|
Benzocyclobutene
Benzocyclobutene (BCB) is a benzene ring fused to a cyclobutane ring. It has chemical formula . BCB is frequently used to create photosensitive polymers. BCB-based polymer dielectrics may be spun on or applied to various substrates for use in Micro Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) and microelectronics processing. Applications include wafer bonding, optical interconnects, low-κ dielectrics, or even intracortical neural implants. Reactions Benzocyclobutene is a strained system which, upon heating to approximately 180 °C, causes the cyclobutene to undergo a conrotatory ring-opening reaction, forming ''o''-xylylene. Since this process destroys the aromaticity of the benzene ring, the reverse reaction is highly favored. ''o''-Xylylenes generated in this way have been used prolifically in cycloaddition reactions, which restore the aromaticity to the benzene ring, while forming a new annulated species. Uses The benzocyclobutene moiety has also appeared in a number of chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
S33005
S33005 is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) that was under development by Servier for the treatment of depression and related disorders. It is structurally related to venlafaxine but has a more complex molecular structure. Venlafaxine appears to be a sigma modulator, but it is not known if S33005 shares this activity. Synthesis "The 1-cyano-benzocyclobutenes used as starting material are obtained, for example, by subjecting a β- rthohalogeno-phenylpropionitrile to intramolecular condensation in the presence of potassium amide, or by brominating a benzocyclobutene in position 1 with ''N''-bromosuccinimide, followed by exchange of the bromine atom for a cyano group by means of sodium cyanide." See also * Milnacipran Milnacipran (trade names Ixel, Savella, Dalcipran, Toledomin) is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) used in the clinical treatment of fibromyalgia, Major depressive disorder, and Neuropathic pain. In the US, it is solel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
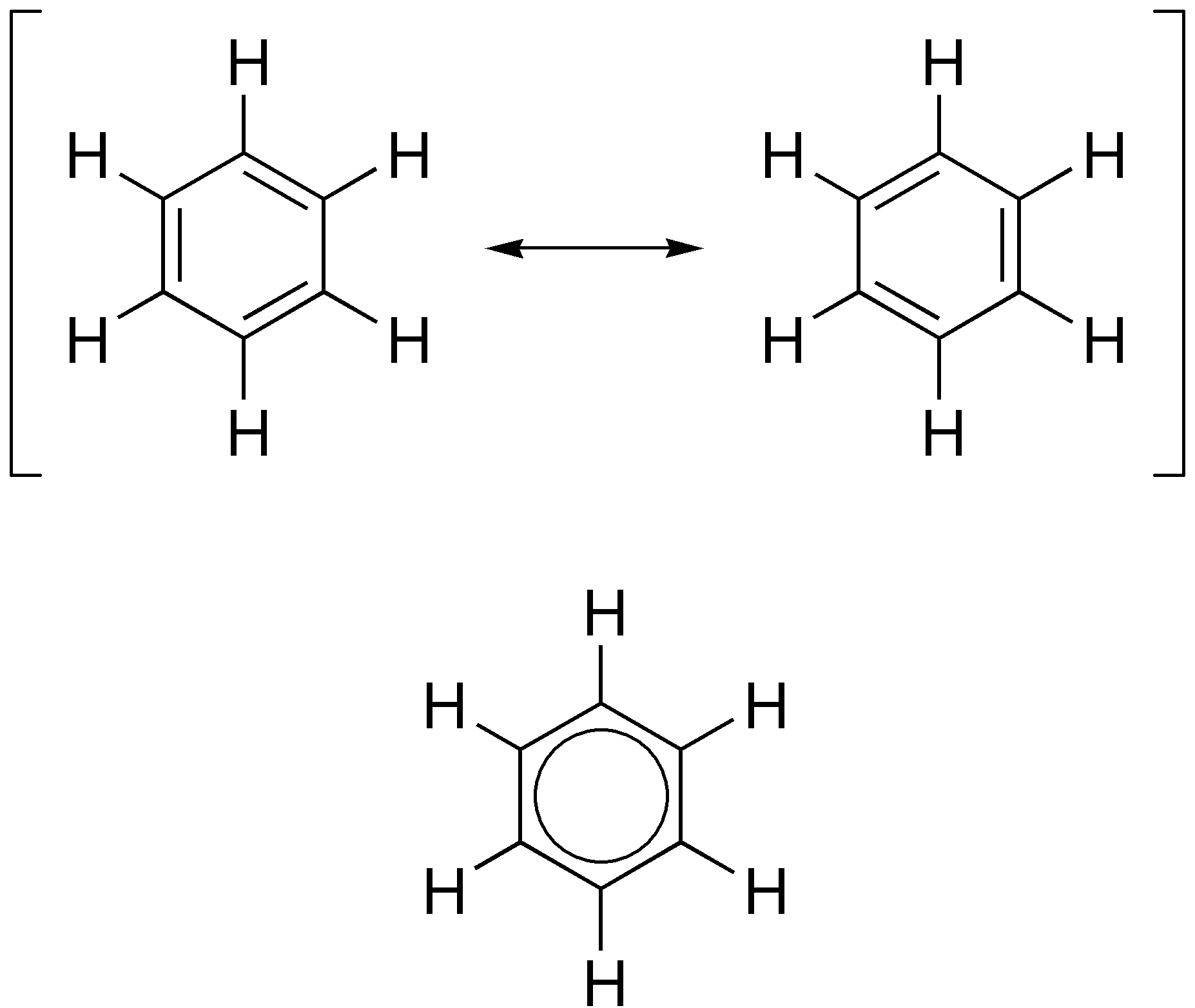
O-xylylene
In organic chemistry, a xylylene (sometimes quinone-dimethide) is any of the constitutional isomers having the formula C6H4(CH2)2. These compounds are related to the corresponding quinones and quinone methides by replacement of the oxygen atoms by CH2 groups. Arene substitution patterns, ''ortho''- and ''para''-xylylene are best known, although neither is stable in solid or liquid form. The ''meta'' form is a diradical. Certain substituted derivatives of xylylenes are however highly stable, such as tetracyanoquinodimethane and the xylylene dichlorides. p-Xylylene ''p''-Xylylene forms upon pyrolysis of ''p''-xylene or, more readily, the α-substituted derivatives. ''p''-Xylylene Dimer (chemistry), dimerizes with moderate efficiency to give ''p''-cyclophane: Further heating of the ''p''-cyclophane gives Parylene, poly(''para''-xylylene). o-Xylylenes o-Xylylenes (''o''-quinodimethanes) are often generated in situ, e.g., by the pyrolysis of the corresponding sulfone. Another met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Benzocyclobutadiene
Benzocyclobutadiene is the simplest polycyclic hydrocarbon, being composed of an aromatic benzene ring fused to an anti-aromatic cyclobutadiene ring. It has chemical formula . Though the benzene ring is stabilized by aromaticity, the cyclobutadiene portion has a destabilizing effect. This results into it being a non-aromatic compound - neither behaving as aromatic nor an antiaromatic one. For this reason, benzocyclobutadiene will readily dimerize or polymerize and it reacts as a dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. Benzocyclobutadiene is used in the production of the pharmaceutical drug naflocort. See also *Pentalene Pentalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon composed of two fused cyclopentadiene rings. It has chemical formula . It is antiaromatic, because it has 4''n'' π electrons where ''n'' is any integer. For this reason it dimerizes even at temperatures a ... References {{reflist Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons Bicyclic compounds Four-membered rings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Low-κ Dielectric
In semiconductor manufacturing, a low-κ is a material with a small relative dielectric constant (κ, kappa) relative to silicon dioxide. Low-κ dielectric material implementation is one of several strategies used to allow continued scaling of microelectronic devices, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's law. In digital circuits, insulating dielectrics separate the conducting parts (wire interconnects and transistors) from one another. As components have scaled and transistors have gotten closer together, the insulating dielectrics have thinned to the point where charge build up and crosstalk adversely affect the performance of the device. Replacing the silicon dioxide with a low-κ dielectric of the same thickness reduces parasitic capacitance, enabling faster switching speeds (in case of synchronous circuits) and lower heat dissipation. In conversation such materials may be referred to as "low-k" (spoken "low-kay") rather than "low-κ" (low-kappa). Low-κ materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity; it is also used to treat binge eating disorder in the form of its inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. ''Amphetamine'' properly refers to a specific chemical, the Racemic mixture, racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an Performance-enhancing substance, athletic performance enhancer and Nootropic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
2C-B
2C-B, also known as 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine or by the slang name Nexus, is a synthetic psychedelic drug of the 2C family, mainly used as a recreational drug. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1974 for use in psychotherapy. To date, there is limited scientific information regarding the drug's pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects in humans. The existing studies primarily classify 2C-B as a stimulant and hallucinogen, and less commonly an entactogen. 2C-B is also known by a number of slang names and appears on the illicit market in multiple forms: as a powder, in capsules or pills. For recreational use, the substance is generally consumed orally or nasally. Use Recreational 2C-B became briefly popular in the United States as substitute for the street drug ecstasy (MDMA) when the latter became illegal in 1985. Many 2C-B users are young adults who attend raves. Although 2C-B is still used in the rave subculture (commonly mistaken for and/o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Structural Analog
A structural analog, also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a chemical compound, compound having a chemical structure, structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronicity, isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analog (chemistry), functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is virtual screening, screened for structural analogs of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ivabradine
Ivabradine, sold under the brand name Procoralan among others, is a medication, which is a pacemaker current (I''f'') inhibitor, used for the symptomatic management of heart-related chest pain and heart failure. Patients who qualify for use of ivabradine for congestive heart failure are patients who have symptomatic heart failure, with reduced ejection fraction, and heart rate at least 70 bpm, and the condition not able to be fully managed by beta blockers. Ivabradine acts by allowing negative chronotropy in the sinoatrial structure, thus reducing the heart rate via specific inhibition of the pacemaker current. It operates by a mechanism different from that of beta blockers and calcium channel blockers, which are two commonly prescribed antianginal classes of cardiac drugs. Ivabradine has no apparent inotropic properties and may be a cardiotonic agent. Medical uses It is used for the symptomatic treatment of chronic stable angina pectoris in patients with normal sinus rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Annulation
In organic chemistry, annulation (; occasionally annelation) is a chemical reaction in which a new ring is constructed on a molecule. : Examples are the Robinson annulation, Danheiser annulation and certain cycloadditions. Annular molecules are constructed from side-on condensed cyclic segments, for example helicenes and acenes. In transannulation a bicyclic molecule is created by intramolecular carbon-carbon bond formation in a large monocyclic ring. An example is the samarium(II) iodide induced ketone - alkene cyclization of ''5-methylenecyclooctanone'' which proceeds through a ketyl intermediate: : Benzannulation The term benzannulated compounds refers to derivatives of cyclic compounds (usually aromatic) which are fused to a benzene Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cycloaddition Reaction
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity". The resulting reaction is a cyclization reaction. Many but not all cycloadditions are concerted and thus pericyclic. Nonconcerted cycloadditions are not pericyclic. As a class of addition reaction In organic chemistry, an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecule A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, ..., cycloadditions permit carbon–carbon bond formation without the use of a nucleophile or electrophile. Cycloadditions can be described using two systems of notation. An older but still common notation is based on the size of linear arrangements of atoms in the reactants. It uses parentheses: whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |