|
Bald Knoll
Bald Knoll, also called Black Knoll, Buck Knoll or Corral Knoll, is a cinder cone in Utah, in the Southwestern United States. It is the youngest volcano at the southwest portion of the Paunsaugunt Plateau and it consists of basaltic lava with a well-preserved volcanic crater A volcanic crater is an approximately circular depression in the ground caused by Volcano, volcanic activity. It is typically a bowl-shaped feature containing one or more vents. During Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, molten magm ... at its summit. References Volcanoes of Utah Cinder cones of the United States Basin and Range Province Landforms of Kane County, Utah {{Utah-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In The United States
A list of volcanoes in the United States and its territories. Alaska American Samoa Arizona California Colorado Hawaii /[./[Https://www.sci.news/geology/puhahonu-shield-volcano-08435.html Puhahonu - - - Unknown Idaho Illinois Louisiana Michigan Mississippi Missouri Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico Sierra Grande -. -. -. 2.41 to 2.88 million years ago Northern Mariana Islands Oregon Texas Utah Virginia Washington Wyoming See also *Geothermal energy in the United States *List of Cascade volcanoes * List of large volume volcanic eruptions in the Basin and Range Province * List of volcanoes in Canada *List of volcanoes in Mexico *List of volcanoes in Russia *List of volcanic craters in Alaska *List of volcanic craters in Ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
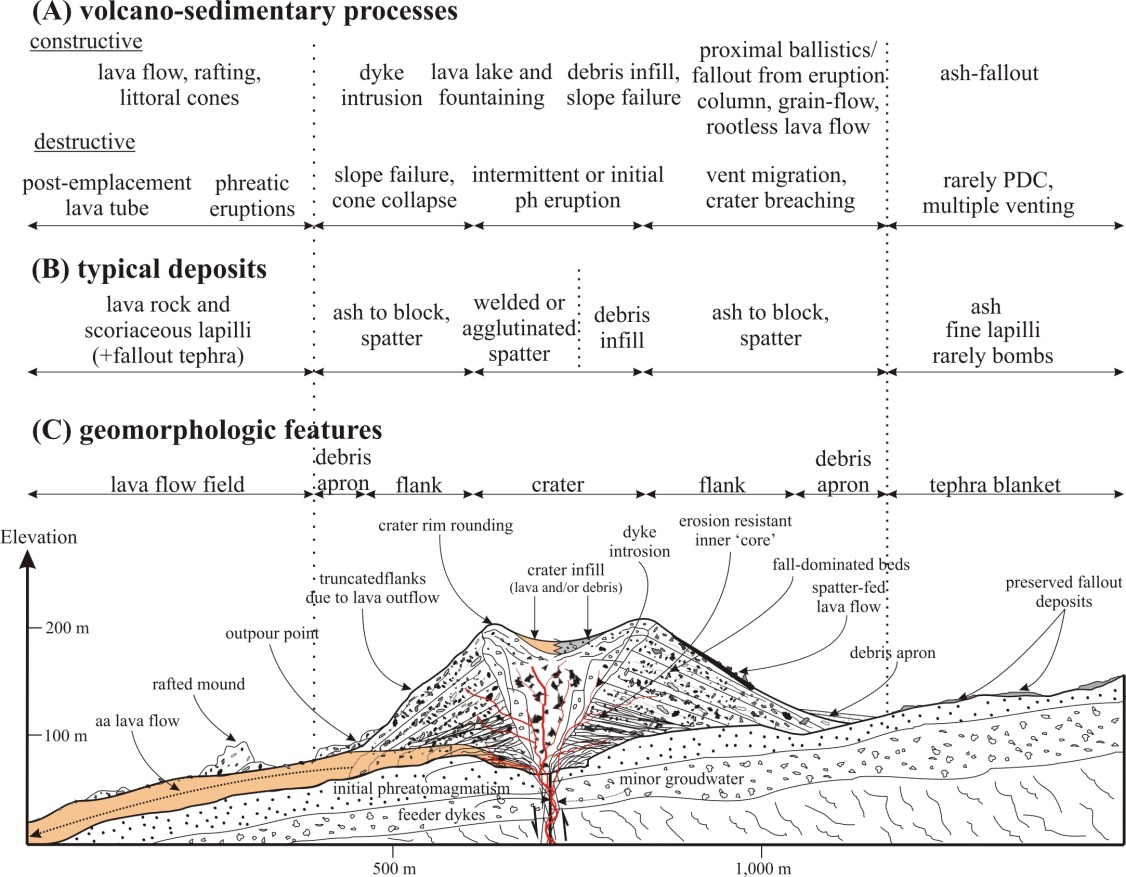
Cinder Cone
A cinder cone (or scoria cone) is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30 and 40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. Mechanics of eruption Cinder cones range in size from tens to hundreds of meters tall and often have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. They are composed of loose pyroclastic material (cinder or scoria), which distinguishes them from ''spatter cones'', which are composed of agglomerated volcanic bombs. The pyroclastic material making up a cinder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinder Cone
A cinder cone (or scoria cone) is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30 and 40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. Mechanics of eruption Cinder cones range in size from tens to hundreds of meters tall and often have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. They are composed of loose pyroclastic material (cinder or scoria), which distinguishes them from ''spatter cones'', which are composed of agglomerated volcanic bombs. The pyroclastic material making up a cinder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its west by Nevada. Utah also touches a corner of New Mexico in the southeast. Of the fifty U.S. states, Utah is the 13th-largest by area; with a population over three million, it is the 30th-most-populous and 11th-least-densely populated. Urban development is mostly concentrated in two areas: the Wasatch Front in the north-central part of the state, which is home to roughly two-thirds of the population and includes the capital city, Salt Lake City; and Washington County in the southwest, with more than 180,000 residents. Most of the western half of Utah lies in the Great Basin. Utah has been inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous groups such as the ancient Puebloans, Navajo and Ute. The Spanish were the first Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by metropolitan area are Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson. Prior to 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of Nuevo México's Pueblos and Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854. While the region's boundaries are not officially defined, there have been attempts to do so. One such definition is from the Mojave Desert in California in the west (117° west longitude) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paunsaugunt Plateau
The Paunsaugunt Plateau (pronounced "PAWN-suh-gant") is a dissected plateau, rising to an elevation of , in southwestern Utah in the United States. Located in northern Kane County and southwestern Garfield County, it is approximately wide, and extends southward from the Sevier Plateau approximately , terminating in the Pink Cliffs at the southern end. It is drained by the East Fork Sevier River which flows northward on the plateau, to the meet the main branch (Sevier River) which flows in a valley along the western side of the plateau. The plateau is highly dissected along the eastern flank, which is drained by the Paria River in the Colorado River watershed, and is protected as Bryce Canyon National Park. A section of the Great Basin Divide is along the plateau, and much of the plateau is part of Dixie National Forest. The plateau receives approximately of snow per year and experiences approximately 200 days of freeze-and-thaw cycles. Utah's Highway 12, an All-American Roa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater
A volcanic crater is an approximately circular depression in the ground caused by Volcano, volcanic activity. It is typically a bowl-shaped feature containing one or more vents. During Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, molten magma and volcanic gases rise from an underground magma chamber, through a conduit, until they reach the crater's vent, from where the gases escape into the atmosphere and the magma is erupted as lava. A volcanic crater can be of large dimensions, and sometimes of great depth. During certain types of explosive eruptions, a volcano's magma chamber may empty enough for an area above it to subside, forming a type of larger depression known as a caldera. Geomorphology In most volcanoes, the crater is situated at the top of a mountain formed from the erupted volcanic deposits such as lava flows and tephra. Volcanoes that terminate in such a summit crater are usually of a conical form. Other volcanic craters may be found on the flanks of volcanoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Utah
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinder Cones Of The United States
Cinder is an alternate term for scoria. Cinder or Cinders may also refer to: In computing *Cinder (programming library), a C++ programming library for visualization *Cinder, OpenStack's block storage component *Cyber Insider Threat, CINDER, a digital threat method Other uses *Ember, also called cinder * ''Cinder'' (album), by the Dirty Three *Cinder (bear), a bear rescued with burns after 2014 wildfires in Washington, United States * ''Cinders'' (1913 film), a 1913 silent film * ''Cinders'' (1920 film), a 1920 film starring Hoot Gibson * ''Cinders'' (1926 film), a 1926 British film starring Betty Balfour * ''Cinder'' (novel), a novel by Marissa Meyer ** Linh Cinder, the character from the novel and ''The Lunar Chronicles'' series *Cinder (Killer Instinct), a character in ''Killer Instinct'' * ''Cinders'' (visual novel), a 2012 visual novel adaption of Cinderella by MoaCube *Cinder toffee, a British name for honeycomb toffee *Cinder, American hard rock band formerly signed to Gef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basin And Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins. The physiography of the province is the result of tectonic extension that began around 17 million years ago in the early Miocene epoch. The numerous ranges within the province in the United States are collectively referred to as the "Great Basin Ranges", although many are not actually in the Great Basin. Major ranges include the Snake Range, the Panamint Range, the White Mountains, and the Sandia Mountains. The highest point fully within the province is White Mountain Peak in California, while the lowest point is the Badwater Basin in Death Valley at . The province's climate is arid, with numerous ecoregions. Most North American deserts are located within it. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |