|
Cis-reg
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which gene regulation, regulate the transcription (genetics), transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryogenesis, embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes (pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulation of gene expression, regulate expression of nearby genes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhancer (genetics)
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins ( activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcription factors. Enhancers are ''cis''-acting. They can be located up to 1 Mbp (1,000,000 bp) away from the gene, upstream or downstream from the start site. There are hundreds of thousands of enhancers in the human genome. They are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The first discovery of a eukaryotic enhancer was in the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene in 1983. This enhancer, located in the large intron, provided an explanation for the transcriptional activation of rearranged Vh gene promoters while unrearranged Vh promoters remained inactive. Locations In eukaryotic cells the structure of the chromatin complex of DNA is folded in a way that functionally mimics the supercoiled state characteristic of prokaryotic DNA, so although the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhancers
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins ( activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcription factors. Enhancers are ''cis''-acting. They can be located up to 1 Mbp (1,000,000 bp) away from the gene, upstream or downstream from the start site. There are hundreds of thousands of enhancers in the human genome. They are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The first discovery of a eukaryotic enhancer was in the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene in 1983. This enhancer, located in the large intron, provided an explanation for the transcriptional activation of rearranged Vh gene promoters while unrearranged Vh promoters remained inactive. Locations In eukaryotic cells the structure of the chromatin complex of DNA is folded in a way that functionally mimics the supercoiled state characteristic of prokaryotic DNA, so although the enh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
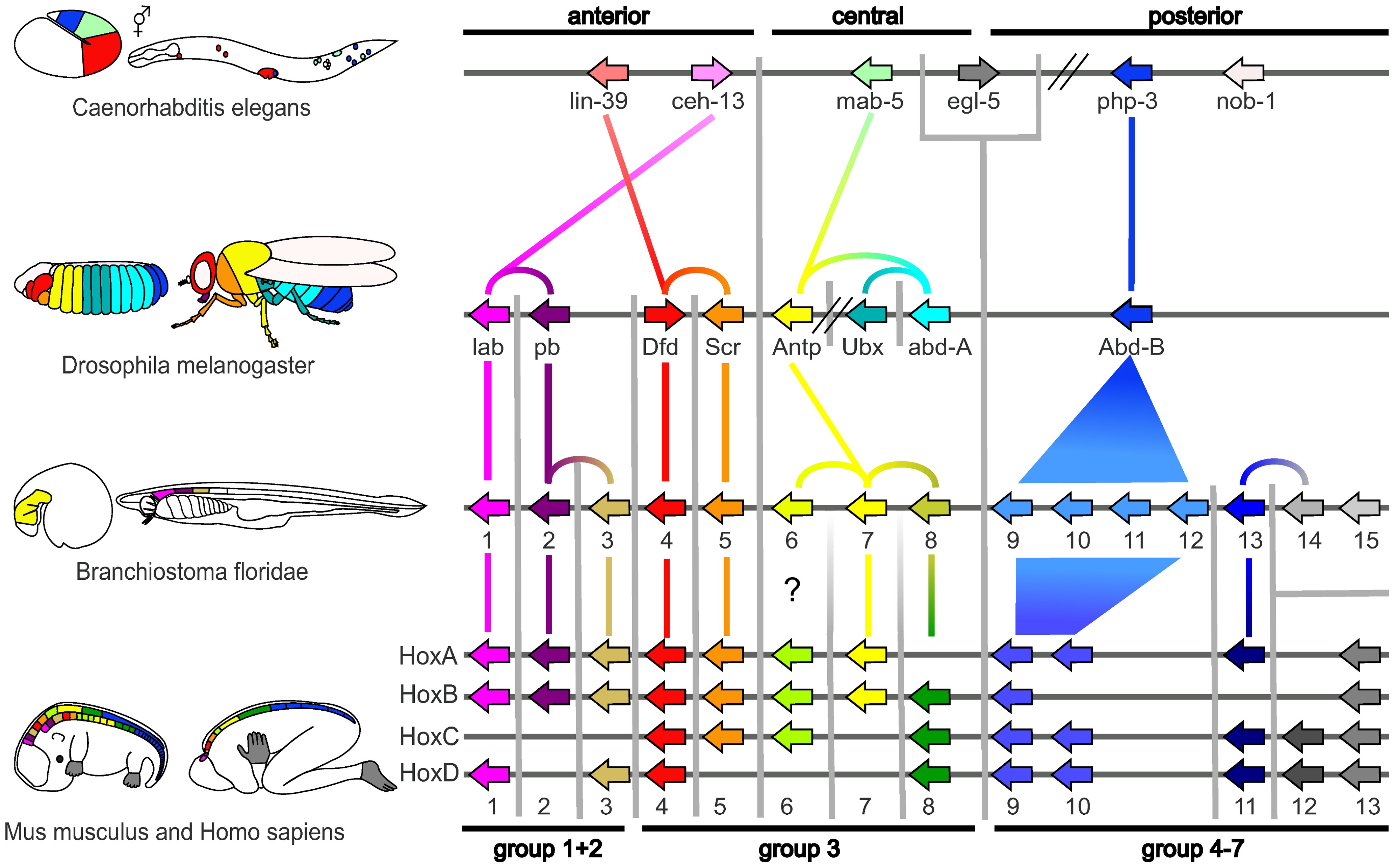
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoologists did not know how embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are controlled by similar genes such as ''pax-6'', from the evo-devo gene toolk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-regulatory Element
Trans-regulatory elements (TRE) are DNA sequences encoding upstream regulators (ie. trans-acting factors), which may modify or Regulation of gene expression, regulate the expression of distant genes. Trans-acting factors interact with Cis-regulatory element, cis-regulatory elements to regulate gene expression. TRE mediates expression profiles of a large number of genes via trans-acting factors. While TRE mutations affect gene expression, it is also one of the main driving factors for evolutionary divergence in gene expression. Trans vs cis elements Trans-regulatory elements work through an Intermolecular force, intermolecular interaction between two different molecules and so are said to be "Trans-acting, acting in trans". For example (1) a Transcription (genetics), transcribed and Translation (biology), translated transcription factor protein derived from the trans-regulatory element; and a (2) DNA Regulatory sequence, regulatory element that is adjacent to the regulated gene. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Regulatory Networks
A gene (or genetic) regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of molecular regulators that interact with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins which, in turn, determine the function of the cell. GRN also play a central role in morphogenesis, the creation of body structures, which in turn is central to evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo). The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein or any combination of two or more of these three that form a complex, such as a specific sequence of DNA and a transcription factor to activate that sequence. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through transcribed RNA or translated protein). In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promoter (biology)
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism. Promoters control gene expression in bacteria and eukaryotes. RNA polymerase must attach to DNA near a gene for transcription to occur. Promoter DNA sequences provide an enzyme binding site. The -10 sequence is TATAAT. -35 sequences are conserved on average, but not in most promoters. Artificial promoters with conserved -10 and -35 elements transcribe more slowly. All D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism. Promoters control gene expression in bacteria and eukaryotes. RNA polymerase must attach to DNA near a gene for transcription to occur. Promoter DNA sequences provide an enzyme binding site. The -10 sequence is TATAAT. -35 sequences are conserved on average, but not in most promoters. Artificial promoters with conserved -10 and -35 elements transcribe more slowly. All D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulator (genetics)
An insulator is a type of cis-regulatory element known as a long-range regulatory element. Found in multicellular eukaryotes and working over distances from the promoter element of the target gene, an insulator is typically 300 bp to 2000 bp in length. Insulators contain clustered binding sites for sequence specific DNA-binding proteins and mediate intra- and inter-chromosomal interactions. Insulators function either as an enhancer-blocker or a barrier, or both. The mechanisms by which an insulator performs these two functions include loop formation and nucleosome modifications. There are many examples of insulators, including the CTCF insulator, the ''gypsy'' insulator, and the β-globin locus. The CTCF insulator is especially important in vertebrates, while the ''gypsy'' insulator is implicated in ''Drosophila.'' The β-globin locus was first studied in chicken and then in humans for its insulator activity, both of which utilize CTCF. The genetic implications of insulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulator Gene
A regulator gene, regulator, or regulatory gene is a gene involved in controlling the expression of one or more other genes. Regulatory sequences, which encode regulatory genes, are often at the five prime end (5') to the start site of transcription of the gene they regulate. In addition, these sequences can also be found at the three prime end (3') to the transcription start site. In both cases, whether the regulatory sequence occurs before (5') or after (3') the gene it regulates, the sequence is often many kilobases away from the transcription start site. A regulator gene may encode a protein, or it may work at the level of RNA, as in the case of genes encoding microRNAs. An example of a regulator gene is a gene that codes for a repressor protein that inhibits the activity of an operator (a gene which binds repressor proteins thus inhibiting the translation of RNA to protein via RNA polymerase). In prokaryotes, regulator genes often code for repressor proteins. Repressor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy (from Greek , 'more', and , 'way') occurs when one gene influences two or more seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits. Such a gene that exhibits multiple phenotypic expression is called a pleiotropic gene. Mutation in a pleiotropic gene may have an effect on several traits simultaneously, due to the gene coding for a product used by a myriad of cells or different targets that have the same signaling function. Pleiotropy can arise from several distinct but potentially overlapping mechanisms, such as gene pleiotropy, developmental pleiotropy, and selectional pleiotropy. Gene pleiotropy occurs when a gene product interacts with multiple other proteins or catalyzes multiple reactions. Developmental pleiotropy occurs when mutations have multiple effects on the resulting phenotype. Selectional pleiotropy occurs when the resulting phenotype has many effects on fitness (depending on factors such as age and gender). An example of pleiotropy is phenylketonuria, an inherited d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory Elements
A regulatory sequence is a segment of a nucleic acid molecule which is capable of increasing or decreasing the expression of specific genes within an organism. Regulation of gene expression is an essential feature of all living organisms and viruses. Description In DNA, regulation of gene expression normally happens at the level of RNA biosynthesis (transcription). It is accomplished through the sequence-specific binding of proteins (transcription factors) that activate or inhibit transcription. Transcription factors may act as activators, repressors, or both. Repressors often act by preventing RNA polymerase from forming a productive complex with the transcriptional initiation region ( promoter), while activators facilitate formation of a productive complex. Furthermore, DNA motifs have been shown to be predictive of epigenomic modifications, suggesting that transcription factors play a role in regulating the epigenome. In RNA, regulation may occur at the level of protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |