|
Battle Of Angol
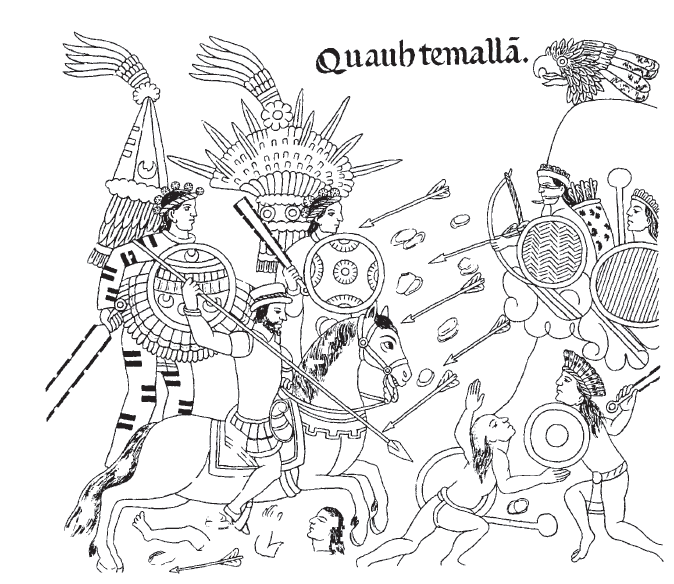
The Battle of Angol was a battle fought between the Mapuche and the Spanish Empire on 25 March 1564 as part of Arauco War. In Angol, Los Infantes captain Lorenzo Bernal del Mercado had discovered that the rebels had constructed a ''pukara'' close by, establishing a blockade of the city, additionally natives under the toqui Illangulién had chosen an impregnable position in a marsh. A Mapuche detachment located themselves in a third position awaiting reinforcements from their main body at the old position. Seeing that this position was weak the Spanish engaged this position. In the battle the Spanish drove the Mapuche out of their ''pukara'' and pursued them down to the river bank and drove them into the river, where they were trapped and 1,000 Mapuches were killed, including the toqui Illanguelén. History In Angol, Los Infantes captain Lorenzo Bernal del Mercado had discovered that the rebels had constructed a ''pukara'' close by, establishing a blockade of the city. Lorenzo B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arauco War
The Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía. The conflict began at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquerors attempting to establish cities and force Mapuches into servitude. It subsequently evolved over time into phases comprising drawn-out sieges, slave-hunting expeditions, pillaging raids, punitive expeditions, and renewed Spanish attempts to secure lost territories. Abduction of women and war rape was common on both sides. After many initial Spanish successes in penetrating Mapuche territory, the Battle of Curalaba in 1598 and the following destruction of the Seven Cities marked a turning point in the war leading to the establishment of a clear frontier between the Spanish domains and the land of the independent Mapuche. From the 17th to the late 18th century a series of parliaments were held between royal governors and Mapuche lonkos and the war devolved to sporadic pillaging carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angol
Angol is a commune and capital city of the Malleco Province in the Araucanía Region of southern Chile. It is located at the foot of the Nahuelbuta Range and next to the Vergara River, that permitted communications by small boats to the Bío-Bío River and Concepción. This strategic position explains the successive foundations of this city during the Arauco War. It was first founded in 1553 as a "conquistador" fort of ''Confines'', the fort was later destroyed and rebuilt several times and it was not until the Pacification of Araucania in the late 19th century that it was rebuilt with the name of Angol. The city has a current population of approximately 53,000. Within the electoral divisions of Chile, it belongs to the 48th electoral district and the 14th senatorial circumscription. History Modern Angol was first founded in 1553 as the conquistador fort of ''Los Confines'' by Pedro de Valdivia, the fort was later that year abandoned and destroyed by the Mapuche after the Bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was, in conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, territories in Western Europe], Africa, and various islands in Spanish East Indies, Asia and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming the first empire known as "the empire on which the sun never sets", and reached its maximum extent in the 18th century. An important element in the formation of Spain's empire was the dynastic union between Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon in 1469, known as the Catholic Monarchs, which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their habitat once extended from Aconcagua Valley to Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of extended families, under the direction of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorenzo Bernal Del Mercado
Lorenzo Bernal del Mercado (1530–1593) was a Spanish captain who was one of the more successful soldiers in the Arauco War in Chile rising to the rank of Maestre de Campo and temporary Capitán General of the Captaincy General of Chile. Lorenzo Bernal del Mercado was born in Cantalapiedra, Salamanca in 1530. He was the son of Francisco Martinez Nieto and Ana Bernal del Mercado. He traveled to the Americas in 1541 with the expedition of Blasco Nuñez de Vela, recently named Viceroy of Peru. From Peru, he went to Bolivia where he had some success. In 1549, he joined with Pedro de Valdivia coming to Chile from the valley of Potosí, Valdivia gave him an encomienda in the area of the present Valdivia, naming him temporary captain of the new city. The death of Valdivia at the hands of Lautaro made so deep an impression on him that he left his encomienda and served under Francisco de Villagra in the war. Bernal del Mercado showed intelligence, bravery and an energetic characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illangulién
Illangulién, ''Quiromanite'', ''Queupulien'' or ''Antiguenu'', was the Mapuche toqui (war leader) elected to replace Lemucaguin or Caupolicán the younger in 1559 following the Battle of Quiapo to his death in battle in the Battle of Angol in 1564. After the campaign of García Hurtado de Mendoza that culminated in the Battle of Quiapo, many of the Mapuche warriors were dead or wounded and the population had been decimated by the effects of war, starvation and epidemic disease. Elected to by the remaining leaders shortly after the battle of Quiapo, Illangulién decided to let the nation offer apparent submission to the Spanish while he and a few warriors secretly retreated into the marshes of Lumaco. There they constructed a base where they would gather their strength and train a new generation of warriors for a future revolt. After the murder of the hated encomendero Pedro de Avendaño in July 1561 triggered a new general rising of the Mapuche greater than the previous ones. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Auxiliaries
Indian auxiliaries were those indigenous peoples of the Americas who allied with Spain and fought alongside the conquistadors during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. These auxiliaries acted as guides, translators and porters, and in these roles were also referred to as ''yanakuna'', particularly during the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire. The term was also used for formations composed of indigenous warriors which were used by the Spanish for reconnaissance and combat duties. Indian auxiliaries continued to be used by the Spanish to maintain control over their colonies in the Americas; frequently stationed on the frontier, they were often used to suppress anti-colonial revolts such as Arauco War. History The formations of auxiliary Indians arose commonly from alliances established by the Spaniards, exploiting ethnic and tribal antagonisms that they found during their occupation of the territory they were attempting to conquer. Hernán Cortés was one of the first c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pukara
Pukara (Aymara and Quechuan "fortress", Hispanicized spellings ''pucara, pucará'') is a defensive hilltop site or fortification built by the prehispanic and historic inhabitants of the central Andean area (from Ecuador to central Chile and northwestern Argentina). In some cases, these sites acted as temporary fortified refuges during periods of increased conflict, while other sites show evidence for permanent occupation. Emerging as a major site type during the Late Intermediate Period (c. 1000-1430AD), the pukara form was adopted in some areas by the Inca military in contested borderlands of the Inca Empire. The Spanish also referred to the Mapuche earthen forts built during the Arauco War in the 16th and 17th centuries by this term. Today, the term is commonly found in toponyms of the Andes region, e.g. Andalicán, Pucará de Angol, Camiña, Cañete, Nama, Quiapo, Tilcara, Turi, Pucara del Cerro La Muralla, Pukara of La Compañía, Pukara de Lasana, Pucará de Belén, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toqui
Toqui (or Toki) ( Mapudungun for ''axe'' or ''axe-bearer'') is a title conferred by the Mapuche (an indigenous Chilean and Argentinian people) on those chosen as leaders during times of war. The toqui is chosen in an assembly or parliament ('' coyag'') of the chieftains (loncos) of various clans (Rehues) or confederation of clans (Aillarehues), allied during the war at hand. The toqui commanded strict obedience of all the warriors and their loncos during the war, would organize them into units and appoint leaders over them. This command would continue until the toqui was killed, abdicated (Cayancaru), was deposed in another parliament (as in the case of Lincoyan, for poor leadership), or upon completion of the war for which he was chosen. Some of the more famous Toqui in the Arauco War with the Spanish introduced tactical innovations. For example, Lautaro introduced infantry tactics to defeat horsemen. Lemucaguin was the first Toqui to use firearms and artillery in battle. Non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alonso De Góngora Marmolejo
Alonso de Góngora Marmolejo (1523–1575) was a Spanish conquistador and chronicler of the early conquest and settlement of the Captaincy General of Chile, and the start of the Arauco War. Biography Marmolejo was born in the town of Carmona, Andalucía, in 1523. He was the son of the regidor of the town, Juan Jiménez de Góngora Marmolejo and of Teresa Núñez de Tanfarva. In April 1551 he came as a soldier to Santiago, Chile and shortly after was transferred to Concepción to join the expedition that Pedro de Valdivia had prepared to continue his southern conquests. He attended the foundation of Valdivia, where he lived and was regidor in 1555. In 1557 he was transferred from Valdivia by sea to serve Don García Hurtado de Mendoza who had just arrived as new Governor and was on Quiriquina Island. Góngora participated in the campaign there and later was part of the garrison of the fort of Tucapel and helped frustrate Caupolicán's attack on the fort that resulted in his bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Mariño De Lobera
Pedro Mariño de Lobera (1528–1594) was a Galician soldier, conquistador and chronicler of the Arauco War in the Captaincy General of Chile. Biography A professional soldier who served in the war between Spain and France, he went to the Americas in 1545. Mariño joined the forces of Pedro de La Gasca in Havana, Cuba, when he received the order of King Carlos V to end the revolt of Gonzalo Pizarro in Peru. He was then transferred to Lima where he remained until his trip to Chile, in 1551. In Chile he participated actively next to Pedro de Valdivia and Francisco de Villagra in the first campaigns made to the South, as an outstanding soldier. Also, he was present in the campaigns of the governors García Hurtado de Mendoza and Rodrigo de Quiroga. Later, in payment of his services, an encomienda in the city of Valdivia was granted to him. He was the corregidor of the city, rendering his aid to the victims of the flood caused by the 1575 Valdivia earthquake. Later he was also co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)