|
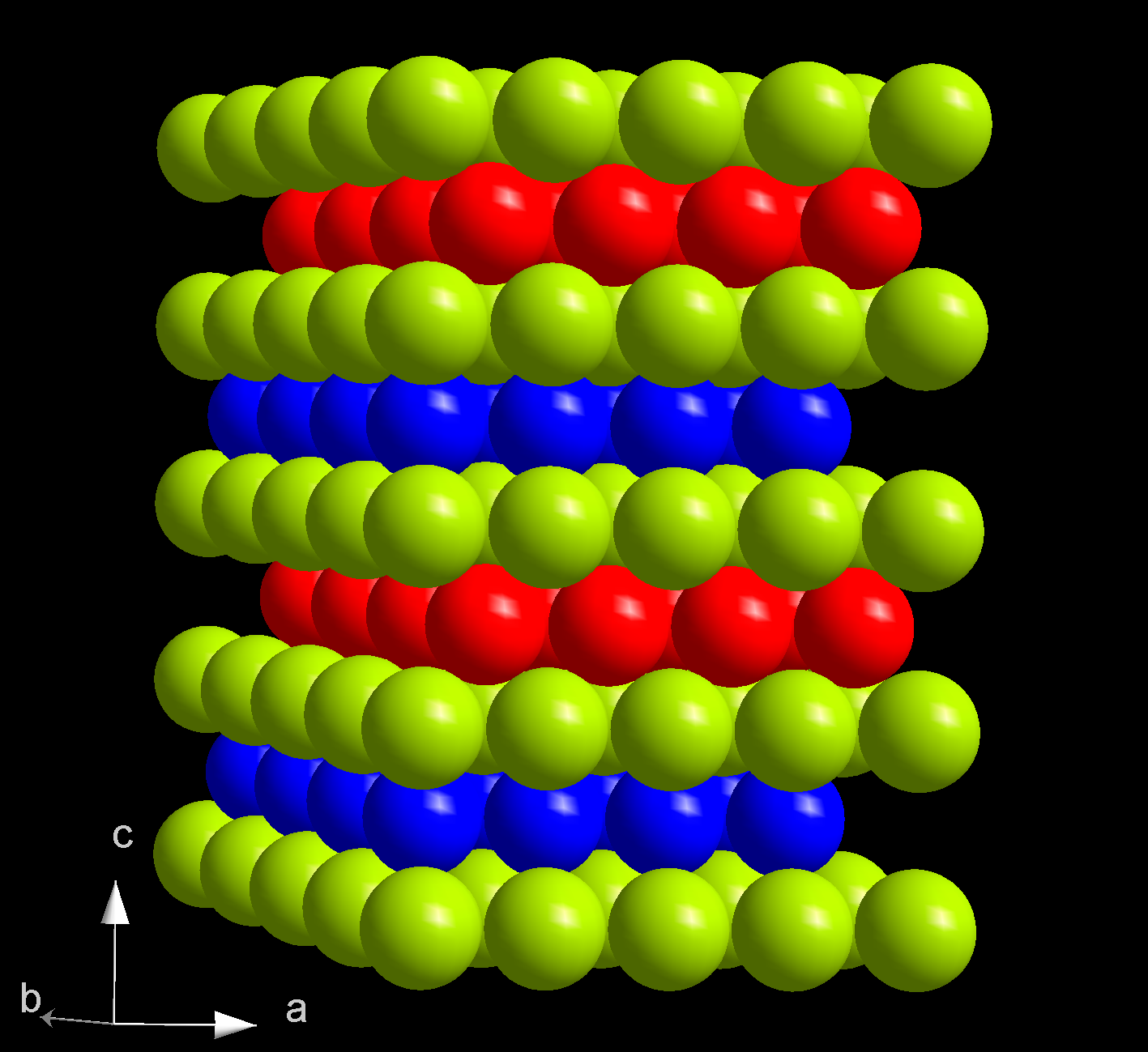
Berkelium Tetrafluoride
Berkelium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and fluorine with the chemical formula . Synthesis Berkelium tetrafluoride may be formed by the fluorination of berkelium trioxide, dioxide, or trifluoride with elemental fluorine at elevated temperatures: :: :: Physical properties Berkelium(IV) fluoride forms light brown crystals of monoclinic crystal structure of uranium tetrafluoride type. Cell parameters: a = 1.2396 nm, b = 1.0466 nm, c = 0.8118 nm, angle β = 126.33°. Chemical properties Berkelium tetrafluoride is reduced by lithium Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ... at elevated temperatures to metallic berkelium: :: References {{Actinide halides Fluorides Berkelium compounds Actinide halides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curium(III) Fluoride
Curium(III) fluoride or curium trifluoride is the chemical compound composed of curium and fluorine with the formula CmF3. It is a white, nearly insoluble salt that has the same crystal structure as LaF3. It precipitates as a hydrate when fluoride ions are added to a weakly acidic Cm(III) solution; alternatively it can be synthesized by reacting hydrofluoric acid with Cm(OH)3. The anhydrous form is then obtained by desiccation or by treatment with hydrogen fluoride Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock i ... gas. References Curium compounds Fluorides {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkelium Trifluoride
Berkelium(III) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and fluorine with the chemical formula . Synthesis The compound can be prepared by treating with a gaseous mixture of and HF at 600 °C. Physical properties Berkelium trifluoride forms a yellow-green solid with two structures. At low temperature, it is orthorhombic ( structure), with lattice parameters a = 670 pm, b = 709 pm, and c = 441 pm. At high temperature, it is trigonal ( structure), with lattice parameters a = 697 pm and c = 714 pm. The transition temperature of is between 350 and 600 °C. Chemical properties Berkelium trifluoride is reduced by lithium Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ... to obtain metallic berkelium: :: References {{Actinide halides Fluorides Berkeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkelium
Berkelium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (then the University of California Radiation Laboratory) where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium. The major isotope of berkelium, 249Bk, is synthesized in minute quantities in dedicated high-flux nuclear reactors, mainly at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee, United States, and at the Research Institute of Atomic Reactors in Dimitrovgrad, Russia. The production of the second-most important isotope, 247Bk, involves the irradiation of the rare isotope 244Cm with high-energy alpha particles. Just over one gram of berkelium has been produced in the United States since 1967. There is no practical appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reactive, as it reacts with all other elements except for the light inert gases. Among the elements, fluorine ranks 24th in universal abundance and 13th in terrestrial abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning 'flow' gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist Henri Moissan isolate elemental fluorine using low-temperature electrolysis, a process still employed for modern pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Education
The ''Journal of Chemical Education'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal available in both print and electronic versions. It is published by the Division of Chemical Education of the American Chemical Society and was established in 1924 by Neil Gordon. The journal covers research on chemical education Chemistry education (or chemical education) is the study of teaching and learning chemistry. It is one subset of STEM education or discipline-based education research (DBER). Topics in chemistry education include understanding how students learn ..., and its target audience includes instructors of chemistry from middle school through graduate school and some scientists in commerce, industry, and government. References External links * Chemical education journals American Chemical Society academic journals Monthly journals Publications established in 1924 English-language journals {{chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkelium(III) Oxide
Berkelium(III) oxide is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and oxygen with the chemical formula . Synthesis Berkelium(III) oxide can be prepared from berkelium(IV) oxide by reduction with hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...: :: Physical properties The compound forms a yellow-green solid with a melting point of 1920 °C. It forms a body-centered cubic crystal lattice with a = 1088.0 ± 0.5 pm. Insoluble in water. References Oxides Berkelium compounds {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Tetrafluoride
Uranium tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula UF4. It is a green solid with an insignificant vapor pressure and low solubility in water. Uranium in its tetravalent (uranous) state is important in various technological processes. In the uranium refining industry it is known as green salt. Production UF4 is prepared from UO2 in a fluidized bed by reaction with HF. The UO2 is derived from mining operations. Around 60,000 tonnes per year are prepared in this way annually. A common impurity is UO2F2. UF4 is susceptible to hydrolysis as well. UF4 is formed by the reaction of UF6 with hydrogen gas in a vertical tube-type reactor. UF4 is less stable than the uranium oxides and reacts slowly with moisture at ambient temperature, forming UO2 and HF, the latter of which is very corrosive and toxic; it is thus less favourable for long-term disposal. The bulk density of UF4 varies from about 2.0 g/cm3 to about 4.5 g/cm3 depending on the production process and the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Chemistry (journal)
''Inorganic Chemistry'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society since 1962. It covers research in all areas of inorganic chemistry. The current editor-in-chief is William B. Tolman (Washington University). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 5.436. See also * ''Organometallics ''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is organometallic and organometalloid chemistry. This peer-reviewed journal has an impact factor of 3.837 as reported by the 2021 Journal Cit ...'' References External links * American Chemical Society academic journals Biweekly journals Publications established in 1962 English-language journals Inorganic chemistry journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic And Nuclear Chemistry Letters
''Polyhedron'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of inorganic chemistry. It was established in 1955 as the ''Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry'' and is published by Elsevier. Abstracting and indexing ''Polyhedron'' is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 3.052. References External links * {{Official Website, http://www.journals.elsevier.com/polyhedron/ Inorganic chemistry journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1955 English-language journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds, such as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The nucleus of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotopes foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier
Elsevier () is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', the '' Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services also include digital tools for data management, instruction, research analytics and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group (known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier), a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2021 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,700 journals; as of 2018 its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 e-books, with over one billion annual downloads. Researchers have criticized Elsevier for its high profit marg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |