|
Bengal Fur Society
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predominantly covering present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal. Geographically, it consists of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta system, the largest river delta in the world and a section of the Himalayas up to Nepal and Bhutan. Dense woodlands, including hilly rainforests, cover Bengal's northern and eastern areas, while an elevated forested plateau covers its central area; the highest point is at Sandakphu. In the littoral southwest are the Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest. The region has a monsoon climate, which the Bengali calendar divides into six seasons. Bengal, then known as Gangaridai, was a leading power in ancient South Asia, with extensive trade networks forming connections to as far away as Roman Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
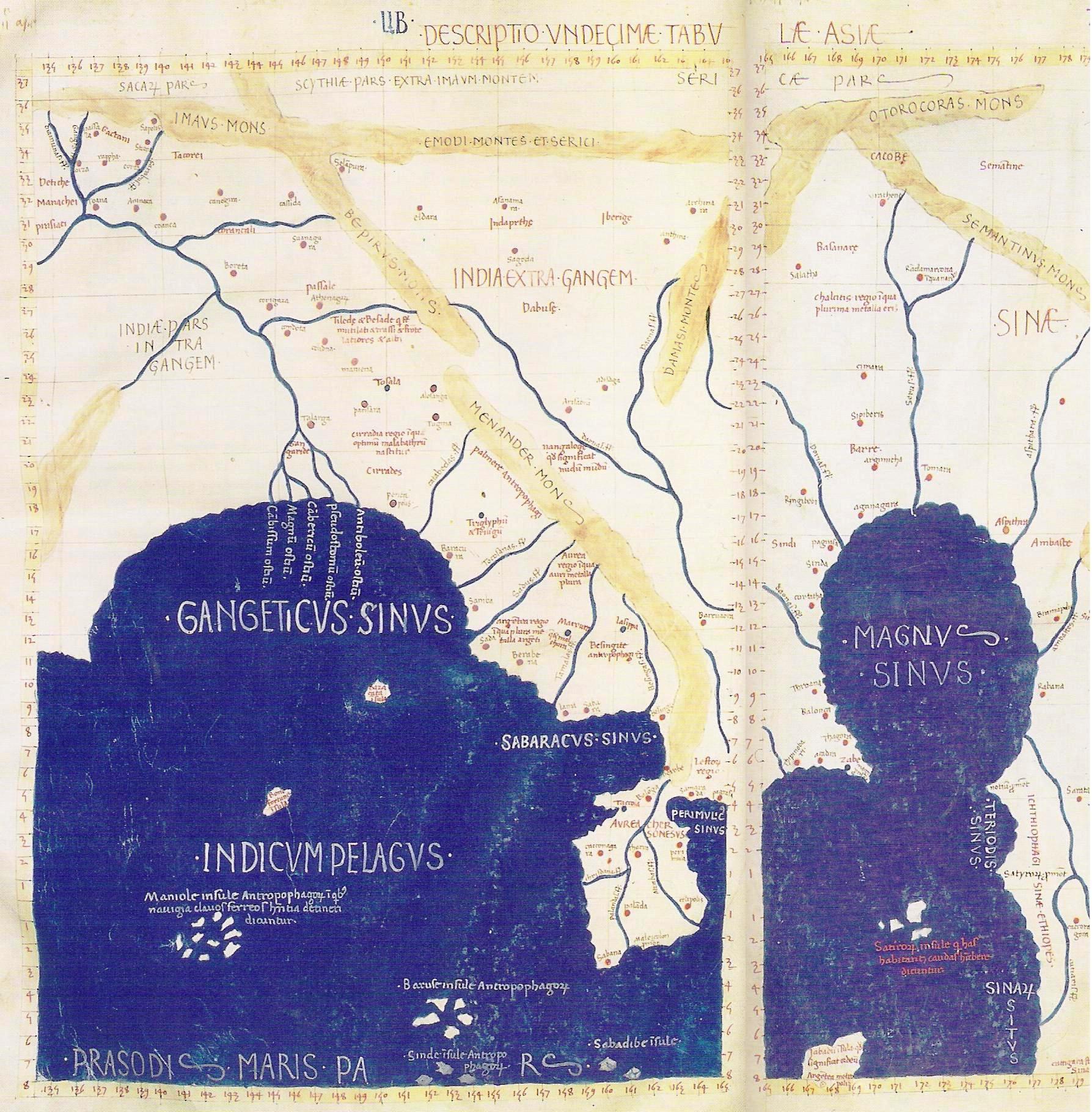
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age India
In the prehistory of the Indian subcontinent, the Iron Age succeeded Bronze Age India and partly corresponds with the megalithic cultures of India. Other Iron Age archaeological cultures of India were the Painted Grey Ware culture (1300–300 BCE) and the Northern Black Polished Ware (700–200 BCE). This corresponds to the transition of the Janapadas or principalities of the Vedic period to the sixteen Mahajanapadas or region-states of the early historic period, culminating in the emergence of the Maurya Empire towards the end of the period. The earliest evidence of iron smelting predates the emergence of the Iron Age proper by several centuries. North India R. Tewari (2003) radiocarbon dated iron artefacts in Uttar Pradesh, including furnaces, tuyeres, and slag between c. 1800 and 1000 BCE. The use of iron and iron working was prevalent in the Central Ganga Plain and the Eastern Vindhyas from the early second millennium BCE. The beginning of the use of iron has been traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sena Dynasty
The Sena dynasty was a Hindu dynasty during the early medieval period on the Indian subcontinent, that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. The empire at its peak covered much of the north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. The rulers of the Sena Dynasty traced their origin to the south Indian region of Karnataka. The dynasty's founder was Samanta Sena. After him came Hemanta Sena who usurped power and styled himself, king, in 1095 AD. His successor Vijaya Sena (ruled from 1096 AD to 1159 AD) helped lay the foundations of the dynasty, and had an unusually long reign of over 60 years. Ballala Sena conquered Gaur from the Pala, became the ruler of the Bengal Delta, and made Nadia the capital as well. Ballala Sena married Ramadevi a princess of the Western Chalukya Empire which indicates that the Sena rulers maintained close social contact with south India. Lakshmana Sena succeeded Ballala Sena in 1179, ruled Bengal for approximately 20 years, and expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire (r. 750-1161 CE) was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix ''Pāla'' ("protector" in Prakrit). The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century AD. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati (Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jaggadala. The Pālas were astute diplomats and military conquerors. Their army was noted for its vast war elephant corps. Their navy performed both mercantile and defensive roles in the Bay of Bengal. At its zenith under emperors Dharmapala and Devapala in the early ninth century, the Pala empire extended their dominance into the northern Indian region, with its territory stretching across the Gangetic pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauda Kingdom
The Gauḍa Kingdom (Gāuṛ Rājya) or Shashankas, was a classic kingdom during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal (modern-day West Bengal and Bangladesh) in 4th century CE or possibly earlier. Location and extent A Buddhist Mahāyāna Text Mañjuśrī-Mūlakalpa records the existence of Gauda Kingdom in Bengal before it was replaced by Gupta Empire in the 4th century. King Loka who was born in Vardhamāna ( Bardhamān) is mentioned who must have ruled in the early 4th century CE. King Shashanka is often attributed with creating the first separate political entity in a unified Bengal called Gauda. He reigned in 7th century, and some historians place his rule approximately between 590 and 625. His capital was at Karnasubarna, south-west of Baharampur, headquarters of Murshidabad district. The Chinese monk, Xuanzang (Hiuen Tsang) travelled from the country of Karnasubarna to a region in the present-day state of Orissa r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Gupta Dynasty
The Later Gupta dynasty ruled the Magadha region in eastern India between the 6th and 8th centuries CE. The Later Guptas succeeded the imperial Guptas as the rulers of Magadha, but there is no evidence connecting the two dynasties; these appear to be two distinct families. The Later Guptas are so-called because the names of their rulers ended with the suffix "-gupta" ( Late Brahmi: ''gu-pta''), which they might have adopted to portray themselves as the successors of the imperial Guptas. History After the decline of the Gupta Empire, the Later Guptas succeeded them as the rulers of Magadha. The daughter of the dynasty's founder Krishnagupta is said to have married prince Adityavarman of the Maukhari dynasty. According to the Aphsad inscription of Ādityasena, Krishnagupta's grandson Jivitagupta carried out military expeditions in the Himalayan region and southwestern Bengal. During the reign of Jivitagupta's son Kumaragupta, the dynasty developed a rivalry with the Maukharis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Golden Age of India by historians. The ruling dynasty of the empire was founded by the king Sri Gupta; the most notable rulers of the dynasty were Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Skandagupta. The 5th-century CE Sanskrit poet Kalidasa credits the Guptas with having conquered about twenty-one kingdoms, both in and outside India, including the kingdoms of Parasikas, the Hunas, the Kambojas, tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys, the Kinnaras, Kiratas, and others.Raghu Vamsa v 4.60–75 The high points of this period are the great cultural developments which took place primarily during the reigns of Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Kumaragupta I. Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as Mahabharata and Ramay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunga Empire
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra Shunga, Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of the Maurya Empire. Its capital was Pataliputra, but later emperors such as Bhagabhadra also held court at Besnagar (modern Vidisha) in eastern Malwa. Pushyamitra ruled for 36 years and was succeeded by his son Agnimitra. There were ten Shunga rulers. However, after the death of Agnimitra, the second king of the dynasty, the empire rapidly disintegrated:K.A. Nilkantha Shastri (1970)''A Comprehensive History of India: Volume 2'' p.108: "Soon after Agnimitra there was no 'Sunga empire'." inscriptions and coins indicate that much of northern and central India consisted of small kingdoms and city-states that were independent of any Shunga hegemony.Bhandare, Shailendra. "Numismatics and History: The Maurya-Gupta Interlude in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. Quote: "Magadha power came to extend over the main cities and communication routes of the Ganges basin. Then, under Chandragupta Maurya (c.321–297 bce), and subsequently Ashoka his grandson, Pataliputra became the centre of the loose-knit Mauryan 'Empire' which during Ashoka's reign (c.268–232 bce) briefly had a presence throughout the main urban centres and arteries of the subcontinent, except for the extreme south." The Maurya Empire was centralized by the conquest of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, and its capital city was located at Pataliputra (modern Patna). Outside this imperial center, the empire's geographical extent was dependent on the loyalty of military commanders who controlled the armed cities sprinkling it. During Asho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanda Empire
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded their empire to include a larger part of northern India. Ancient sources differ considerably regarding the names of the Nanda kings and the duration of their rule, but based on the Buddhist tradition recorded in the '' Mahavamsa'', they appear to have ruled during ''circa'' 345–322 BCE, although some theories date the start of their rule to fifth century BCE. The Nandas built on the successes of their Haryanka and Shaishunaga predecessors, and instituted a more centralised administration. Ancient sources credit them with amassing great wealth, which was probably a result of introduction of new currency and taxation system. Ancient texts also suggest that the Nandas were unpopular among their subjects because of their low status birth, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangaridai
Gangaridai ( gr, Γανγαρίδαι; Latin: ''Gangaridae'') is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE-2nd century AD) to describe a people or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent. Some of these writers state that Alexander the Great withdrew from the Indian subcontinent because of the strong war elephant force of the Gangaridai. A number of modern scholars locate Gangaridai in the Ganges Delta of the Bengal region, although alternative theories also exist. Gange or Ganges, the capital of the Gangaridai (according to Ptolemy), has been identified with several sites in the region, including Chandraketugarh and Wari-Bateshwar. Names The Greek writers use the names "Gandaridae" (Diodorus), "Gandaritae", and "Gandridae" (Plutarch) to describe these people. The ancient Latin writers use the name "Gangaridae", a term that seems to have been coined by the 1st century poet Virgil. Some modern etymologies of the word Gangaridai split it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanga Kingdom
Vanga was an ancient kingdom and geopolitical division within the Ganges delta in the Indian subcontinent. The kingdom is one of the namesakes of the Bengal region. It was located in southern Bengal, with the core region including present-day southern West Bengal (India) and southwestern Bangladesh. Vanga features prominently in the epics and tales of ancient India as well as in the history of Sri Lanka. Vanga was probably the center of the Gangaridai Empire mentioned by numerous Greco-Roman writers. The exact capital of ancient Vanga kingdom could not be identified. After the rule of Gupta empire, ancient Bengal was divided into two independent states. They were the Gauda Kingdom and Vanga kingdom and archaeologists think that Kotalipara in present-day Bangladesh was the capital of the independent Vanga kingdom. Indian and Greco-Roman writers referred to the region's war elephants. In Indian history, Vanga is notable for its strong navy. There are numerous references to Vang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)