|
Battle Of Apros
The Battle of Apros occurred between the forces of the Byzantine Empire, under co-emperor Michael IX Palaiologos, and the forces of the Catalan Company, at Apros on July 1305. The Catalan Company had been hired by the Byzantines as mercenaries against the Turks, but despite the Catalans' successes against the Turks, the two allies distrusted each other, and their relationship was strained by the Catalans' financial demands. Eventually, Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos and his son and co-ruler Michael IX had the Catalan leader, Roger de Flor, assassinated with his entourage in April 1305. In July, the Byzantine army, comprising a large contingent of Alans as well as many Turcopoles, confronted the Catalans and their own Turkish allies near Apros in Thrace. Despite the Imperial Army's numerical superiority, the Alans withdrew after the first charge, whereupon the Turcopoles deserted ''en block'' to the Catalans. Prince Michael was injured and left the field and the Catalans won ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apros
Aprus or Apros ( grc, Ἄπρος), also Apri or Aproi (Ἄπροι), was a town of ancient Thrace and, later, a Roman city established in the Roman province of Europa. History Stephanus of Byzantium collects a quote of Theopompus that mentions Aprus. Pliny the Elder notes that Aprus is situated in the interior of Thrace, 22 M.P. from Resisto (likely the same as Bisanthe), 50 Roman miles from Bizya and 180 Roman miles from Philippi. The city was re-founded as Colonia Claudia Aprensis in the mid-1st century AD, probably in connection with the emperor Claudius's annexation of Thracia, and was intended for retired members of the Roman military. It was situated on the Via Egnatia that ran from the Adriatic coast in the province of Illyricum to Byzantium, the city that was to become Constantinople. In the 4th century, Aprus was the principal city of the region southwest of Heraclea, the capital of the province. The city was called Theodosiopolis in documents of the 6th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turcopoles
During the period of the Crusades, turcopoles (also "turcoples" or "turcopoli"; from the el, τουρκόπουλοι, literally "sons of Turks") were locally recruited mounted archers and light cavalry employed by the Byzantine Empire and the Crusader states. A leader of these auxiliaries was designated as Turcopolier, a title subsequently given to a senior officer in the Knights Templars and the Order of the Hospital of St John of Jerusalem, in charge of the coastal defences of Rhodes and Malta. Byzantine origins The crusaders first encountered turcopoles in the Byzantine army during the First Crusade. These auxiliaries were from diverse Turkic origins; including Pechenegs, Oghuz Turks, Uzes, Cumans, and Bulgars. Some Byzantine turcopole units under the command of General Tatikios accompanied the First Crusade and may have provided a model for the subsequent employment of indigenous auxiliary light horse in the crusader states. Composition It has been argued that, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Tekirdağ Province
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Byzantine Empire
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles In Medieval Thrace
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1305
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Athens
The Duchy of Athens (Greek: Δουκᾶτον Ἀθηνῶν, ''Doukaton Athinon''; Catalan: ''Ducat d'Atenes'') was one of the Crusader states set up in Greece after the conquest of the Byzantine Empire during the Fourth Crusade as part of the process known as Frankokratia, encompassing the regions of Attica and Boeotia, and surviving until its conquest by the Ottoman Empire in the 15th century. History Establishment of the Duchy The first duke of Athens (as well as of Thebes, at first) was Otto de la Roche, a minor Burgundian knight of the Fourth Crusade. Although he was known as the "Duke of Athens" from the foundation of the duchy in 1205, the title did not become official until 1260. Instead, Otto proclaimed himself "Lord of Athens" (in Latin ''Dominus Athenarum'', in French ''Sire d'Athenes''). The local Greeks called the dukes "Megas Kyris" ( el, Μέγας Κύρης, "Great Lord"), from which the shortened form "Megaskyr", often used even by the Franks to refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Cephissus
The Battle of Halmyros, known by earlier scholars as the Battle of the Cephissus or Battle of Orchomenos, was fought on 15 March 1311, between the forces of the Frankish Duchy of Athens and its vassals under Walter of Brienne against the mercenaries of the Catalan Company, resulting in a decisive victory for the mercenaries. Engaged in conflict with their original employers, the Byzantine Empire, the Catalan Company had traversed the southern Balkans and arrived in southern Greece in 1309. The new Duke of Athens, Walter of Brienne, hired them to attack the Greek ruler of neighbouring Thessaly. Although the Catalans conquered much of the region for him, Walter refused to pay them and prepared to forcibly expel them from their gains. The two armies met at Halmyros in southern Thessaly (or at the Boeotic Cephissus, near Orchomenos, according to an earlier interpretation). The Catalans were considerably outnumbered and weakened by the reluctance of their Turkish auxiliaries to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
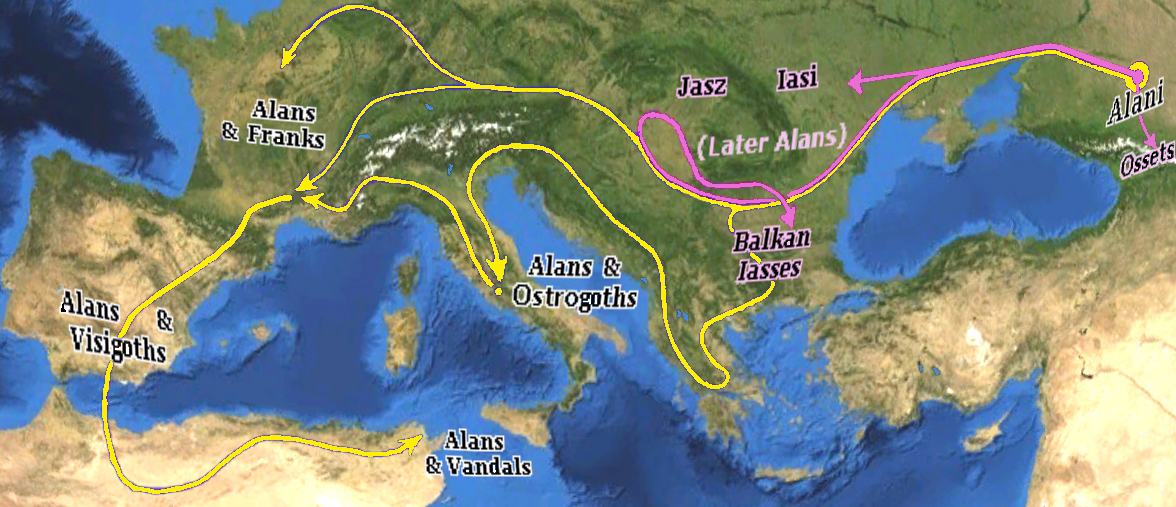
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey ( East Thrace). The region's boundaries are based on that of the Roman Province of Thrace; the lands inhabited by the ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into the region of Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'' was first used by the Greeks when referring to the Thracian tribes, from ancient Greek Thrake (Θρᾴκη), descending from ''Thrāix'' (Θρᾷξ). It referred originally to the Thracians, an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' first referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger De Flor
Roger de Flor (1267 – 30 April 1305), also known as Ruggero/Ruggiero da Fiore or Rutger von Blum or Ruggero Flores, was an Italian military adventurer and condottiere active in Aragonese Sicily, Italy, and the Byzantine Empire. He was the commander of the Great Catalan Company and held the title Count of Malta. Biography Roger de Flor was born in Brindisi in the Kingdom of Sicily, the second son of an Italian noblewoman of Brindisi and a German falconer named Richard von Blum (''Blume'' means flower in German) in the service of Emperor Frederick II. Richard von Blum was killed fighting at the Battle of Tagliacozzo in 1268. At eight years old Roger de Flor was sent to sea in a galley belonging to the Knights Templars. He entered the order and became captain of a galley called "El falcó". After rescuing wealthy survivors during the siege of Acre by the Mamluk Sultan Al-Ashraf Khalil in 1291, he went to Cyprus. Following intrigues and personal disputes he was accused of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg , caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia'' , succession = Byzantine emperor , reign = 11 December 1282 –24 May 1328 , coronation = 8 November 1272 , cor-type1 = Coronation , regent = Michael IX Palaiologos , reg-type = Co-emperor , predecessor = Michael VIII Palaiologos (alone) , successor = Andronikos III Palaiologos , spouse = Anna of HungaryYolande of Montferrat , issue = Michael IX PalaiologosConstantine Palaiologos John PalaiologosTheodore I, Marquis of MontferratDemetrios Palaiologos Simonis (Simonida Nemanjić), Queen of SerbiaIrene Palaiologina (wife of John II Doukas), Sebastokratorissa of Thessaly , issue-link = #Family , issue-pipe = more... , dynasty = Palaiologos , father = Michael VIII Palaiologos , mother = Theodora Palaiologina , birth_date = 25 March 1259 , birth_place = Nicaea, Empire of Nicaea( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)