|
Battle Of Pinos
The Battle of Pinos was a naval engagement between a Spanish fleet under Admiral Bernardino Delgadillo y Avellaneda and the surviving ships of Francis Drake's expedition to the Spanish West Indies, now in command of Drake's lieutenant, Sir Thomas Baskerville, which took place off the Island of Pinos during the Anglo-Spanish war of 1585. The Spanish squadron was victorious, capturing two English ships. Background After failed attacks against San Juan de Puerto Rico and Panamá, during which Francis Drake and John Hawkins had perished from dysentery, the English fleet anchored in Portobello to reorganize and careen their ships prior to return to England. Sir Thomas Baskerville, Colonel-General of the landing forces, was then elected by his officers as the new commander of the retreating fleet,Corbett p. 29 whose number of ships soon decreased to 18, as two of them, the ''Delight'' and the ''Elizabeth'', had to be burned or sunk due to lack of crew.Ullivarri p. 168 Two generals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Spanish War (1585)
Anglo-Spanish War may refer to: * Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), including the Spanish Armada and the English Armada * Anglo-Spanish War (1625–1630), part of the Thirty Years' War * Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660), part of the Franco-Spanish War * Portuguese Restoration War (1662–1668), English support for Portugal * War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1713), British support to Archduke Charles * War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718–1720) * Anglo-Spanish War (1727–1729) (1727–1729) * War of Jenkins' Ear (1739-1748), later merged into the War of the Austrian Succession * Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), part of the Seven Years' War * Anglo-Spanish War (1779–1783), linked to the American Revolutionary War * Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), part of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars * The Spanish American wars of independence (1815–1832), British supporting role to the Decolonization of the Americas * First Carlist War (1833–1840), British support to Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-rigged Pinnace
The full-rigged pinnace was the larger of two types of vessel called a pinnace in use from the sixteenth century. Etymology The word ''pinnace'', and similar words in many languages (as far afield as Indonesia, where the boat "pinisi" took its name from the Dutch ''pinas''), came ultimately from the Spanish ''pinaza'' c. 1240, from ''pino'' (pine tree), from the wood of which the ships were constructed. The word came into English from the Middle French ''pinasse''. Design "The pinnace is perhaps the most confusing of all the early seventeenth-century types of vessels. Pinnace was more of a use than a type name, for almost any vessel could have been a pinnace or tender to a larger one. Generally speaking, pinnaces were lightly built, single-decked, square-sterned vessels suitable for exploring, trading, and light naval duties. On equal lengths, pinnaces tended to be narrower than other types. Although primarily sailing vessels, many pinnaces carried sweeps for moving in calms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content 25.563 g = 0.822 oz t fine silver. It was widely used as the first world currency, international currency because of its uniformity in standard and milling characteristics. Some countries countermarked the Spanish dollar so it could be used as their local currency. Because the Spanish dollar was widely used in Europe, the Americas, and the Far East, it became the first world currency by the late 18th century. The Spanish dollar was the coin upon which the original United States dollar was based (at 0.7735 oz t = 24.0566 g), and it remained legal tender in the United States until the Coinage Act of 1857. Many other currencies around the world, such as the Japanese yen and the Yuan (currency), Chinese yuan, were initially based on the Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanlúcar De Barrameda
Sanlúcar de Barrameda (), or simply Sanlúcar, is a city in the northwest of Cádiz province, part of the autonomous community of Andalucía in southern Spain. Sanlúcar is located on the left bank at the mouth of the Guadalquivir River opposite the Doñana National Park, 52 km from the provincial capital Cádiz and 119 km from Sevilla capital of the autonomous region Andalucía. Its population is 68,656 inhabitants ( National Institute of Statistics 2019). Sanlúcar has been inhabited since ancient times, and is assumed to have belonged to the realm of the Tartessian civilization. The town of San Lucar was granted to the Spanish nobleman Alonso Pérez de Guzmán in 1297. Its strategic location made the city a starting point for the exploration, colonization and evangelization of America between the 15th and 17th centuries. Sanlúcar lost much of its strategic value after 1645 because of the disgrace of the House of Medina Sidonia, the general decline of Spain und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
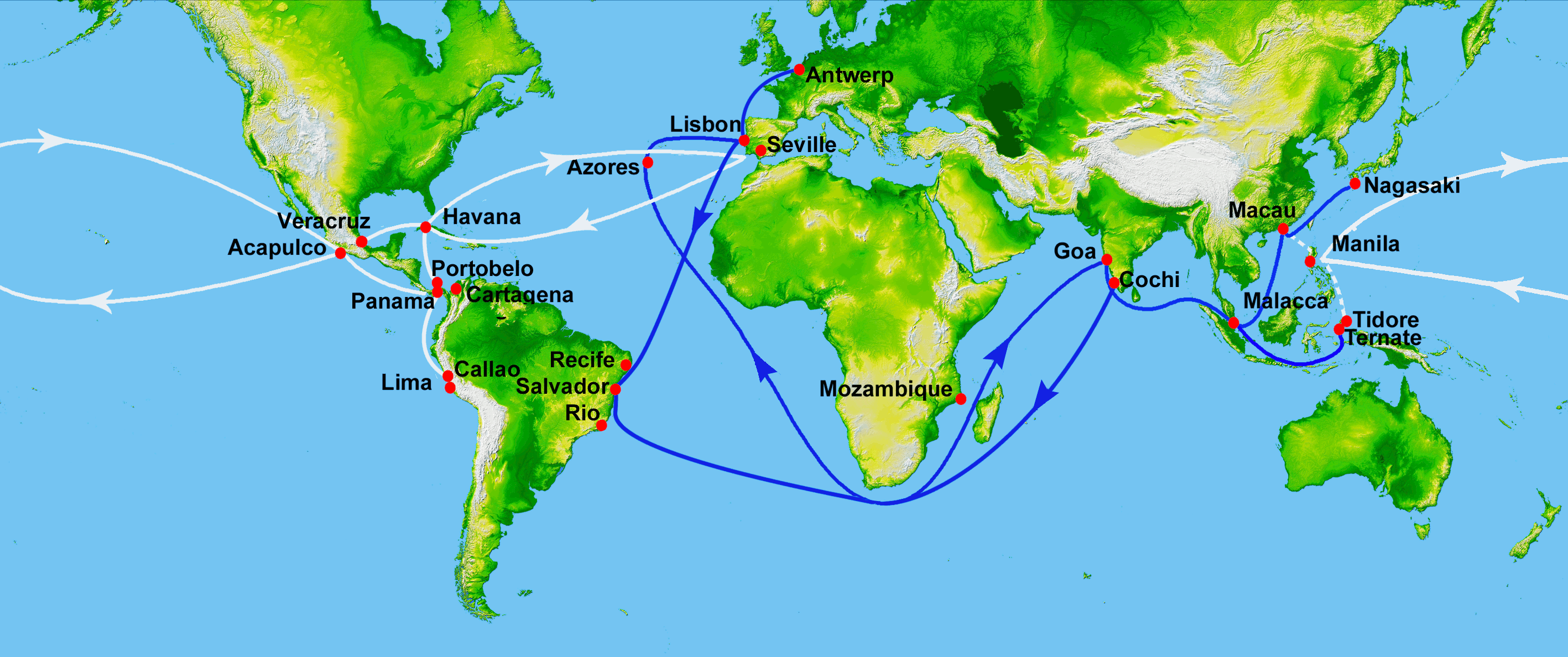
Spanish Treasure Fleet
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to 1790, which linked Spain with its territories in the Americas across the Atlantic. The convoys were general purpose cargo fleets used for transporting a wide variety of items, including agricultural goods, lumber, various metal resources such as silver and gold, gems, pearls, spices, sugar, tobacco, silk, and other exotic goods from the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire to the Spanish mainland. Spanish goods such as oil, wine, textiles, books and tools were transported in the opposite direction. The West Indies fleet was the first permanent transatlantic trade route in history. Similarly, the related Manila galleon trade was the first permanent trade route across the Pacific. The Spanish West and East Indies fleets are considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Bahama Channel
The Old Bahama Channel ( es, Canal Viejo de Bahama) is a strait of the Caribbean region, between Cuba and the Bahamas. Geography The strait/channel is located off the Atlantic coast of north-central and northeastern mainland and the Sabana-Camagüey Archipelago of Cuba, and south of the Great Bahama Bank of the Bahamas. It is approximately long and 13.6 miles (22 km) wide at its narrowest place. It divides the northernmost bank of the Caribbean islands into two nearly equal parts. To the north and northeast is the Great Bahama Bank and the Bahama Islands; and to the south the bank on which the island of Cuba rests. The Old Bahama Channel is connected at its north-western extremity end to the Florida Straits by two arms, enclosing Cay Sal Bank, of which the northern is called Santaren Channel and the southern Nicholas Channel. It is considered as terminating on the east between Cape Maysi in Cuba, and Inagua island in the Bahamas. However, it can also be considered to include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.Cuba ''''. . The city has a population of 2.3million inhabitants, and it spans a total of – making it the largest city by area, the most populous city, and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baggage
Baggage or luggage consists of bags, cases, and containers which hold a traveler's personal articles while the traveler is in transit. A modern traveler can be expected to have packages containing clothing, toiletries, small possessions, trip necessities. On the return trip, travelers may have souvenirs and gifts. For some people, luggage and the style thereof is representative of the owner's wealth and status. Luggage is constructed to protect the items during travel either with a hard shell or a durable soft material. Luggage often has internal subdivisions or sections to aid in securing items. Handles are typically provided to facilitate carrying, and some luggage may have wheels and/or telescoping handles or leashes to make moving them easier. Baggage (not luggage), or ''baggage train'', can also refer to the train of people and goods, both military and of a personal nature, which commonly followed pre-modern armies on campaign. Overview Luggage has changed over time. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape San Antonio, Cuba
Cape San Antonio ( es, Cabo San Antonio), is a cape which forms the western extremity of the Guanahacabibes Peninsula and the western extremity of Cuba. It extends into the Yucatán Channel, and is part of the municipality of Sandino, in Pinar del Río Province. According to the International Hydrographic Organization, it marks the division point between the Caribbean Sea to the south and Gulf of Mexico to the north. See also * Cape Maisí * Cape Corrientes * Cabo San Antonio Lighthouse References External links Cape San Antonio on havanajournal.com San Antonio ("Cradle of Freedom") , image_map = , mapsize = 220px , map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1= U.S. state, State , subdivision_name1 = Texas , s ... Sandino, Cuba Geography of Pinar del Río Province {{Cuba-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinar Del Río
Pinar del Río is the capital city of Pinar del Río Province, Cuba. With a population of 139,336 (2004) in a municipality of 190,332, it is the List of cities in Cuba, 10th-largest city in Cuba. Inhabitants of the area are called ''Pinareños''. History Pinar del Río was one of the last major cities in Cuba founded by the Spanish, on September 10, 1867. The city and province was founded as ''Nueva Filipinos, Filipinas'' (New Philippines) in response to an influx of Asian laborers coming from the Philippine Islands to work on tobacco plantations. Pinar del Río's history begins with the Guanahatabey, a group of nomadic Indians who lived in caves and procured most of their livelihood from the sea. Less advanced than the other indigenous natives who lived on the island, the Guanahatabey were a peaceful and passive race whose culture came about largely independently of the Taíno and Siboney cultures further east. The Guanahatabey were extinct by the time of the Spanish arrival in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cienfuegos
Cienfuegos (), capital of Cienfuegos Province, is a city on the southern coast of Cuba. It is located about from Havana and has a population of 150,000. Since the late 1960s, Cienfuegos has become one of Cuba's main industrial centers, especially in the energy and sugar sectors. The city is dubbed ''La Perla del Sur'' (Pearl of the South). Although ''Cienfuegos'' literally translates to "one hundred fires" (''cien'', "one hundred"; ''fuegos'', "fires"), the city takes its name from the surname of José Cienfuegos, Captain General of Cuba (1816–19). In 2005, UNESCO inscribed the '' Urban Historic Centre of Cienfuegos'' on the World Heritage List, citing Cienfuegos as the best extant example of early 19th century Spanish Enlightenment implementation in urban planning. The downtown area contains six buildings from 1819–50, 327 buildings from 1851–1900, and 1188 buildings from the 20th century. There is no other place in the Caribbean which contains such a remarkable cluster o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |