|
Banswara (Vidhan Sabha Consitucy)
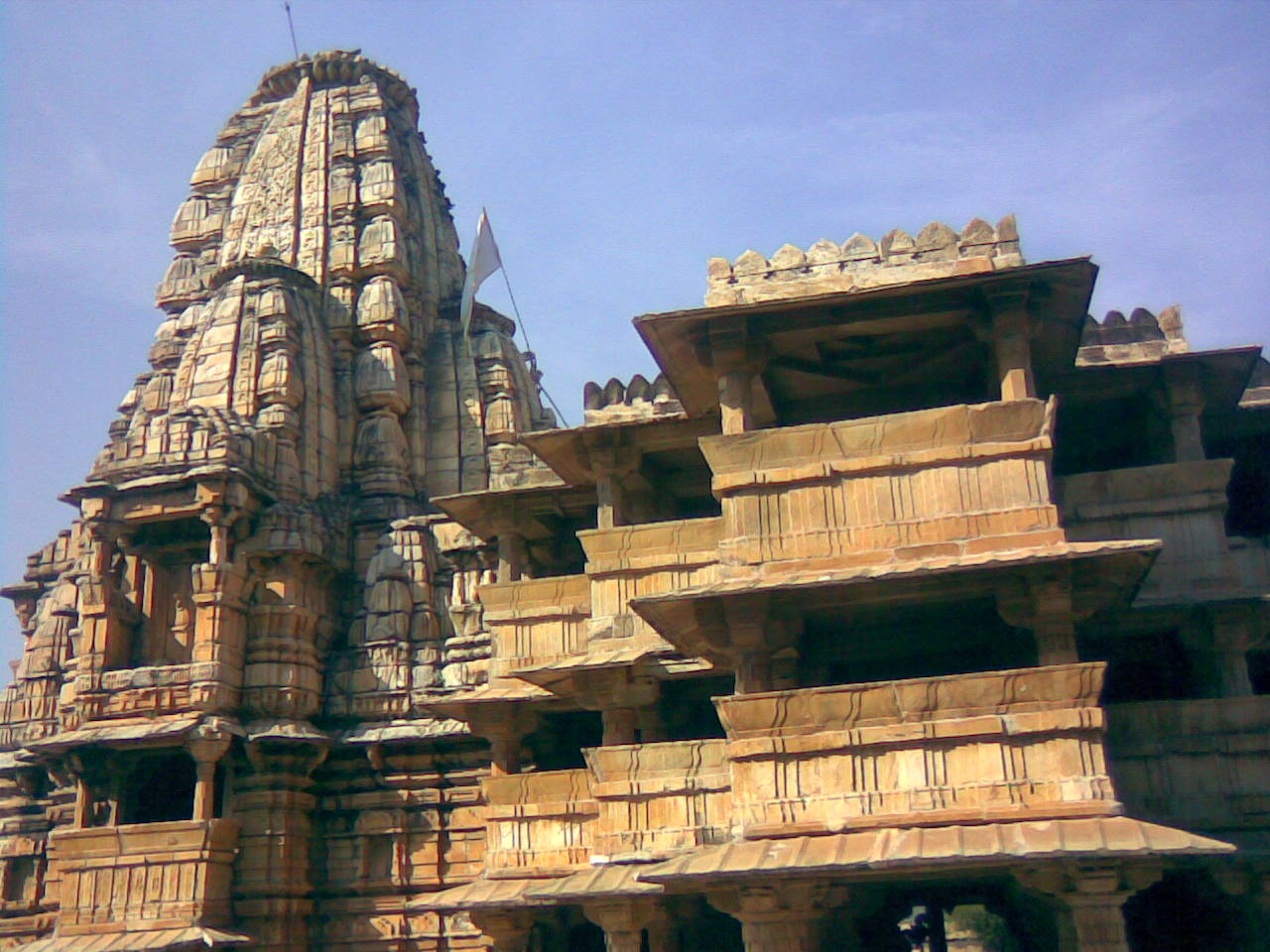
Banswara is a city in the Banswara district in southern Rajasthan, India. The name, Banswara, came from king ‘Bansiya Bhil’ Banswara is also known as "City of a Hundred Islands", "The Green City", which is often referred to as "Cherrapunji of Rajasthan", because it receives the most rain in Rajasthan, as well as for the numerous islands in the Mahi River, often referred to as "Mahati", an alternate name for Mahi river, in Vayu Purana text, which flows through the city. It is the greenest city in Rajasthan due to the heavy rainfall which it receives. The city has a population of 101,017, of whom 51,585 are male and 49,432 are female. History Banswara ("the bamboo city") was a Rajput feudatory state in Rajputana in British India. It borders Gujarat and was bounded on the north by the princely states of Dungarpur and Udaipur or Mewar; on the northeast and east by Partapgarh; on the south by the dominions of Holkar and the state of Jabua and on the west by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vayu Purana
The ''Vayu Purana'' ( sa, वायुपुराण, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas of Hinduism. ''Vayu Purana'' is mentioned in the manuscripts of the Mahabharata and other Hindu texts, which has led scholars to propose that the text is among the oldest in the Puranic genre. Vayu and Vayaviya Puranas do share a very large overlap in their structure and contents, possibly because they once were the same, but with continuous revisions over the centuries, the original text became two different texts, and the Vayaviya text came also to be known as the ''Brahmanda Purana''. The ''Vayu Purana'', according to the tradition and verses in other Puranas, contains 24,000 verses (shlokas). However, the surviving manuscripts have about 12,000 verses. The text was continuously revised over the centuries, and its extant manuscripts are very different. Some manuscripts have four ''padas'' (parts) with 112 chapters, and some two ''khandas'' with 111 chapters. Compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagad
Vagad (also known as Vagar, Hindi: वागड) is a region in southeastern Rajasthan state of western India. Its boundaries are roughly defined by those of the districts of Dungarpur and Banswara. Major cities of the region are Dungarpur and Banswara. Geography Vagad is bounded on the north by Mewar region of Rajasthan, on the southeast and eastby Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh, and on the west and southwest by Gujarat state. The region mostly lies in the upper watershed of the Mahi River and its tributaries, which is said to be the lifeline of Vagad. The Mahi flows north through the district (Banswara) from its origin in the Vindhya Range of Madhya Pradesh, entering the district (Banswara) from the southeast and flowing north towards the northern end of the district, where it turns southwest to form the boundary between Banswara and Dungarpur districts before entering Gujarat and emptying into the Gulf of Cambay. Vagad has rich flora and fauna. The forests include mainly tea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rewa Kantha
Rewa Kantha was a political agency of British India, managing the relations (indirect rule) of the British government's Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states. It stretched for about 150 miles between the plain of Gujarat and the hills of Malwa, from the Tapti River to the Mahi River crossing the Rewa (or Narmada) River, from which it takes its name. The political agent, who was also District collector of the ''prant'' (British District) of the Panchmahal, resided at Godhra. History The native states came under British subsidiary alliances after the Third Anglo-Maratha War of the early 19th century. The total surface was 4,971.75 square miles, comprising 3,412 villages, with a population of 479,055, yielding 2,072,026 Rupeese state revenue and paying 147,826 Rupees tribute (mostly to the Gaikwar Baroda State). In 1937 the princely states of the Rewa Kantha Agency were merged with Baroda State in order to form the Baroda and Gujarat States Agency, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
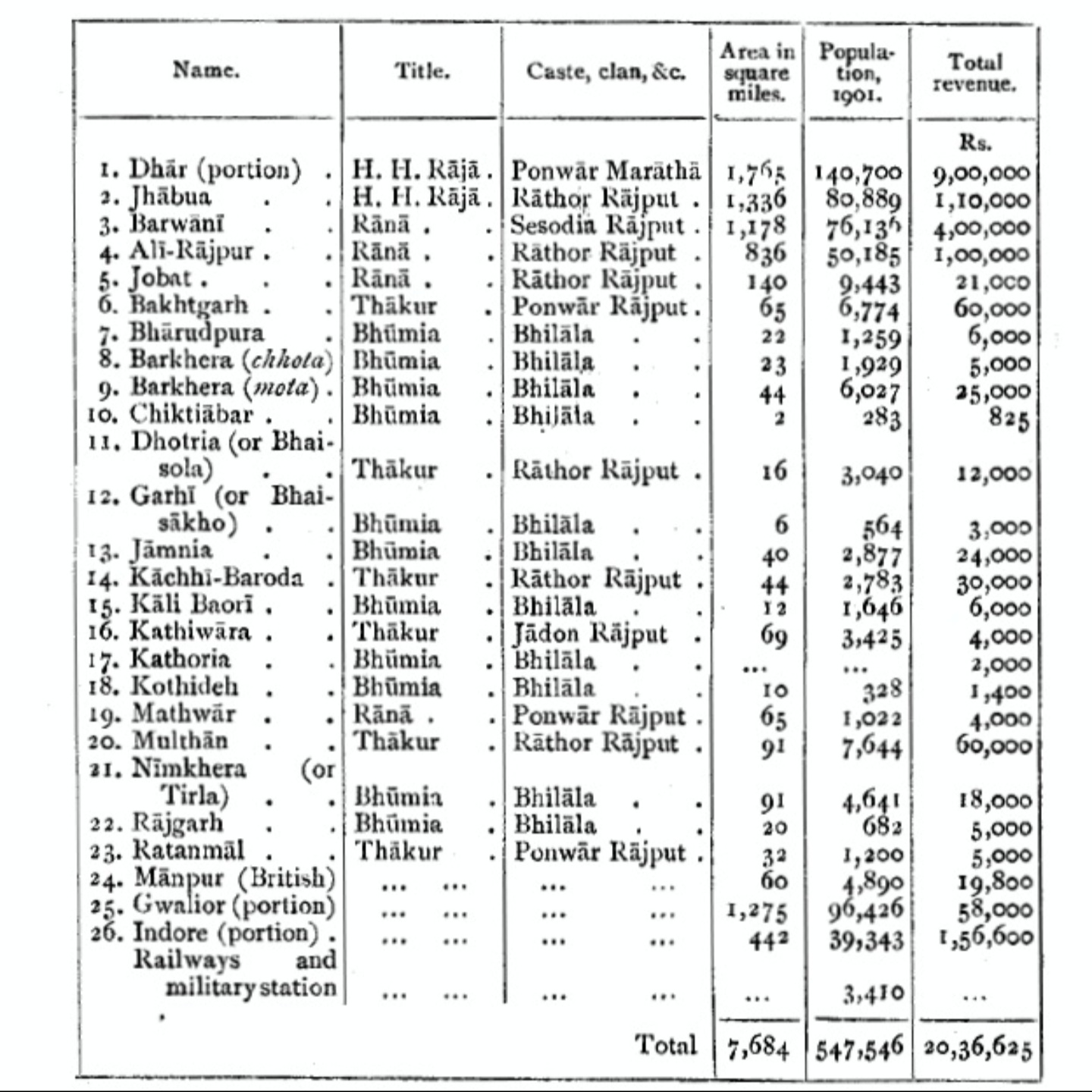
Jhabua State
Jhabua State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It had its capital in Jhabua town. Most of the territory of the princely state was inhabited by the Bhil people, who constituted a majority of the population. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs.1,10,000. History The state of Jhabua was founded by Kesho Das or Kishan Das, in 1584. He was granted the title of ''Raja'' by Mughal Emperor Akbar as a reward for a successful campaign in Bengal, and for punishing the Bhil Chiefs of Jhabua Labana, who had murdered the wife and daughters of the Imperial Viceroy of Gujarat. Khushal Singh was the ruler of Jhabua in 1698, he gave much of his lands to his brothers and sons and was too weak to rule his state effectively. This allowed the Marathas to actively invade Jhabua on a regular basis. Raja Shiv Singh was an infant and therefore the states administration during this time was managed by the raja's mother and the nobles. The Marathas under Holk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indore State
Indore State, also known as Holkar State, was a kingdom in India. Its rulers belonged to the Holkar dynasty. After 1857, Indore became a 19-gun salute Maratha princely state (a rare high rank) under the British Raj. Indore state was located in the present-day Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. The capital of the state was the city of Indore. The state had an area of 24,605 km2 and a population of 1,325,089 in 1931. Other important towns besides Indore were Rampura, Khargone, Maheshwar, Mehidpur, Barwaha, and Bhanpura; there were a total of 3,368 villages. History By 1720, the headquarters of the local ''pargana'' (an Indian local administrative unit) was transferred from Kampel to Indore due to the increasing commercial activity in the city. On 18 May 1724, the ''Nizam'' accepted the rights of the Maratha Peshwa Baji Rao I to collect ''chauth'' (taxes) from the area. In 1733, the ''Peshwa'' assumed full control of Malwa and appointed his commander Malhar Rao Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratapgarh District, Rajasthan
Pratapgarh district is the 33rd district of Rajasthan, created on 26 January 2008. It is a part of Udaipur Division and has been carved out from the erstwhile tehsils of Chittorgarh, Udaipur and Banswara districts. Pratapgarh town (Pin Code 312605, STD Code 01478) is the administrative headquarters of the district. History The rulers of 'Partabgadh-Raj' were descendants of Sisodia clan of Mewar Rajputs. Vasundhara Raje, the then Chief Minister of Rajasthan, announced Pratapgarh to be an independent district in 2008. Well known for pure gold and glass-inlay handmade unique jewellery called " Thewa", Pratapgarh, as the 33rd district of Rajasthan, came into existence on 26 January 2008, comprising five Tehsils/ sub-divisions, Pratapgarh, Chhotee Sadri, Dhariyawad, Arnod and Peepalkhoont. The district is dotted with ''good number of ancient and historical sites'', but in want of a detailed study either by the Archaeological Survey of India or by the Department of Archaeology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Mandsaur of Madhya Pradesh and some parts of Gujarat. For centuries, the region was ruled by Rajputs. The princely state of Udaipur emerged as an administrative unit during the period of British East India Company governance in India and remained until the end of the British Raj era. The Mewar region lies between the Aravali Range to the northwest, Ajmer to the north, Gujarat and the Vagad region of Rajasthan to the south, the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh state to the south and the Hadoti region of Rajasthan to the east. Etymology The word "Mewar" is vernacular form of "Medapata" ( IAST: Medapāṭa), the ancient name of the region. The earliest epigraph that mentions the word "Medapata" is a 996–997 CE (1053 VS) inscription discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of the kingdom of Mewar in the former Rajputana Agency. It was founded in 1559 by Udai Singh II of the Sisodia clan of Rajput, when he shifted his capital from the city of Chittorgarh to Udaipur after Chittorgarh was besieged by Akbar. It remained as the capital city till 1818 when it became a British princely state, and thereafter the Mewar province became a part of Rajasthan when India gained independence in 1947. The city is located in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, near the Gujarat border. It is surrounded by the Aravali Range, which separates it from the Thar Desert. It is placed almost in the middle of two major Indian metro cities, around 660 km from Delhi and 800 km from Mumbai. Besides, connectivity with Gujar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungarpur
Dungarpur is a city in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Dungarpur District. It is the fastest developing town in the southern part of Rajasthan, alongside Aspur ''tehsil''. History Dungarpur is the seat of the elder branch of the Guhilot of Mewar family. The seat of the younger branch is that of the Maharana of Udaipur, Rajasthan, Udaipur. The city was founded in 1282 A.D. by Rawal Veer Singh, who was the eldest son of the ruler of Mewar, Karan Singh.Dungarpur, History and Genealogy ''Queensland University''. They are descendants of Bappa Rawal, eighth ruler of the Guhilot dynasty and founder of the Mewar dynasty (r. 734–753). The chiefs of Dungarpur bear the title of ''Maharawal'' as they are descendants of Mahup, the eldest son of Karan Singh, the chief of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_in_Indore%2C_MP_(5102818067).jpg)




