|
Battle Of Hartmannswillerkopf
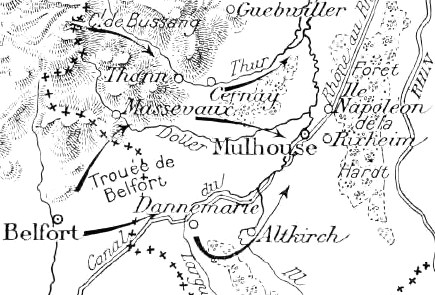
The Battle of Hartmannswillerkopf (french: bataille du Vieil-Armand) was a series of engagements during the First World War fought for the control of the Hartmannswillerkopf peak in Alsace in 1914 and 1915. The peak is a pyramidal rocky spur in the Vosges mountains, about north of Thann, standing at and overlooking the Alsace Plain, Rhine valley and the Black Forest in Germany. Hartmanswillerkopf was captured by the French army during the Battle of Mulhouse 1914). From the vantage point, Mulhouse and the Mulhouse–Colmar railway could be seen and the French railway from Thann to Cernay and Belfort shielded from German observation. The two French invasions and captures of Mulhouse by the French VII Corps ( Louis Bonneau) and then the Army of Alsace (General Paul Pau), were repulsed by the German 7th Army ( Josias von Heeringen). Both sides then stripped the forces in Alsace to reinforce the armies fighting on the Marne, Aisne and further north. For the rest of 1914 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main theatres of war during the First World War. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The German advance was halted with the Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, which changed little except during early 1917 and in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties during attacks and counter-attacks and no significant advances were made. Among the most costly of these offensives were the Battle of Verdun, in 1916, with a combined 700 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Army Of Alsace (WWI)
The Army of Alsace (french: Armée d'Alsace) was a French field army of the First World War that operated from 11 to 28 August 1914. Formation On 7 August 1914, the French VII Corps (General Bonneau) captured Mulhouse but were forced out three days later by German counter-attacks. Bonneau was dismissed by Joffre and the VII Corps was expanded, becoming the under command of Paul Pau Paul Marie Cesar Gerald Pau, (29 November 1848, Montélimar – 2 January 1932) was a French soldier and general who served in the Franco-Prussian War and in World War I. He took part in the Franco-Prussian War, suffering the loss of his low .... The reinforcements were * 44th Division * 55th Reserve Division * 58th Reserve division * 63rd Reserve division * 66th Reserve division * 8th Cavalry Division A new attack was launched, Mulhouse was taken and the Germans were even pushed over the Rhine. French defeats in Lorraine and the Ardennes forced the to withdrew from Mulhouse, to a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Capture Of Mulhouse, 8 August 1914
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfort
Belfort (; archaic german: Beffert/Beffort) is a city in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in Northeastern France, situated between Lyon and Strasbourg, approximately from the France–Switzerland border. It is the prefecture of the Territoire de Belfort department. Belfort is from Paris, from Strasbourg, from Lyon and from Zürich. The residents of the city are called "Belfortains". The city is located on the river Savoureuse, on a strategically important natural route between the Rhine and the Rhône – the Belfort Gap (''Trouée de Belfort'') or Burgundian Gate (''Porte de Bourgogne''). It is located approximately south from the base of the Ballon d'Alsace mountain range, source of the Savoureuse. The city of Belfort has 46,443 inhabitants (2019).Téléc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cernay, Haut-Rhin
Cernay (; german: Sennheim; gsw-FR, Sanna) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is situated on the river Thur, 17 km northwest of Mulhouse. Second World War The SS had an "ideology school" for their soldiers, where " race theory" was part of the curriculum.Verdens Gang, 2010-11-11,''Frivillig til tjeneste i helvete'' (An interview of former soldier Bjørn Lindstad),pages 44,45: "''Du gikk på SS-ideologiskole i Sennheim og beskriver detaljert i boken om raselære og jødehets. Ble du ideologisk påvirket? — Sikkert, det ville vært rart ellers. Senere erfarte vi at jøder ikke var slik propagandaen fremstilte dem.''" Population See also * Communes of the Haut-Rhin department The following is a list of the 366 communes of the French department of Haut-Rhin. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the European Parliament. Located at the border with Germany in the historic region of Alsace, it is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin department. In 2019, the city proper had 287,228 inhabitants and both the Eurométropole de Strasbourg (Greater Strasbourg) and the Arrondissement of Strasbourg had 505,272 inhabitants. Strasbourg's metropolitan area had a population of 846,450 in 2018, making it the eighth-largest metro area in France and home to 14% of the Grand Est region's inhabitants. The transnational Eurodistrict Strasbourg-Ortenau had a population of 958,421 inhabitants. Strasbourg is one of the ''de facto'' four main capitals of the European Union (alongside Brussels, Luxembourg and Frankfurt), as it is the seat of several European ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altkirch
Altkirch (, ; gsw, label= Alsatian, Àltkìrech) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France. The town is traditionally regarded as the capital of Sundgau. Etymology The name of the commune means ''old church'' ( gsw-FR, Àlta Kìrch or ''Àlta Kìrech''; german: Alte Kirche). History In the 1370s, the citizens of Altkirch made battle and won against a company of Gugler mercenaries. Demography Its inhabitants are known as ''Altkirchois''. The resident population number of 5500 is rather deceptive as some 15,500 people will be in town on a typical working day (4500 working, 3000 studying, 3000 for medical treatment and another 5000 divided between shopping, administrative offices, cultural and sporting activities). Sister cities * Azerbaijan (Nagorno-Karabakh) Füzuli (2016) See also * Château d'Altkirch - destroyed castle in the town. * Communes of the Haut-Rhin department The following is a list of the 366 communes of the Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colmar
Colmar (, ; Alsatian: ' ; German during 1871–1918 and 1940–1945: ') is a city and commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France. The third-largest commune in Alsace (after Strasbourg and Mulhouse), it is the seat of the prefecture of the Haut-Rhin department and of the subprefecture of the Colmar-Ribeauvillé arrondissement. The city is renowned for its well-preserved old town, its numerous architectural landmarks, and its museums, among which is the Unterlinden Museum, which houses the '' Isenheim Altarpiece''. Colmar is situated on the Alsatian Wine Route and considers itself to be the "capital of Alsatian wine" ('). History Colmar was first mentioned by Charlemagne in his chronicle about Saxon wars. This was the location where the Carolingian Emperor Charles the Fat held a diet in 884. Colmar was granted the status of a free imperial city by Emperor Frederick II in 1226. In 1354 it joined the Décapole city league.G. Köb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning '' mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace after Strasbourg. Mulhouse is famous for its museums, especially the (also known as the , 'National Museum of the Automobile') and the (also known as , 'French Museum of the Railway'), respectively the largest automobile and railway museums in the world. An industrial town nicknamed "the French Manchester", Mulhouse is also the main seat of the Upper Alsace University, where the secretariat of the European Physical Society is found. Administration Mulhouse is a commune with a population of 108,312 in 2019.Téléchargement du fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Col De La Schlucht
The Col de la Schlucht (elevation ) is a mountain pass in the Vosges Mountains of France. On the west side lies the historical region of Lorraine (Lothringen in German), on the east side lies the historical region of Alsace (Elsass in German). The pass takes its name from the German word "Schlucht", meaning "gorge" or "ravine". It connects Munster, Haut-Rhin, Munster (Haut-Rhin) with Gérardmer (Vosges) (east–west, via the D417) and is also crossed by the Route des Crêtes (north–south, D61 and D430). Near the Col, along the ''Route des Crêtes (D430)'' is the River source, source of the Meurthe (river), Meurthe. The climb over the pass has been used several times in the Tour de France cycle race. History Between 1871 and 1918, the pass was a border crossing between Lorraine (region), Lorraine (France) and Alsace, which had been ceded to Germany under the Treaty of Frankfurt (1871), Treaty of Frankfurt. Prior to World War I, the pass could be accessed via two separate tramw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gérardmer
Gérardmer (; or archaic ''Geroldsee'', and ''Giraumoué'' in local Vosgian) is a commune in the Vosges department in Grand Est in northeastern France. Population Culture The Festival international du film fantastique de Gérardmer (literally ''Gérardmer International Festival of fantastic film'', formerly named 'Fantastic'Arts' from 1994 to 2008) is an international festival of horror and fantastic films which has been held each year since 1994 in Gérardmer. Notable people * Maximilien Kelsch (1844–1906), industrialist and politician, born in Gérardmer * Paul Cuny (1872–1925), industrialist and politician, born in Gérardmer * Edward Gardère (1909–1997), fencer, born in Gérardmer * André Gardère (1913–1977), fencer, born in Gérardmer * Gilberte Cournand (1913–2005), journalist and dance critic, gallery owner and bookseller, born in Gérardmer * Claude Vanony (1935), storyteller and humorist, born in Gérardmer * Patrick Rémy (1965), cross-country sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josias Von Heeringen
Josias von Heeringen (9 March 1850 – 9 October 1926) was a German general of the imperial era who served as Prussian Minister of War and saw service in the First World War. Early life Heeringen was born in Kassel in the Electorate of Hesse. He was the son of Josias von Heeringen (1809–1885) and his wife Karoline von Starkloff (1817–1871). His younger brother August von Heeringen (* 26. November 1855 in Kassel; † 29. September 1927 in Berlin), served as a naval officer and was a Chief of the German Imperial Admiralty Staff. Josias von Heeringen married in 1874 Augusta von Dewall. Career After having served on various posts, in 1887 he became a major in the Prussian Ministry of War. From 1892 to 1895, he was a department head on the German General Staff. In 1898 he was appointed a Major-General and chosen to head the Army Administration Department of the Ministry of War. In 1901 he was made a Generalleutnant and in 1903 became head of the 22nd Division. In 1906 he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
