Oocyte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an
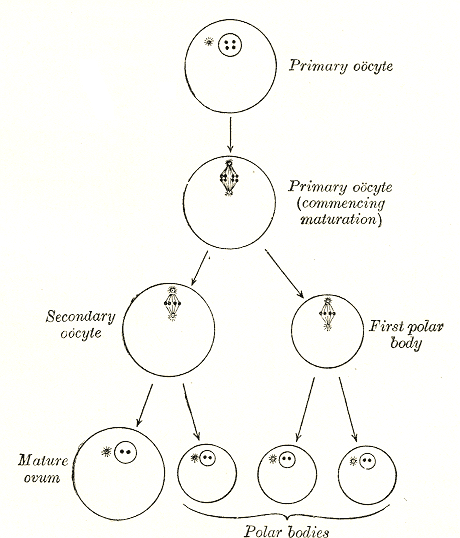 The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of
The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of
 Because the fate of an oocyte is to become fertilized and ultimately grow into a fully functioning organism, it must be ready to regulate multiple cellular and developmental processes. The oocyte, a large and complex cell, must be supplied with numerous molecules that will direct the growth of the embryo and control cellular activities. As the oocyte is a product of female
Because the fate of an oocyte is to become fertilized and ultimately grow into a fully functioning organism, it must be ready to regulate multiple cellular and developmental processes. The oocyte, a large and complex cell, must be supplied with numerous molecules that will direct the growth of the embryo and control cellular activities. As the oocyte is a product of female

immature ovum
An immature ovum is a cell that goes through the process of oogenesis to become an ovum. It can be an oogonium, an oocyte, or an ootid. An oocyte, in turn, can be either primary or secondary, depending on how far it has come in its process of me ...
, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation.
Formation
 The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of
The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilize ...
.
Characteristics
Cytoplasm
Oocytes are rich incytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development.
Nucleus
During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has the 23rd (sex) chromosome as 23,X (female-determining), whereas sperm can have 23,X (female-determining) or 23,Y (male-determining).Nest
The space within an ovum or immature ovum is located is the cell-nest.Cumulus-oocyte complex
The cumulus-oocyte complex contains layers of tightly packed cumulus cells surrounding the oocyte in the Graafian follicle. The oocyte is arrested in Meiosis II at the stage of metaphase II and is considered a secondary oocyte. Before ovulation, the cumulus complex goes through a structural change known as cumulus expansion. The granulosa cells transform from tightly compacted to an expanded mucoid matrix. Many studies show that cumulus expansion is critical for the maturation of the oocyte because the cumulus complex is the oocyte's direct communication with the developing follicle environment. It also plays a significant role in fertilization, though the mechanisms are not entirely known and are species specific.Maternal contributions
 Because the fate of an oocyte is to become fertilized and ultimately grow into a fully functioning organism, it must be ready to regulate multiple cellular and developmental processes. The oocyte, a large and complex cell, must be supplied with numerous molecules that will direct the growth of the embryo and control cellular activities. As the oocyte is a product of female
Because the fate of an oocyte is to become fertilized and ultimately grow into a fully functioning organism, it must be ready to regulate multiple cellular and developmental processes. The oocyte, a large and complex cell, must be supplied with numerous molecules that will direct the growth of the embryo and control cellular activities. As the oocyte is a product of female gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic di ...
, the maternal contribution to the oocyte and consequently the newly fertilized egg, is enormous. There are many types of molecules that are maternally supplied to the oocyte, which will direct various activities within the growing zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
.
Avoidance of damage to germ-line DNA
The DNA of a cell is vulnerable to the damaging effect of oxidative free radicals produced as byproducts of cellular metabolism. DNA damage occurring in oocytes, if not repaired, can be lethal and result in reduced fecundity and loss of potential progeny. Oocytes are substantially larger than the average somatic cell, and thus considerable metabolic activity is necessary for their provisioning. If this metabolic activity were carried out by the oocyte's metabolic machinery, the oocyte genome would be exposed to the reactive oxidative by-products generated. Thus it appears that a process evolved to avoid this vulnerability of germline DNA. It was proposed that, in order to avoid damage to the DNA genome of the oocytes, the metabolism contributing to the synthesis of much of the oocyte's constituents was shifted to other maternal cells that then transferred these constituents to oocytes. Thus, oocytes of many organisms are protected from oxidative DNA damage while storing up a large mass of substances to nurture the zygote in its initial embryonic growth.mRNAs and proteins
During the growth of the oocyte, a variety of maternally transcribed messenger RNAs, or mRNAs, are supplied by maternal cells. These mRNAs can be stored in mRNP (message ribonucleoprotein) complexes and be translated at specific time points, they can be localized within a specific region of the cytoplasm, or they can be homogeneously dispersed within the cytoplasm of the entire oocyte. Maternally loadedprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s can also be localized or ubiquitous throughout the cytoplasm. The translated products of the mRNAs and the loaded proteins have multiple functions; from regulation of cellular "house-keeping" such as cell cycle progression and cellular metabolism, to regulation of developmental processes such as fertilization, activation of zygotic transcription, and formation of body axes. Below are some examples of maternally inherited mRNAs and proteins found in the oocytes of the African clawed frog
The African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'', also known as the xenopus, African clawed toad, African claw-toed frog or the ''platanna'') is a species of African aquatic frog of the family Pipidae. Its name is derived from the three short claws o ...
.

Mitochondria
The oocyte receives mitochondria from maternal cells, which will go on to control embryonic metabolism and apoptotic events. The partitioning of mitochondria is carried out by a system of microtubules that will localize mitochondria throughout the oocyte. In certain organisms, such as mammals, paternal mitochondria brought to the oocyte by the spermatozoon are degraded through the attachment of ubiquitinated proteins. The destruction of paternal mitochondria ensures the strictly maternal inheritance of mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA.Nucleolus
In mammals, the nucleolus of the oocyte is derived solely from maternal cells. The nucleolus, a structure found within the nucleus, is the location where rRNA is transcribed and assembled into ribosomes. While the nucleolus is dense and inactive in a mature oocyte, it is required for proper development of the embryo.Ribosomes
Maternal cells also synthesize and contribute a store of ribosomes that are required for the translation of proteins before the zygotic genome is activated. In mammalian oocytes, maternally derived ribosomes and some mRNAs are stored in a structure called cytoplasmic lattices. These cytoplasmic lattices, a network of fibrils, protein, and RNAs, have been observed to increase in density as the number of ribosomes decrease within a growing oocyte.Prophase I arrest
Female mammals and birds are born possessing all the oocytes needed for future ovulations, and these oocytes are arrested at the prophase I stage ofmeiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately r ...
. In humans, as an example, oocytes are formed between three and four months of gestation within the fetus and are therefore present at birth. During this prophase I arrested stage ( dictyate), which may last for many years, four copies of the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
are present in the oocytes. The arrest of ooctyes at the four genome copy stage appears to provide the informational redundancy needed to repair damage in the DNA of the germline. The repair process used likely involves homologous recombinational repair. Prophase arrested oocytes have a high capability for efficient repair of DNA damages. DNA repair capability appears to be a key quality control mechanism in the female germ line and a critical determinant of fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
.
Paternal contributions
The spermatozoon that fertilizes an oocyte will contribute itspronucleus
A pronucleus () is the nucleus of a sperm or egg cell during the process of fertilization. The sperm cell becomes a pronucleus after the sperm enters the ovum, but before the genetic material of the sperm and egg fuse. Contrary to the sperm cell, ...
, the other half of the zygotic genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
. In some species, the spermatozoon will also contribute a centriole, which will help make up the zygotic centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle prog ...
required for the first division. However, in some species, such as in the mouse, the entire centrosome is acquired maternally. Currently under investigation is the possibility of other cytoplasmic contributions made to the embryo by the spermatozoon.
During fertilization, the sperm provides three essential parts to the oocyte: (1) a signalling or activating factor, which causes the metabolically dormant oocyte to activate; (2) the haploid paternal genome; (3) the centrosome, which is responsible for maintaining the microtubule system. See anatomy of sperm
Abnormalities
* Nondisjunction—a failure of proper homolog separation in meiosis I, or sister chromatid separation in meiosis II can lead toaneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any ...
, in which the oocyte has the wrong number of chromosomes, for example 22,X or 24,X. This is the cause of conditions like Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual dis ...
and Edwards syndrome
Edwards syndrome, also known as trisomy 18, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features inc ...
in humans. It is more likely with advanced maternal age
Advanced maternal age, in a broad sense, is the instance of a woman being of an older age at a stage of reproduction, although there are various definitions of specific age and stage of reproduction.nuclei, although it is thought they never mature.
Micrograph of a primary oocyte and follicle of a monkey
{{s-end Germ cells de:Eizelle
See also
*Cortical granule
Cortical granules are regulatory secretory organelles (ranging from 0.2 um to 0.6 um in diameter) found within oocytes and are most associated with polyspermy prevention after the event of fertilization. Cortical granules are found among ...
* Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources
Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources is a strategy wherein samples of animal genetic materials are preserved cryogenically."Cryoconservation of Animal Genetic Resources", Rep. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, ...
* Folliculogenesis
:''Although the process is similar in many animals, this article will deal exclusively with human folliculogenesis.''
In biology, folliculogenesis is the maturation of the ovarian follicle, a densely packed shell of somatic cells that contains a ...
* Oocyte maturation inhibitor
* Polar body
A polar body is a small haploid cell that is formed at the same time as an egg cell during oogenesis, but generally does not have the ability to be fertilized. It is named from its polar position in the egg.
When certain diploid cells in animals ...
* Symmetry breaking and cortical rotation
Symmetry breaking in biology is the process by which uniformity is broken, or the number of points to view invariance are reduced, to generate a more structured and improbable state. That is to say, symmetry breaking is the event where symmetry ...
* Oocyte abnormalities
References
Sources
*External links
Micrograph of a primary oocyte and follicle of a monkey
{{s-end Germ cells de:Eizelle