of many RNA secondary structures. As an important secondary structure of RNA, it can direct RNA folding, protect structural stability for messenger RNA (mRNA), provide recognition sites for RNA binding proteins, and serve as a substrate for enzymatic reactions. Formation and stability The formation of a stem-loop structure is dependent on the stability of the resulting helix and loop regions. The first prerequisite is the presence of a sequence that can fold back on itself to form a paired double helix. The stability of this helix is determined by its length, the number of mismatches or bulges it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Prime Untranslated Region
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression. During gene expression, an mRNA molecule is transcribed from the DNA sequence and is later translated into a protein. Several regions of the mRNA molecule are not translated into a protein including the 5' cap, 5' untranslated region, 3′ untranslated region and poly(A) tail. Regulatory regions within the 3′-untranslated region can influence polyadenylation, translation efficiency, localization, and stability of the mRNA. The 3′-UTR contains both binding sites for regulatory proteins as well as microRNAs (miRNAs). By binding to specific sites within the 3′-UTR, miRNAs can decrease gene expression of various mRNAs by either inhibiting translation or directly causing degradation of the transcript. The 3� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-reg
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which gene regulation, regulate the transcription (genetics), transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryogenesis, embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes (pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulation of gene expression, regulate expression of nearby genes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecta
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory Element
A regulatory sequence is a segment of a nucleic acid molecule which is capable of increasing or decreasing the expression of specific genes within an organism. Regulation of gene expression is an essential feature of all living organisms and viruses. Description In DNA, regulation of gene expression normally happens at the level of RNA biosynthesis (transcription). It is accomplished through the sequence-specific binding of proteins (transcription factors) that activate or inhibit transcription. Transcription factors may act as activators, repressors, or both. Repressors often act by preventing RNA polymerase from forming a productive complex with the transcriptional initiation region ( promoter), while activators facilitate formation of a productive complex. Furthermore, DNA motifs have been shown to be predictive of epigenomic modifications, suggesting that transcription factors play a role in regulating the epigenome. In RNA, regulation may occur at the level of prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, ''D. melanogaster'' continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, five Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect. ''D. melanogaster'' is typically used in research owing to its rapid life cycle, relatively simple genetics with only four pairs of chromosomes, and large number of offspring per generation. It was originally an African species, with all non-African lineages having a common origin. Its geographic range includes all continents, including islands. ''D. melanogaster'' is a common pest in homes, restaurants, and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicoid
Homeotic protein bicoid is encoded by the ''bcd'' maternal effect gene in ''Drosophilia''. Homeotic protein bicoid concentration gradient patterns the anterior-posterior (A-P) axis during ''Drosophila'' embryogenesis. Bicoid was the first protein demonstrated to act as a morphogen. Although bicoid is important for the development of ''Drosophila'' and other higher dipterans, it is absent from most other insects, where its role is accomplished by other genes. Role in axial patterning ''Bicoid'' mRNA is actively localized to the anterior of the fruit fly egg during oogenesis along microtubules by the motor protein dynein, and retained there through association with cortical actin. Translation of ''bicoid'' is regulated by its 3′ UTR and begins after egg deposition. Diffusion and convection within the syncytium produce an exponential gradient of Bicoid protein within roughly one hour, after which Bicoid nuclear concentrations remain approximately constant through cellulariza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
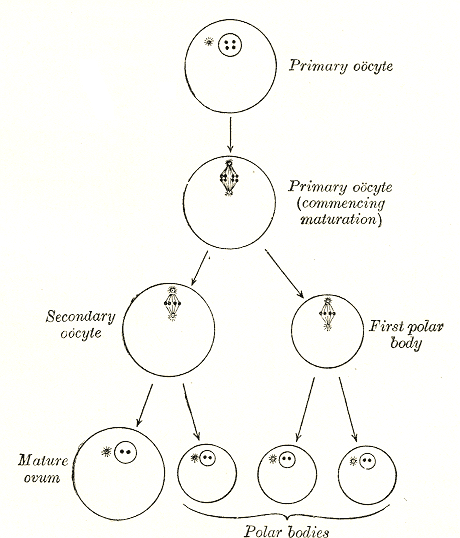
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramaticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |