Southwestern United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural
 The geography of the region is mainly made up of four features: the Mojave, Sonoran, and
The geography of the region is mainly made up of four features: the Mojave, Sonoran, and  Formed approximately 8000 years ago, the Chihuahuan Desert is a relatively dry desert, although it is slightly wetter than the Sonoran Desert to the west. The Chihuahuan Desert spreads across the southeastern portion of the region, covering from southeastern Arizona, across southern New Mexico, and the portion of western Texas included in the Southwest. While it is the second largest desert in the United States, only a third of the desert is within the United States, with the rest in Mexico. El Paso and Albuquerque are the major US cities in this desert, with other smaller cities being Las Cruces and Roswell in New Mexico and Willcox in Arizona.
The elevation in the Chihuahuan varies from about , as there are several larger mountain ranges, such as the
Formed approximately 8000 years ago, the Chihuahuan Desert is a relatively dry desert, although it is slightly wetter than the Sonoran Desert to the west. The Chihuahuan Desert spreads across the southeastern portion of the region, covering from southeastern Arizona, across southern New Mexico, and the portion of western Texas included in the Southwest. While it is the second largest desert in the United States, only a third of the desert is within the United States, with the rest in Mexico. El Paso and Albuquerque are the major US cities in this desert, with other smaller cities being Las Cruces and Roswell in New Mexico and Willcox in Arizona.
The elevation in the Chihuahuan varies from about , as there are several larger mountain ranges, such as the  When people think of the desert southwest, the landscape of the Sonoran Desert is what mostly comes to mind. The Sonoran Desert makes up the southwestern portion of the Southwest; most of the desert lies in Mexico, but its United States component lies on the southeastern border of California, and the western 2/3 of southern Arizona. Rainfall averages between per year, and the desert's most widely known inhabitant is the
When people think of the desert southwest, the landscape of the Sonoran Desert is what mostly comes to mind. The Sonoran Desert makes up the southwestern portion of the Southwest; most of the desert lies in Mexico, but its United States component lies on the southeastern border of California, and the western 2/3 of southern Arizona. Rainfall averages between per year, and the desert's most widely known inhabitant is the  The Colorado Plateau varies from the large stands of forests in the west, including the largest stand of
The Colorado Plateau varies from the large stands of forests in the west, including the largest stand of 
 Human history in the Southwest begins with the arrival of the
Human history in the Southwest begins with the arrival of the  According to archeological finds, the Ancestral Pueblo people, also known as the Anasazi (although that term is becoming more and more disused), began settling in the area in approximately 1500 BC. Eventually, they would spread throughout the entire northern section of the Southwest. This culture would go through several different eras lasting from approximately 1500 BC through the middle of the 15th century AD: the Basketmaker I, II, and III phases followed by the Pueblo I, II, III, and IV. As the Puebloans transitioned from a nomadic lifestyle to one based on agriculture, their first domiciles were pithouses. The Mogollon culture developed later than the Puebloan, arising in the eastern area of the region at around 300 BC. Their range would eventually extend deep into what would become Mexico, and dominate the southeastern portion of the Southwest. Their settlements would evolve over time from pit-dwellings through pueblos and finally also incorporating cliff-dwellings. The Hohokam were the last of these ancestral cultures to develop, somewhere around AD 1, but they would grow to be the most populous of the three by AD 1300, despite being the smallest of the three in terms of area, covering most of the southwest portion. Beginning in approximately AD 600, the Hohokam began to develop an extensive series of irrigation canals; of the three major cultures in the Southwest, only the Hohokam developed irrigation as a means of watering their agriculture.
Not long after the Hohokam reached the height of their culture, all three major cultures in the Southwest began to decline for unknown reasons, although severe drought and encroachment from other peoples have been postulated. By the end of the 15th century, all three cultures had disappeared. The modern Indian tribes of the Isleta Pueblo, Isleta, Hopi, Zuni people, Zuni, Sandia Pueblo, Sandia, Cochiti Pueblo, Cochiti, Santa Ana Pueblo, Santa Ana, Taos Pueblo, Taos, Acoma Pueblo, Acoma, and Laguna Pueblo, Laguna trace their ancestry back to the ancestral Puebloans, while the Pima people, Akimel O'odham and Tohono O'odham people, Tohono O'odham claim descent from Hohokam. The area previously occupied by the Mogollon was taken over by an unrelated tribe, the Apache. While it is unclear whether any of the modern Indian tribes are descended from the Mogollon, some archeologists and historians believe that they mixed with Ancestral Puebloans and became part of the Hopi and Zuni.
According to archeological finds, the Ancestral Pueblo people, also known as the Anasazi (although that term is becoming more and more disused), began settling in the area in approximately 1500 BC. Eventually, they would spread throughout the entire northern section of the Southwest. This culture would go through several different eras lasting from approximately 1500 BC through the middle of the 15th century AD: the Basketmaker I, II, and III phases followed by the Pueblo I, II, III, and IV. As the Puebloans transitioned from a nomadic lifestyle to one based on agriculture, their first domiciles were pithouses. The Mogollon culture developed later than the Puebloan, arising in the eastern area of the region at around 300 BC. Their range would eventually extend deep into what would become Mexico, and dominate the southeastern portion of the Southwest. Their settlements would evolve over time from pit-dwellings through pueblos and finally also incorporating cliff-dwellings. The Hohokam were the last of these ancestral cultures to develop, somewhere around AD 1, but they would grow to be the most populous of the three by AD 1300, despite being the smallest of the three in terms of area, covering most of the southwest portion. Beginning in approximately AD 600, the Hohokam began to develop an extensive series of irrigation canals; of the three major cultures in the Southwest, only the Hohokam developed irrigation as a means of watering their agriculture.
Not long after the Hohokam reached the height of their culture, all three major cultures in the Southwest began to decline for unknown reasons, although severe drought and encroachment from other peoples have been postulated. By the end of the 15th century, all three cultures had disappeared. The modern Indian tribes of the Isleta Pueblo, Isleta, Hopi, Zuni people, Zuni, Sandia Pueblo, Sandia, Cochiti Pueblo, Cochiti, Santa Ana Pueblo, Santa Ana, Taos Pueblo, Taos, Acoma Pueblo, Acoma, and Laguna Pueblo, Laguna trace their ancestry back to the ancestral Puebloans, while the Pima people, Akimel O'odham and Tohono O'odham people, Tohono O'odham claim descent from Hohokam. The area previously occupied by the Mogollon was taken over by an unrelated tribe, the Apache. While it is unclear whether any of the modern Indian tribes are descended from the Mogollon, some archeologists and historians believe that they mixed with Ancestral Puebloans and became part of the Hopi and Zuni.
 Prior to the arrival of Europeans, the Southwestern United States was inhabited by a very large population of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indian tribes. The area once occupied by the ancestral Puebloans became inhabited by several American Indian tribes, the most populous of which were the Navajo people, Navajo, Ute people, Ute, Southern Paiute, and Hopi. The Navajo, along with the Hopi, were the earliest of the modern Indian tribes to develop in the Southwest. Around AD 1100 their culture began to develop in the Four Corners area of the region. The Navahos Pre-modern human migration, migrated from northwestern Canada and eastern Alaska, where the majority of Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan speakers reside. The Ute were found over most of modern-day Utah and Colorado, as well as northern New Mexico and Arizona. The Paiutes roamed an area which covered over 45,000 square miles of southern Nevada and California, south-central Utah, and northern Arizona. The Hopi settled the lands of the central and western portions of northern Arizona. Their village of Oraibi, Arizona, Oraibi, settled in approximately AD 1100, is, along with Acoma Pueblo, Acoma Sky City in New Mexico, one of the oldest continuously occupied settlements in the United States. The Mogollon area became occupied by the Apaches and the Zuni. The Apache migrated into the American Southwest from the northern areas of North America at some point between 1200 and 1500. They settled throughout New Mexico, eastern Arizona, northern Mexico, parts of western Texas, and southern Colorado. The Zuni count their direct ancestry through the ancestral Puebloans. The modern-day Zuni established a culture along the Zuni River in far-eastern Arizona and western New Mexico. Both major tribes of the O'odham tribe settled in the southern and central Arizona, in the lands once controlled by their ancestors, the Hohokam.
Prior to the arrival of Europeans, the Southwestern United States was inhabited by a very large population of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indian tribes. The area once occupied by the ancestral Puebloans became inhabited by several American Indian tribes, the most populous of which were the Navajo people, Navajo, Ute people, Ute, Southern Paiute, and Hopi. The Navajo, along with the Hopi, were the earliest of the modern Indian tribes to develop in the Southwest. Around AD 1100 their culture began to develop in the Four Corners area of the region. The Navahos Pre-modern human migration, migrated from northwestern Canada and eastern Alaska, where the majority of Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan speakers reside. The Ute were found over most of modern-day Utah and Colorado, as well as northern New Mexico and Arizona. The Paiutes roamed an area which covered over 45,000 square miles of southern Nevada and California, south-central Utah, and northern Arizona. The Hopi settled the lands of the central and western portions of northern Arizona. Their village of Oraibi, Arizona, Oraibi, settled in approximately AD 1100, is, along with Acoma Pueblo, Acoma Sky City in New Mexico, one of the oldest continuously occupied settlements in the United States. The Mogollon area became occupied by the Apaches and the Zuni. The Apache migrated into the American Southwest from the northern areas of North America at some point between 1200 and 1500. They settled throughout New Mexico, eastern Arizona, northern Mexico, parts of western Texas, and southern Colorado. The Zuni count their direct ancestry through the ancestral Puebloans. The modern-day Zuni established a culture along the Zuni River in far-eastern Arizona and western New Mexico. Both major tribes of the O'odham tribe settled in the southern and central Arizona, in the lands once controlled by their ancestors, the Hohokam.
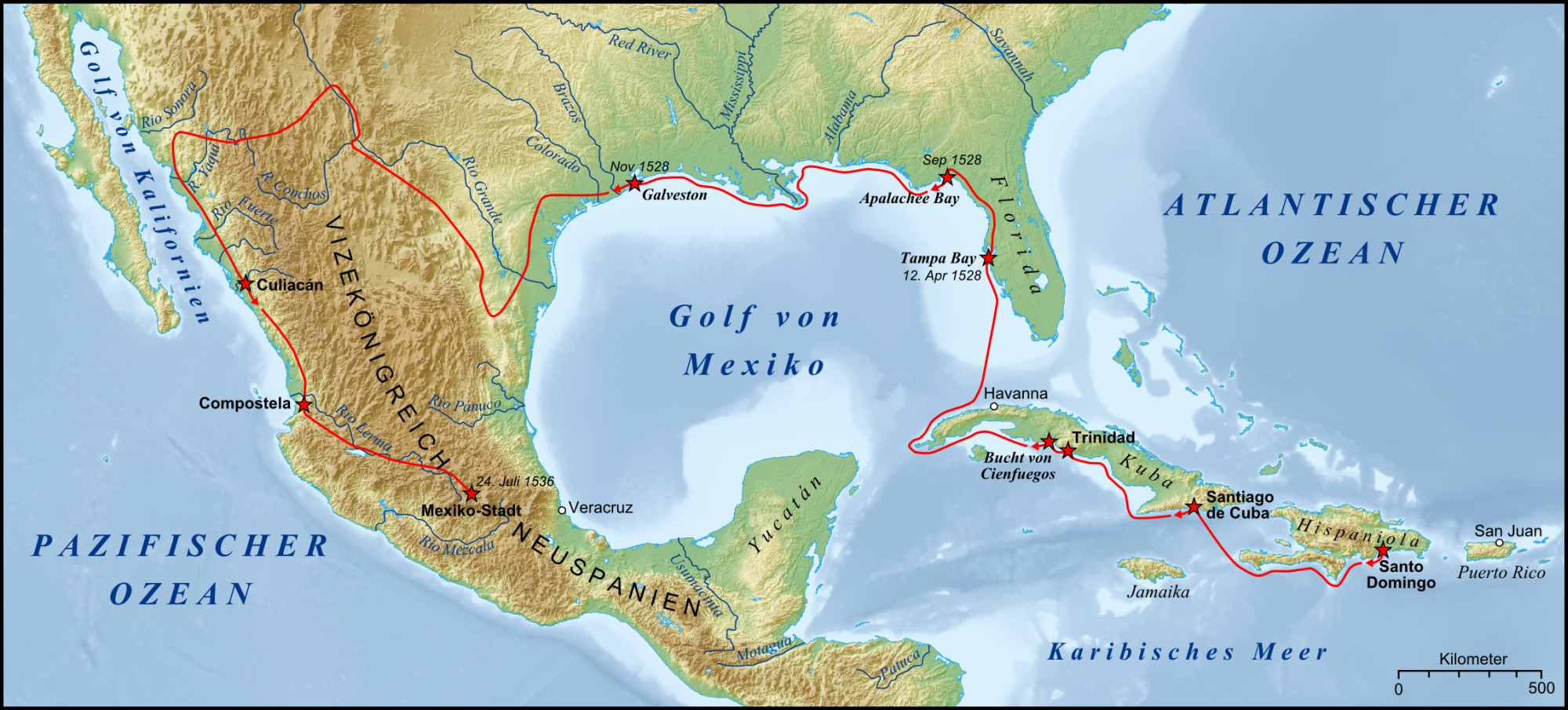 The first European intrusion into the region came from the south. In 1539, a Jesuit Franciscan named Marcos de Niza led an expedition from Mexico City which passed through eastern Arizona. The following year Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, based on reports from survivors of the Narváez expedition (1528–36) who had crossed eastern Texas on their way to Mexico City, led an expedition to discover the Seven Golden Cities of Cíbola. The 1582-3 expedition of Antonio de Espejo explored New Mexico and eastern Arizona; and this led to Juan de Oñate's establishment of the Spanish province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in 1598, with a capital founded near Ohkay Owingeh, New Mexico, Ohkay Oweenge Pueblo, which he called San Juan de los Caballeros. Oñate's party also attempted to establish a settlement in Arizona in 1599, but were turned back by inclement weather. In 1610, Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe was founded, making it the oldest capital in United States.
In 1664 Juan Archuleta led an expedition into what is now Colorado, becoming the first European to enter. A second Spanish expedition was led into Colorado by Juan Ulibarrí in 1706, during which he claimed the Colorado territory for Spain.
From 1687 to 1691 the Jesuit priest, Eusebio Kino established several missions in the Santa Cruz River (Arizona), Santa Cruz River valley; and Kino further explored southern and central Arizona in 1694, during which he discovered the ruins of Casa Grande. Beginning in 1732, Spanish settlers began to enter the region, and the Spanish started bestowing land grants in Mexico and the Southwest US. In 1751, the O'odham rebelled against the Spanish incursions, but the revolt was unsuccessful. In fact, it had the exact opposite effect, for the result of the rebellion was the establishment of the Presidio San Ignacio de Tubac, presidio at Tubac, Arizona, Tubac, the first permanent European settlement in Arizona.
In 1768, the Spanish created the Las Californias Province, Provincia de las Californias, which included California and the Southwest US. Over approximately the next 50 years, the Spanish continued to explore the Southwest, and in 1776 the City of Tucson was founded when the Presidio San Augustin del Tucson was created, relocating the presidio from Tubac.
In 1776, two Franciscan priests, Francisco Atanasio Domínguez and Silvestre Vélez de Escalante, led an Dominguez–Escalante Expedition, expedition from Santa Fe heading to California. After passing through Colorado, they became the first Europeans to travel into what is now Utah. Their journey was halted by bad weather in October, and they turned back, heading south into Arizona before turning east back to Santa Fe.
In 1804 Spain divided the Provincia de las Californias, creating the province
The first European intrusion into the region came from the south. In 1539, a Jesuit Franciscan named Marcos de Niza led an expedition from Mexico City which passed through eastern Arizona. The following year Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, based on reports from survivors of the Narváez expedition (1528–36) who had crossed eastern Texas on their way to Mexico City, led an expedition to discover the Seven Golden Cities of Cíbola. The 1582-3 expedition of Antonio de Espejo explored New Mexico and eastern Arizona; and this led to Juan de Oñate's establishment of the Spanish province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in 1598, with a capital founded near Ohkay Owingeh, New Mexico, Ohkay Oweenge Pueblo, which he called San Juan de los Caballeros. Oñate's party also attempted to establish a settlement in Arizona in 1599, but were turned back by inclement weather. In 1610, Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe was founded, making it the oldest capital in United States.
In 1664 Juan Archuleta led an expedition into what is now Colorado, becoming the first European to enter. A second Spanish expedition was led into Colorado by Juan Ulibarrí in 1706, during which he claimed the Colorado territory for Spain.
From 1687 to 1691 the Jesuit priest, Eusebio Kino established several missions in the Santa Cruz River (Arizona), Santa Cruz River valley; and Kino further explored southern and central Arizona in 1694, during which he discovered the ruins of Casa Grande. Beginning in 1732, Spanish settlers began to enter the region, and the Spanish started bestowing land grants in Mexico and the Southwest US. In 1751, the O'odham rebelled against the Spanish incursions, but the revolt was unsuccessful. In fact, it had the exact opposite effect, for the result of the rebellion was the establishment of the Presidio San Ignacio de Tubac, presidio at Tubac, Arizona, Tubac, the first permanent European settlement in Arizona.
In 1768, the Spanish created the Las Californias Province, Provincia de las Californias, which included California and the Southwest US. Over approximately the next 50 years, the Spanish continued to explore the Southwest, and in 1776 the City of Tucson was founded when the Presidio San Augustin del Tucson was created, relocating the presidio from Tubac.
In 1776, two Franciscan priests, Francisco Atanasio Domínguez and Silvestre Vélez de Escalante, led an Dominguez–Escalante Expedition, expedition from Santa Fe heading to California. After passing through Colorado, they became the first Europeans to travel into what is now Utah. Their journey was halted by bad weather in October, and they turned back, heading south into Arizona before turning east back to Santa Fe.
In 1804 Spain divided the Provincia de las Californias, creating the province

 Of the states of which at least a portion make up the Southwest, Texas was the first to achieve statehood. On December 29, 1845, the Republic of Texas was annexed, bypassing the status of becoming a territory, and immediately became a state. Initially, its borders included parts of what would become several other states: almost half of New Mexico, a third of Colorado, and small portions of Kansas, Oklahoma, and Wyoming. Texas current borders were set in the Compromise of 1850, where Texas ceded land to the federal government in exchange for $10 million, which would go to paying off the debt Texas had accumulated in its war with Mexico.
Following the Mexican Cession, the lands of what had been the Mexican territory of Alta California were in flux: portions of what is now New Mexico were claimed, but never controlled, by Texas. With the Compromise of 1850, the states of Texas and California were created (Texas as a slave state, and California as a free state), as well as the Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory. The New Mexico Territory consisted of most of Arizona and New Mexico (excluding a strip along their southern borders), a small section of southern Colorado, and the very southern tip of Nevada; while the Utah Territory consisted of Utah, most of Nevada, and portions of Wyoming and Colorado. The New Mexico Territory was expanded along its southern extent, to its current border, with the signing of the Gadsden Purchase Treaty on December 30, 1853, which was ratified by the U.S. Congress, with some slight alterations, in April 1854.
Of the states of which at least a portion make up the Southwest, Texas was the first to achieve statehood. On December 29, 1845, the Republic of Texas was annexed, bypassing the status of becoming a territory, and immediately became a state. Initially, its borders included parts of what would become several other states: almost half of New Mexico, a third of Colorado, and small portions of Kansas, Oklahoma, and Wyoming. Texas current borders were set in the Compromise of 1850, where Texas ceded land to the federal government in exchange for $10 million, which would go to paying off the debt Texas had accumulated in its war with Mexico.
Following the Mexican Cession, the lands of what had been the Mexican territory of Alta California were in flux: portions of what is now New Mexico were claimed, but never controlled, by Texas. With the Compromise of 1850, the states of Texas and California were created (Texas as a slave state, and California as a free state), as well as the Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory. The New Mexico Territory consisted of most of Arizona and New Mexico (excluding a strip along their southern borders), a small section of southern Colorado, and the very southern tip of Nevada; while the Utah Territory consisted of Utah, most of Nevada, and portions of Wyoming and Colorado. The New Mexico Territory was expanded along its southern extent, to its current border, with the signing of the Gadsden Purchase Treaty on December 30, 1853, which was ratified by the U.S. Congress, with some slight alterations, in April 1854.

 The Colorado Territory was organized on February 28, 1861, created out of lands then currently in the Utah, Kansas, Nebraska, and New Mexico territories. The Nevada Territory was also organized in 1861, on March 2, with land taken from the existing Utah Territory. Initially, only the western 2/3 of what is currently the State of Nevada was included in the territory, with its boundary to the east being the 39th meridian west from Washington, and to the south the 37th parallel north, 37th parallel. In 1862 Nevada's eastern border shifted to the 38th meridian west from Washington, and finally to its current position at the 37th meridian west from Washington in 1866. The boundary modification in 1866 also included adding the southern triangular tip of the present-day state, taken from the Arizona Territory.
From July 24–27, 1861 a Confederate force under the command of Lt. Colonel John Robert Baylor forced the surrender of the small Union garrison stationed at Fort Fillmore, near Mesilla, New Mexico. On August 1, 1861, Baylor declared the creation of the Confederate Arizona, Arizona Territory, and claimed it for the Confederacy, with Mesilla as its capital. The territory, which had been formed by the portion of the existing New Mexico Territory below the 34th parallel, became official on February 14, 1862.
The Colorado Territory was organized on February 28, 1861, created out of lands then currently in the Utah, Kansas, Nebraska, and New Mexico territories. The Nevada Territory was also organized in 1861, on March 2, with land taken from the existing Utah Territory. Initially, only the western 2/3 of what is currently the State of Nevada was included in the territory, with its boundary to the east being the 39th meridian west from Washington, and to the south the 37th parallel north, 37th parallel. In 1862 Nevada's eastern border shifted to the 38th meridian west from Washington, and finally to its current position at the 37th meridian west from Washington in 1866. The boundary modification in 1866 also included adding the southern triangular tip of the present-day state, taken from the Arizona Territory.
From July 24–27, 1861 a Confederate force under the command of Lt. Colonel John Robert Baylor forced the surrender of the small Union garrison stationed at Fort Fillmore, near Mesilla, New Mexico. On August 1, 1861, Baylor declared the creation of the Confederate Arizona, Arizona Territory, and claimed it for the Confederacy, with Mesilla as its capital. The territory, which had been formed by the portion of the existing New Mexico Territory below the 34th parallel, became official on February 14, 1862.

 Nevada was admitted to the Union on October 31, 1864, becoming the 36th state. This was followed by the admittance to the Union of Colorado, which became the 38th state on August 1, 1876. Confederate Arizona was short-lived, however. By May 1862, Confederate forces had been driven out of the region by union troops. That same month a bill was introduced into the U.S. Congress, and on February 24, 1863 Abraham Lincoln signed the Arizona Organic Act, which officially created the U.S. Arizona Territory, Territory of Arizona, splitting the New Mexico Territory at the 107th meridian.
Utah, as shown above, evolved out of the Utah Territory, as pieces of the original territory created in 1850 were carved out: parts were ceded to Nevada, Wyoming, and Colorado in 1861; another section to Nevada in 1862; and the final section to Nevada in 1866. In 1890, the LDS church issued the 1890 Manifesto, which officially banned polygamy for members of the church. It was the last roadblock for Utah entering the Union, and on January 4, 1896, Utah was officially granted statehood, becoming the 45th state.
In 1869, John Wesley Powell led a 3-month expedition which explored the Grand Canyon and the Colorado River. In 1875, he would publish a book describing his explorations, ''Report of the Exploration of the Columbia River of the West and Its Tributaries'', which was later republished as ''The Exploration of the Colorado River and Its Canyons''.
In 1877 silver was discovered in southeastern Arizona. The notorious mining town of Tombstone, Arizona was born to service the miners. The town would become immortalized as the scene of what is considered the greatest gunfight in the history of the Old West, the Gunfight at the O.K. Corral.
Copper was also discovered in 1877, near Bisbee, Arizona, Bisbee and Jerome, Arizona, Jerome in Arizona, which became an important component of the economy of the Southwest. Production began in 1880 and was made more profitable by the expansion of the railroad throughout the territory during the 1880s.
Nevada was admitted to the Union on October 31, 1864, becoming the 36th state. This was followed by the admittance to the Union of Colorado, which became the 38th state on August 1, 1876. Confederate Arizona was short-lived, however. By May 1862, Confederate forces had been driven out of the region by union troops. That same month a bill was introduced into the U.S. Congress, and on February 24, 1863 Abraham Lincoln signed the Arizona Organic Act, which officially created the U.S. Arizona Territory, Territory of Arizona, splitting the New Mexico Territory at the 107th meridian.
Utah, as shown above, evolved out of the Utah Territory, as pieces of the original territory created in 1850 were carved out: parts were ceded to Nevada, Wyoming, and Colorado in 1861; another section to Nevada in 1862; and the final section to Nevada in 1866. In 1890, the LDS church issued the 1890 Manifesto, which officially banned polygamy for members of the church. It was the last roadblock for Utah entering the Union, and on January 4, 1896, Utah was officially granted statehood, becoming the 45th state.
In 1869, John Wesley Powell led a 3-month expedition which explored the Grand Canyon and the Colorado River. In 1875, he would publish a book describing his explorations, ''Report of the Exploration of the Columbia River of the West and Its Tributaries'', which was later republished as ''The Exploration of the Colorado River and Its Canyons''.
In 1877 silver was discovered in southeastern Arizona. The notorious mining town of Tombstone, Arizona was born to service the miners. The town would become immortalized as the scene of what is considered the greatest gunfight in the history of the Old West, the Gunfight at the O.K. Corral.
Copper was also discovered in 1877, near Bisbee, Arizona, Bisbee and Jerome, Arizona, Jerome in Arizona, which became an important component of the economy of the Southwest. Production began in 1880 and was made more profitable by the expansion of the railroad throughout the territory during the 1880s.
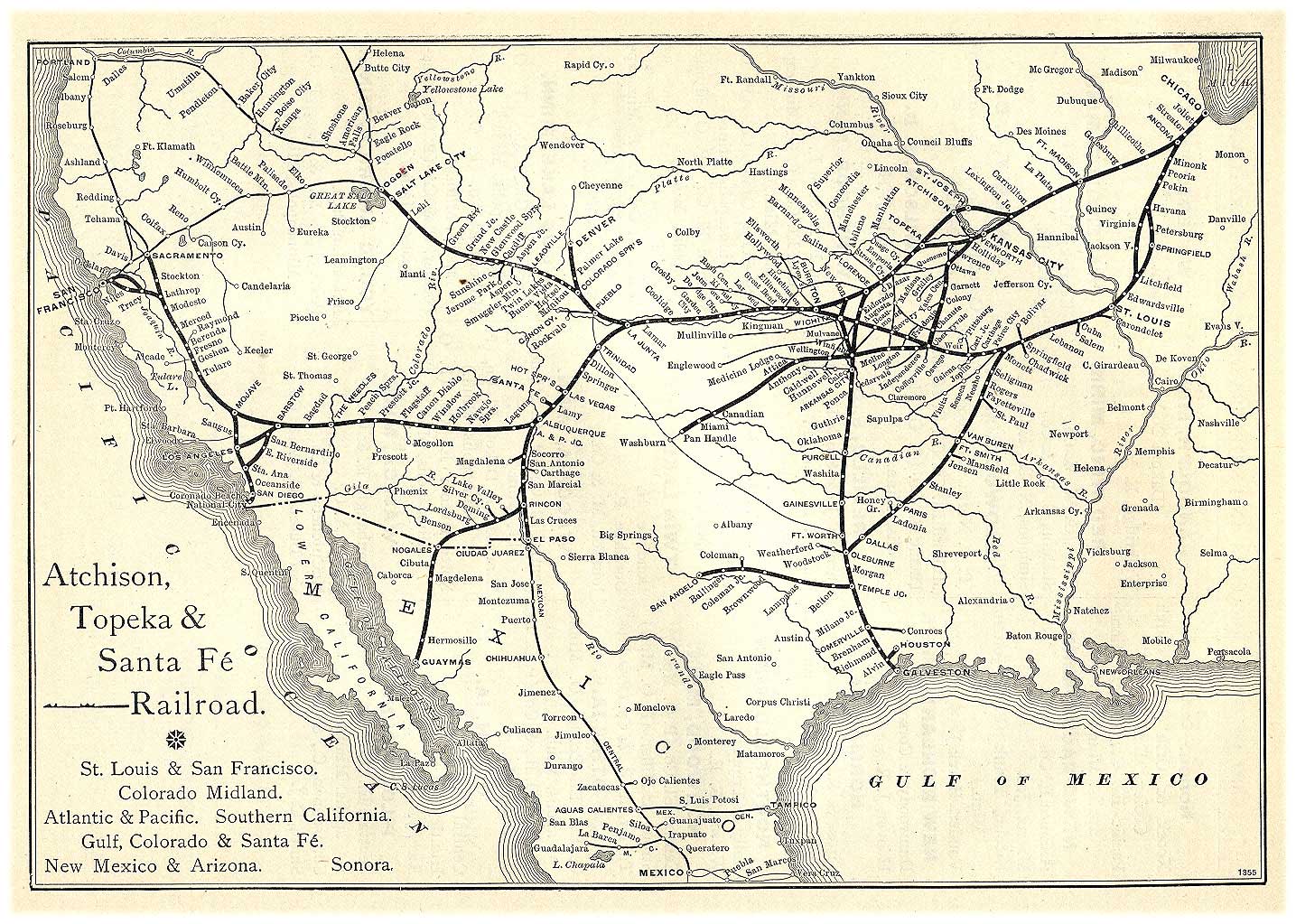 The early 1880s also saw the completion of the second transcontinental railroad, which ran through the heart of the Southwest, called the "Santa Fe Route". It ran from Chicago, down through Topeka, then further south to Albuquerque, before heading almost due west through northern Arizona to Los Angeles.
The repeal of the Sherman Silver Purchase Act in 1893 led to the decline of the silver mining industry in the region.
In 1901, the Santa Fe Railroad reached the South Rim of the Grand Canyon, opening the way for a tourism boom, a trend led by restaurant and hotel entrepreneur Fred Harvey (entrepreneur), Fred Harvey.
The last two territories within the Southwest to achieve statehood were New Mexico and Arizona. By 1863, with the splitting off of the Arizona Territory, New Mexico reached its modern borders. They became states within forty days of one another. On January 6, 1912, New Mexico became the 47th state in the Union. Arizona would shortly follow, becoming the last of the 48 contiguous United States on February 14, 1912.
The early 1880s also saw the completion of the second transcontinental railroad, which ran through the heart of the Southwest, called the "Santa Fe Route". It ran from Chicago, down through Topeka, then further south to Albuquerque, before heading almost due west through northern Arizona to Los Angeles.
The repeal of the Sherman Silver Purchase Act in 1893 led to the decline of the silver mining industry in the region.
In 1901, the Santa Fe Railroad reached the South Rim of the Grand Canyon, opening the way for a tourism boom, a trend led by restaurant and hotel entrepreneur Fred Harvey (entrepreneur), Fred Harvey.
The last two territories within the Southwest to achieve statehood were New Mexico and Arizona. By 1863, with the splitting off of the Arizona Territory, New Mexico reached its modern borders. They became states within forty days of one another. On January 6, 1912, New Mexico became the 47th state in the Union. Arizona would shortly follow, becoming the last of the 48 contiguous United States on February 14, 1912.
 The 1930s saw the beginning of the ski industry in the Southwest. Resorts were established in Colorado in areas such as Estes Park, Gunnison, Colorado#Winter, Gunnison, and on Loveland Pass. New Mexico's oldest ski area is Sandia Peak Ski Area at the eastern edge of Albuquerque, which opened to skiers in 1936. At the end of the decade, in 1939, with the establishment of Alta Ski Area, Development of Skiing in Utah, Utah's skiing began to be developed.
Due to the ski conditions in the state, during WWII, the 10th Mountain Division established Camp Hale in Colorado to train elite ski troops.
The 1930s saw the beginning of the ski industry in the Southwest. Resorts were established in Colorado in areas such as Estes Park, Gunnison, Colorado#Winter, Gunnison, and on Loveland Pass. New Mexico's oldest ski area is Sandia Peak Ski Area at the eastern edge of Albuquerque, which opened to skiers in 1936. At the end of the decade, in 1939, with the establishment of Alta Ski Area, Development of Skiing in Utah, Utah's skiing began to be developed.
Due to the ski conditions in the state, during WWII, the 10th Mountain Division established Camp Hale in Colorado to train elite ski troops.
 Parts of the other states make up the various areas that can be included in the Southwest, depending on the source. The Learning Center of the American Southwest (LCAS) does not rely on current state boundaries, and defines the American Southwest as parts of Arizona, Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah.
From this perspective, almost all of the region's physiographical traits, geological formations, and weather are contained within a box between 26° and 38° northern latitude, and 98° 30' and 124° western longitude.
Parts of the other states make up the various areas that can be included in the Southwest, depending on the source. The Learning Center of the American Southwest (LCAS) does not rely on current state boundaries, and defines the American Southwest as parts of Arizona, Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah.
From this perspective, almost all of the region's physiographical traits, geological formations, and weather are contained within a box between 26° and 38° northern latitude, and 98° 30' and 124° western longitude.
 Lawrence Clark Powell, a major bibliographer whose emphasis is on the Southwest, defined the American Southwest in a 1958 ''Arizona Highways'' article as, "the lands lying west of the Pecos, north of the [Mexican] Border, south of the Mesa Verde and the Grand Canyon, and east of the mountains which wall off Southern California and make it a land in itself."
Texas has long been the focal point of this dichotomy, and is often considered, as such, the ''core area'' of "the South's Southwest." While the Trans-Pecos area is generally acknowledged as part of the ''desert Southwest'', most of Texas and large parts of Oklahoma are often placed into a sub-region of the Southern United States, South, which some consider southwestern in the general framework of the original application, meaning the "Western South". This is an area containing the basic elements of Southern Confederate States of America, history, Culture of the Southern United States, culture, Solid South, politics, Bible Belt, religion, and Southern American English, linguistic and settlement patterns, yet blended with traits of the frontier West. While this particular Southwest is notably different in many ways from the classic "Old South" or Southeastern United States, Southeast, these features are strong enough to give it a separate southwestern identity quite different in nature from that of the interior southwestern states to the west.
One of these distinguishing characteristics in Texas—in addition to having been a Confederate States of America, Confederate state during the Civil War—is that Indigenous and Spanish American culture never played a central role in the development of this area in relative comparison to the others, as the vast majority of settlers were Anglo and blacks from the South.Cultural Regions of the United States. Raymond Gastil. University of Washington Press 1975 Although the present-day state of Oklahoma was Indian Territory until the early 20th century, many of these American Indians were from the southeastern United States and became culturally assimilated early on. The majority of members of these tribes also allied themselves with the Confederacy during the Civil War. Combined with that, once the territory was open for settlement, southeastern pioneers made up a disproportionate number of these newcomers. All this contributed to the new state having a character that differed from other parts of the Southwest with large American Indian populations.
The fact that a majority of residents of Texas and Oklahoma—unlike those in other "southwestern" states—self-identify as living in the South and consider themselves southerners rather than the West and westerners—also lends to treating these two states as a somewhat distinct and separate entity in terms of regional classification.
Lawrence Clark Powell, a major bibliographer whose emphasis is on the Southwest, defined the American Southwest in a 1958 ''Arizona Highways'' article as, "the lands lying west of the Pecos, north of the [Mexican] Border, south of the Mesa Verde and the Grand Canyon, and east of the mountains which wall off Southern California and make it a land in itself."
Texas has long been the focal point of this dichotomy, and is often considered, as such, the ''core area'' of "the South's Southwest." While the Trans-Pecos area is generally acknowledged as part of the ''desert Southwest'', most of Texas and large parts of Oklahoma are often placed into a sub-region of the Southern United States, South, which some consider southwestern in the general framework of the original application, meaning the "Western South". This is an area containing the basic elements of Southern Confederate States of America, history, Culture of the Southern United States, culture, Solid South, politics, Bible Belt, religion, and Southern American English, linguistic and settlement patterns, yet blended with traits of the frontier West. While this particular Southwest is notably different in many ways from the classic "Old South" or Southeastern United States, Southeast, these features are strong enough to give it a separate southwestern identity quite different in nature from that of the interior southwestern states to the west.
One of these distinguishing characteristics in Texas—in addition to having been a Confederate States of America, Confederate state during the Civil War—is that Indigenous and Spanish American culture never played a central role in the development of this area in relative comparison to the others, as the vast majority of settlers were Anglo and blacks from the South.Cultural Regions of the United States. Raymond Gastil. University of Washington Press 1975 Although the present-day state of Oklahoma was Indian Territory until the early 20th century, many of these American Indians were from the southeastern United States and became culturally assimilated early on. The majority of members of these tribes also allied themselves with the Confederacy during the Civil War. Combined with that, once the territory was open for settlement, southeastern pioneers made up a disproportionate number of these newcomers. All this contributed to the new state having a character that differed from other parts of the Southwest with large American Indian populations.
The fact that a majority of residents of Texas and Oklahoma—unlike those in other "southwestern" states—self-identify as living in the South and consider themselves southerners rather than the West and westerners—also lends to treating these two states as a somewhat distinct and separate entity in terms of regional classification.

 Landscape features of the core southwestern areas include mountains, canyons, mesas, buttes, high broad basins, plateaus, desert lands, and some plains, characteristic of the Basin and Range Province. The entire southwestern region features semi-arid to arid terrain. The far eastern part of southwestern Texas, for example, the Texas Hill Country, consists of dry, tall, and rugged rocky hills of limestone and granite. South Texas and the Lower Rio Grande Valley, Rio Grande Valley is mostly flat with many places consisting of scrub and bare topsoil, much like the deserts further west.
Landscape features of the core southwestern areas include mountains, canyons, mesas, buttes, high broad basins, plateaus, desert lands, and some plains, characteristic of the Basin and Range Province. The entire southwestern region features semi-arid to arid terrain. The far eastern part of southwestern Texas, for example, the Texas Hill Country, consists of dry, tall, and rugged rocky hills of limestone and granite. South Texas and the Lower Rio Grande Valley, Rio Grande Valley is mostly flat with many places consisting of scrub and bare topsoil, much like the deserts further west.
 Mammal species include the bobcat, coyote, American black bear, black bear, black-tailed jackrabbit, desert cottontail, desert bighorn sheep, mule deer, white-tailed deer, gray fox, Cougar, mountain lion, North American river otter, river otter, long-tailed weasel, western spotted skunk, pronghorn, raccoon, and Ord's kangaroo rat, all of which can be found in parts of every southwestern state. Elk are found in parts of Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Arizona. White-nosed coati, coati, and collared peccaryor ''javelina''in the Southwest are normally found in southern areas of Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas near the Mexican border. Jaguars can be found in the New Mexico Bootheel, bootheel region of Southwestern New Mexico. The Mexican wolf (''Canis lupus baileyi'') was reintroduced to Arizona and New Mexico in 1998.Paquet, P. & Carbyn, L. W. (2003). Gray wolf ''Canis lupus'' and allies", in Feldhamer, George A. et al. ''Wild Mammals of North America: Biology, Management, and Conservation'', JHU Press, pp. 482–510, A U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service study reported a minimum population of 109 Mexican wolves in southwest New Mexico and southeast Arizona at the end of 2014.
There is a large contingent of snakes native to the region. Among them include the rosy boa (''Lichanura trivirgata''); several sub-species of the glossy snake (''Arizona elegans''); the Bogertophis subocularis, Trans-Pecos ratsnake (''Bogertophis subocularis''); several sub-species of shovel-nosed snakes; several sub-species of kingsnake, including the desert kingsnake (''Lampropeltis getula splendida'') and the Lampropeltis pyromelana, Arizona mountain kingsnake (''Lampropeltis pyromelana''); the Micruroides, Arizona coral snake (''Micruroides euryxanthus''); the Crotalus atrox, western diamondback rattlesnake (''Crotalus atrox''); the Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster, Trans-Pecos copperhead (''Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster''); the Crotalus cerastes cercobombus, Sonoran sidewinder (''Crotalus cerastes cercobombus''); the Crotalus cerberus, Arizona black rattlesnake (''Crotalus oreganus cerberus''); the Crotalus viridis, western rattlesnake (''Crotalus viridis''); the Crotalus oreganus abyssus, Grand Canyon rattlesnake (''Crotalus oreganus abyssus''), found only in Arizona; several sub-species of the Crotalus willardi, ridge-nosed rattlesnake (''Crotalus willardi''), the most recent rattlesnake species to be discovered in the United States, including the Crotalus willardi obscurus, New Mexico ridge-nosed rattlesnake (''Crotalus willardi obscurus''), and the Arizona ridge-nosed rattlesnake, the state reptile of Arizona; and the Sistrurus catenatus edwardsii, desert massasauga (''Sistrurus catenatus edwardsii'').
Other reptiles in the region include lizards and turtles. Lizards are highly represented in the region, the most distinctive denizen being the Gila monster, native only to the American Southwest and the state of Sonora in Mexico. The New Mexico whiptail is the List of state symbols of New Mexico, state reptile of New Mexico. Other lizards include: Sonoran collared lizard (''Crotaphytus nebrius''); several types of geckos, including western banded gecko (''Coleonyx variegatus''), the common house gecko (''Hemidactylus frenatus''), and the Mediterranean house gecko (''Hemidactylus turcicus''), the last two species being non-native to the region but have been introduced; the desert iguana (''Dipsosaurus dorsalis''); the chuckwalla (''Sauromalus ater''); the greater earless lizard (''Cophosaurus texanus scitulus''); several sub-species of horned lizards (''Phrynosoma''); numerous species of spiny lizards (''Sceloporus''); Gilbert's skink (''Plestiodon gilberti''); the western skink (''Plestiodon skiltonianus''); Trans-Pecos striped whiptail (''Aspidoscelis inornata heptagrammus''); and the Arizona night lizard (''Xantusia arizonae''). Turtles are less numerous than their other reptilian counterparts, but several are found in the region, including: the Painted turtle#Western painted turtle, western painted turtle (''Chrysemys picta bellii''); the Rio Grande cooter (''Pseudemys gorzugi''); the desert box turtle (''Terrapene ornata luteola''); the Big Bend slider (''Trachemys gaigeae gaigeae''); the Sonora mud turtle (''Kinosternon sonoriense''); and the desert tortoise (''Gopherus agassizii'').
Amphibians include numerous toads and frogs in the American Southwest. Toads which can be found in the region include the Great Plains toad (''Anaxyrus cognatus''); the Anaxyrus debilis, green toad (''Anaxyrus debilis''); the Arizona toad (''Anaxyrus microscaphus''); the New Mexico spadefoot toad, New Mexico spadefoot (''Spea multiplicata stagnalis''); and the Colorado River toad (''Incilius alvarius''), also known as the Sonoran Desert toad. Frog representation includes: Craugastor augusti, western barking frog (''Craugastor augusti''); the canyon tree frog (''Hyla arenicolor''); the Wright's mountain tree frog, Arizona treefrog (''Hyla wrightorum''); the western chorus frog (''Pseudacris triseriata''); Chiricahua leopard frog (''Lithobates chiricahuensis''); and the relict leopard frog (''Lithobates onca''). There are quite a few salamanders throughout the region, including: the barred tiger salamander#Subspecies, Arizona tiger salamander (''Ambystoma mavortium nebulosum'') and the Ensatina#Subspecies, painted ensatina (''Ensatina eschscholtzii picta'').
Despite the Southwest being mostly arid, various fishes are found where water is available, including various species unique to the region. Apache trout and Gila trout are two Salmonidae, salmonids endemic to the area, with the former found only in Arizona and the latter only in Arizona and New Mexico. Desert pupfishes are several closely related species of fish in the genus Cyprinodon, many of which are found in isolated spring-fed ponds hundreds of miles from each other, ranging from far West Texas to Death Valley in California. These pupfishes often thrive in water considerably higher in temperature and dissolved solids than most fish can tolerate. Many of these desert fish species are endangered due to their limited and tenuous habitat, as well as loss of habitat due to human consumption of groundwater and diversion of surface water, as well as the introduction of species such as sportfish for recreation (see: Rio Grande Silvery Minnow v. Bureau of Reclamation).
Mammal species include the bobcat, coyote, American black bear, black bear, black-tailed jackrabbit, desert cottontail, desert bighorn sheep, mule deer, white-tailed deer, gray fox, Cougar, mountain lion, North American river otter, river otter, long-tailed weasel, western spotted skunk, pronghorn, raccoon, and Ord's kangaroo rat, all of which can be found in parts of every southwestern state. Elk are found in parts of Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Arizona. White-nosed coati, coati, and collared peccaryor ''javelina''in the Southwest are normally found in southern areas of Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas near the Mexican border. Jaguars can be found in the New Mexico Bootheel, bootheel region of Southwestern New Mexico. The Mexican wolf (''Canis lupus baileyi'') was reintroduced to Arizona and New Mexico in 1998.Paquet, P. & Carbyn, L. W. (2003). Gray wolf ''Canis lupus'' and allies", in Feldhamer, George A. et al. ''Wild Mammals of North America: Biology, Management, and Conservation'', JHU Press, pp. 482–510, A U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service study reported a minimum population of 109 Mexican wolves in southwest New Mexico and southeast Arizona at the end of 2014.
There is a large contingent of snakes native to the region. Among them include the rosy boa (''Lichanura trivirgata''); several sub-species of the glossy snake (''Arizona elegans''); the Bogertophis subocularis, Trans-Pecos ratsnake (''Bogertophis subocularis''); several sub-species of shovel-nosed snakes; several sub-species of kingsnake, including the desert kingsnake (''Lampropeltis getula splendida'') and the Lampropeltis pyromelana, Arizona mountain kingsnake (''Lampropeltis pyromelana''); the Micruroides, Arizona coral snake (''Micruroides euryxanthus''); the Crotalus atrox, western diamondback rattlesnake (''Crotalus atrox''); the Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster, Trans-Pecos copperhead (''Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster''); the Crotalus cerastes cercobombus, Sonoran sidewinder (''Crotalus cerastes cercobombus''); the Crotalus cerberus, Arizona black rattlesnake (''Crotalus oreganus cerberus''); the Crotalus viridis, western rattlesnake (''Crotalus viridis''); the Crotalus oreganus abyssus, Grand Canyon rattlesnake (''Crotalus oreganus abyssus''), found only in Arizona; several sub-species of the Crotalus willardi, ridge-nosed rattlesnake (''Crotalus willardi''), the most recent rattlesnake species to be discovered in the United States, including the Crotalus willardi obscurus, New Mexico ridge-nosed rattlesnake (''Crotalus willardi obscurus''), and the Arizona ridge-nosed rattlesnake, the state reptile of Arizona; and the Sistrurus catenatus edwardsii, desert massasauga (''Sistrurus catenatus edwardsii'').
Other reptiles in the region include lizards and turtles. Lizards are highly represented in the region, the most distinctive denizen being the Gila monster, native only to the American Southwest and the state of Sonora in Mexico. The New Mexico whiptail is the List of state symbols of New Mexico, state reptile of New Mexico. Other lizards include: Sonoran collared lizard (''Crotaphytus nebrius''); several types of geckos, including western banded gecko (''Coleonyx variegatus''), the common house gecko (''Hemidactylus frenatus''), and the Mediterranean house gecko (''Hemidactylus turcicus''), the last two species being non-native to the region but have been introduced; the desert iguana (''Dipsosaurus dorsalis''); the chuckwalla (''Sauromalus ater''); the greater earless lizard (''Cophosaurus texanus scitulus''); several sub-species of horned lizards (''Phrynosoma''); numerous species of spiny lizards (''Sceloporus''); Gilbert's skink (''Plestiodon gilberti''); the western skink (''Plestiodon skiltonianus''); Trans-Pecos striped whiptail (''Aspidoscelis inornata heptagrammus''); and the Arizona night lizard (''Xantusia arizonae''). Turtles are less numerous than their other reptilian counterparts, but several are found in the region, including: the Painted turtle#Western painted turtle, western painted turtle (''Chrysemys picta bellii''); the Rio Grande cooter (''Pseudemys gorzugi''); the desert box turtle (''Terrapene ornata luteola''); the Big Bend slider (''Trachemys gaigeae gaigeae''); the Sonora mud turtle (''Kinosternon sonoriense''); and the desert tortoise (''Gopherus agassizii'').
Amphibians include numerous toads and frogs in the American Southwest. Toads which can be found in the region include the Great Plains toad (''Anaxyrus cognatus''); the Anaxyrus debilis, green toad (''Anaxyrus debilis''); the Arizona toad (''Anaxyrus microscaphus''); the New Mexico spadefoot toad, New Mexico spadefoot (''Spea multiplicata stagnalis''); and the Colorado River toad (''Incilius alvarius''), also known as the Sonoran Desert toad. Frog representation includes: Craugastor augusti, western barking frog (''Craugastor augusti''); the canyon tree frog (''Hyla arenicolor''); the Wright's mountain tree frog, Arizona treefrog (''Hyla wrightorum''); the western chorus frog (''Pseudacris triseriata''); Chiricahua leopard frog (''Lithobates chiricahuensis''); and the relict leopard frog (''Lithobates onca''). There are quite a few salamanders throughout the region, including: the barred tiger salamander#Subspecies, Arizona tiger salamander (''Ambystoma mavortium nebulosum'') and the Ensatina#Subspecies, painted ensatina (''Ensatina eschscholtzii picta'').
Despite the Southwest being mostly arid, various fishes are found where water is available, including various species unique to the region. Apache trout and Gila trout are two Salmonidae, salmonids endemic to the area, with the former found only in Arizona and the latter only in Arizona and New Mexico. Desert pupfishes are several closely related species of fish in the genus Cyprinodon, many of which are found in isolated spring-fed ponds hundreds of miles from each other, ranging from far West Texas to Death Valley in California. These pupfishes often thrive in water considerably higher in temperature and dissolved solids than most fish can tolerate. Many of these desert fish species are endangered due to their limited and tenuous habitat, as well as loss of habitat due to human consumption of groundwater and diversion of surface water, as well as the introduction of species such as sportfish for recreation (see: Rio Grande Silvery Minnow v. Bureau of Reclamation).
 The southwestern United States features a semi-arid to arid climate, depending on the location. Much of the Southwest is an arid desert climate, but higher elevations in the mountains in each state, with the exception of West Texas, feature alpine climates with very large amounts of snow. The metropolitan areas of Phoenix, Tucson, Las Vegas, and El Paso hardly ever receive any snow at all, as they are strictly desert lands with mountains. Albuquerque receives less snow than other cities, but still receives significant snowfalls occasionally in the winter. Although it snows in this region, the snow in this part of the United States melts rapidly, often before nightfall. This is due mainly to the higher altitude and abundant sunshine in these states.
Nevada and Arizona are both generally arid with desert lands and mountains, and receive large amounts of snow in the higher elevations in and near the mountains. New Mexico, Utah, and Colorado are generally arid, with desert lands and mountains as well. They all receive decent amounts of snow and large amounts of snow in the high elevations in the mountains, although some areas in far southwestern and southern New Mexico do not receive much snow at all at lower elevations. West Texas is generally arid as well but does not receive the same amount of snow that the other southwestern states receive at their high elevations. The terrain of western Texas in the Southwest is the flat, rolling land of the plains, which eventually turns into a desert with some hills. There are significant mountains as well in west Texas upon reaching the Trans-Pecos area.
The southwestern United States features a semi-arid to arid climate, depending on the location. Much of the Southwest is an arid desert climate, but higher elevations in the mountains in each state, with the exception of West Texas, feature alpine climates with very large amounts of snow. The metropolitan areas of Phoenix, Tucson, Las Vegas, and El Paso hardly ever receive any snow at all, as they are strictly desert lands with mountains. Albuquerque receives less snow than other cities, but still receives significant snowfalls occasionally in the winter. Although it snows in this region, the snow in this part of the United States melts rapidly, often before nightfall. This is due mainly to the higher altitude and abundant sunshine in these states.
Nevada and Arizona are both generally arid with desert lands and mountains, and receive large amounts of snow in the higher elevations in and near the mountains. New Mexico, Utah, and Colorado are generally arid, with desert lands and mountains as well. They all receive decent amounts of snow and large amounts of snow in the high elevations in the mountains, although some areas in far southwestern and southern New Mexico do not receive much snow at all at lower elevations. West Texas is generally arid as well but does not receive the same amount of snow that the other southwestern states receive at their high elevations. The terrain of western Texas in the Southwest is the flat, rolling land of the plains, which eventually turns into a desert with some hills. There are significant mountains as well in west Texas upon reaching the Trans-Pecos area.
 The term "High Desert" is also synonymous with this region. The High Desert is generally defined as the
The term "High Desert" is also synonymous with this region. The High Desert is generally defined as the  The desert lands found in Eastern Utah, Northern Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico are usually referred to as the high desert. Colorado has scattered desert lands found in southern, southwestern, western, and northwestern parts of the state. These scattered desert lands are located in and around areas such as, the Roan Plateau, Dinosaur National Monument, Colorado National Monument, Royal Gorge, Cortez, Colorado, Cortez, Dove Creek, Colorado, Dove Creek, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Four Corners Monument, Montrose, Colorado, Montrose, Blue Mesa Reservoir, Pueblo, Colorado, Pueblo, San Luis Valley, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes and Joshua Tree National Park. Besides the
The desert lands found in Eastern Utah, Northern Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico are usually referred to as the high desert. Colorado has scattered desert lands found in southern, southwestern, western, and northwestern parts of the state. These scattered desert lands are located in and around areas such as, the Roan Plateau, Dinosaur National Monument, Colorado National Monument, Royal Gorge, Cortez, Colorado, Cortez, Dove Creek, Colorado, Dove Creek, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Four Corners Monument, Montrose, Colorado, Montrose, Blue Mesa Reservoir, Pueblo, Colorado, Pueblo, San Luis Valley, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes and Joshua Tree National Park. Besides the
 The southwestern United States contains many well-known national parks including Grand Canyon National Park, Grand Canyon in Arizona, Death Valley National Park, Death Valley in California, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes in Colorado, Arches National Park, Arches in Utah, Big Bend National Park, Big Bend in Texas, Great Basin National Park, Great Basin in Nevada, and White Sands National Park, White Sands in New Mexico.
The southwestern United States contains many well-known national parks including Grand Canyon National Park, Grand Canyon in Arizona, Death Valley National Park, Death Valley in California, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes in Colorado, Arches National Park, Arches in Utah, Big Bend National Park, Big Bend in Texas, Great Basin National Park, Great Basin in Nevada, and White Sands National Park, White Sands in New Mexico.
 Arizona parks and monuments include Grand Canyon, Monument Valley (a Navajo Nation park), Petrified Forest National Park, Petrified Forest, and Saguaro National Park, Saguaro national parks; the national monuments of Agua Fria National Monument, Agua Fria, Canyon de Chelly National Monument, Canyon de Chelly, Casa Grande Ruins National Monument, Casa Grande Ruins, Chiricahua National Monument, Chiricahua, Ironwood Forest National Monument, Ironwood Forest, Montezuma Castle National Monument, Montezuma Castle, Navajo National Monument, Navajo, Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, Organ Pipe Cactus, Pipe Spring National Monument, Pipe Spring, Sonoran Desert National Monument, Sonoran Desert, Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument, Sunset Crater, Tonto National Monument, Tonto, Tuzigoot National Monument, Tuzigoot, Vermilion Cliffs National Monument, Vermilion Cliffs, Walnut Canyon National Monument, Walnut Canyon, and Wupatki National Monument, Wupatki. Other federal areas include the Apache–Sitgreaves National Forests and Tumacacori National Historical Park.
Southern California parks and monuments include Death Valley and Joshua Tree National Park, Joshua Tree national parks; the national monuments of Castle Mountains National Monument, Castle Mountains, Mojave Trails National Monument, Mojave Trails, Sand to Snow National Monument, Sand to Snow, and San Gabriel Mountains National Monument, San Gabriel Mountains; and Mojave National Preserve.
Colorado parks and monuments include Great Sand Dunes, Black Canyon of the Gunnison National Park, Black Canyon of the Gunnison, and Mesa Verde National Park, Mesa Verde national parks; the national monuments of Browns Canyon National Monument, Browns Canyon, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Canyons of the Ancients, Colorado National Monument, Colorado, Hovenweep National Monument, Hovenweep, and Yucca House National Monument, Yucca House. Other federal areas include Curecanti National Recreation Area and Bent's Old Fort National Historic Site; as well as the national forests of San Isabel National Forest, San Isabel, San Juan National Forest, San Juan, and Uncompahgre National Forest, Uncompahgre.
Arizona parks and monuments include Grand Canyon, Monument Valley (a Navajo Nation park), Petrified Forest National Park, Petrified Forest, and Saguaro National Park, Saguaro national parks; the national monuments of Agua Fria National Monument, Agua Fria, Canyon de Chelly National Monument, Canyon de Chelly, Casa Grande Ruins National Monument, Casa Grande Ruins, Chiricahua National Monument, Chiricahua, Ironwood Forest National Monument, Ironwood Forest, Montezuma Castle National Monument, Montezuma Castle, Navajo National Monument, Navajo, Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, Organ Pipe Cactus, Pipe Spring National Monument, Pipe Spring, Sonoran Desert National Monument, Sonoran Desert, Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument, Sunset Crater, Tonto National Monument, Tonto, Tuzigoot National Monument, Tuzigoot, Vermilion Cliffs National Monument, Vermilion Cliffs, Walnut Canyon National Monument, Walnut Canyon, and Wupatki National Monument, Wupatki. Other federal areas include the Apache–Sitgreaves National Forests and Tumacacori National Historical Park.
Southern California parks and monuments include Death Valley and Joshua Tree National Park, Joshua Tree national parks; the national monuments of Castle Mountains National Monument, Castle Mountains, Mojave Trails National Monument, Mojave Trails, Sand to Snow National Monument, Sand to Snow, and San Gabriel Mountains National Monument, San Gabriel Mountains; and Mojave National Preserve.
Colorado parks and monuments include Great Sand Dunes, Black Canyon of the Gunnison National Park, Black Canyon of the Gunnison, and Mesa Verde National Park, Mesa Verde national parks; the national monuments of Browns Canyon National Monument, Browns Canyon, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Canyons of the Ancients, Colorado National Monument, Colorado, Hovenweep National Monument, Hovenweep, and Yucca House National Monument, Yucca House. Other federal areas include Curecanti National Recreation Area and Bent's Old Fort National Historic Site; as well as the national forests of San Isabel National Forest, San Isabel, San Juan National Forest, San Juan, and Uncompahgre National Forest, Uncompahgre.
 Nevada has one national park at Great Basin, and the national monuments of Basin and Range National Monument, Basin and Range, Gold Butte National Monument, Gold Butte, and Tule Springs Fossil Beds National Monument, Tule Springs Fossil Beds. Other federal areas include Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest, Lake Mead National Recreation Area, and Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area.
New Mexico has two national parks, at Carlsbad Caverns National Park, Carlsbad Caverns and White Sands. National monuments include Aztec Ruins National Monument, Aztec Ruins, Bandelier National Monument, Bandelier, El Malpais National Monument, El Malpais, El Morro National Monument, El Morro, Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument, Gila Cliff Dwellings, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks National Monument, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks National Monument, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks, Petroglyph National Monument, Petroglyph, Rio Grande del Norte National Monument, Rio Grande del Norte, and Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument, Salinas Pueblo Missions. Other federal park areas include Chaco Culture National Historical Park, Pecos National Historical Park, Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge, and the national forests of Apache National Forest, Apache, Carson National Forest, Carson, Gila National Forest, Gila, Lincoln National Forest, Lincoln, and Santa Fe National Forest, Santa Fe.
West Texas has two national parks, at Big Bend and Guadalupe Mountains National Park, Guadalupe Mountains. Other federal park areas include Chamizal National Memorial and Fort Davis National Historic Site.
Utah national parks include Arches, Bryce Canyon National Park, Bryce Canyon, Canyonlands National Park, Canyonlands, Capitol Reef National Park, Capitol Reef, and Zion National Park, Zion. National monuments include Bears Ears National Monument, Bears Ears, Cedar Breaks National Monument, Cedar Breaks, Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, Grand Staircase–Escalante, Hovenweep (also in Colorado), Natural Bridges National Monument, Natural Bridges, and Rainbow Bridge National Monument, Rainbow Bridge. Other federal areas include Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, Dixie National Forest, and Manti–La Sal National Forest.
Nevada has one national park at Great Basin, and the national monuments of Basin and Range National Monument, Basin and Range, Gold Butte National Monument, Gold Butte, and Tule Springs Fossil Beds National Monument, Tule Springs Fossil Beds. Other federal areas include Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest, Lake Mead National Recreation Area, and Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area.
New Mexico has two national parks, at Carlsbad Caverns National Park, Carlsbad Caverns and White Sands. National monuments include Aztec Ruins National Monument, Aztec Ruins, Bandelier National Monument, Bandelier, El Malpais National Monument, El Malpais, El Morro National Monument, El Morro, Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument, Gila Cliff Dwellings, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks National Monument, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks National Monument, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks, Petroglyph National Monument, Petroglyph, Rio Grande del Norte National Monument, Rio Grande del Norte, and Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument, Salinas Pueblo Missions. Other federal park areas include Chaco Culture National Historical Park, Pecos National Historical Park, Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge, and the national forests of Apache National Forest, Apache, Carson National Forest, Carson, Gila National Forest, Gila, Lincoln National Forest, Lincoln, and Santa Fe National Forest, Santa Fe.
West Texas has two national parks, at Big Bend and Guadalupe Mountains National Park, Guadalupe Mountains. Other federal park areas include Chamizal National Memorial and Fort Davis National Historic Site.
Utah national parks include Arches, Bryce Canyon National Park, Bryce Canyon, Canyonlands National Park, Canyonlands, Capitol Reef National Park, Capitol Reef, and Zion National Park, Zion. National monuments include Bears Ears National Monument, Bears Ears, Cedar Breaks National Monument, Cedar Breaks, Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, Grand Staircase–Escalante, Hovenweep (also in Colorado), Natural Bridges National Monument, Natural Bridges, and Rainbow Bridge National Monument, Rainbow Bridge. Other federal areas include Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, Dixie National Forest, and Manti–La Sal National Forest.
File:Downtown_Phoenix_Aerial_Looking_Northeast.jpg, 1.

 Of the four Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, major professional sports, Phoenix and Las Vegas are the only metropolitan areas in the Southwest that have representatives. While Las Vegas is home to the Las Vegas Raiders NFL football team and the Vegas Golden Knights NHL hockey team, Phoenix is one of only 13 U.S. cities to have representatives in all four: Arizona Diamondbacks in Major League Baseball, Arizona Cardinals in the National Football League, the Phoenix Suns in the National Basketball Association, and the Arizona Coyotes in the National Hockey League. The Greater Phoenix area is home to the Cactus League, one of two spring training leagues for Major League Baseball; fifteen of MLB's thirty teams are now included in the Cactus League. The region has also been the scene of several NFL super bowls. Sun Devil Stadium in Tempe held Super Bowl XXX in 1996, when the Dallas Cowboys defeated the Pittsburgh Steelers. State Farm Stadium in Glendale, Arizona hosted Super Bowl XLII on February 3, 2008, in which the New York Giants defeated the New England Patriots, as well as Super Bowl XLIX, which resulted in the New England Patriots defeating the Seattle Seahawks 28–24. The U.S. Airways Center hosted both the 1995 NBA All-Star Game, 1995 and the 2009 NBA All-Star Games.
In 1997, the Phoenix Mercury were one of the original eight teams to launch the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA). Indoor American football is represented by the Arizona Rattlers located in Phoenix. The region is also host to several major professional golf events: the LPGA's RR Donnelley LPGA Founders Cup, Founder's Cup; the Phoenix Open and the Shriners Hospitals for Children Open (in Las Vegas) of the Professional Golfers' Association of America, PGA; and the Tucson Conquistadores Classic (in Tucson), and the Charles Schwab Cup Championship (in Scottsdale) on the Champions Tour of the PGA.
NASCAR has two venues within the region: The Phoenix International Raceway, was built in 1964 with a one-mile oval, with a one-of-a-kind design, as well as a 2.5-mile road course, and the Las Vegas Motor Speedway, a 1,200-acre (490 ha) complex of multiple tracks for motorsports racing. There are several nationally recognized running events in the region, including The Phoenix Marathon, a qualifier for the Boston Marathon, and the Rock 'n' Roll Marathon Series in both Rock 'n' Roll Arizona Marathon, Phoenix and Rock 'n' Roll Las Vegas Marathon, Las Vegas. Las Vegas is also the end point for the annual Baker to Vegas Challenge Cup Relay, a 120-mile-long foot race by law enforcement teams from around the world, which is the largest law enforcement athletic event in the world. Las Vegas is the premier boxing venue in the country, and is also known for mixed martial arts events.
The Southwest is also home to some of the most prominent rodeos in North America. The Professional Bull Riders association has its headquarters in Pueblo, Colorado. The Professional Bull Riders#World Finals Event Champions, PBR World Finals are held annually in Las Vegas, which also hosts the National Finals Rodeo, which is the nation's premier rodeo event. Other major rodeo events include the week-long Fiesta de los Vaqueros in Tucson, the World's Oldest Rodeo in Prescott, Arizona, the Southwestern International PRCA Rodeo in El Paso, Texas, and the Rodeo de Santa Fe, one of the nation's premier rodeos.
Since the 1950s, Las Vegas has been host to many of professional boxing's largest events, beginning with the Heavyweight non-title bout in 1955 between world light heavyweight champion Archie Moore and perennial contender Niño Valdés. Muhammad Ali fought his last world title bout in Las Vegas against Larry Holmes in 1980, and Floyd Mayweather fought many of his major fights there.
Of the four Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, major professional sports, Phoenix and Las Vegas are the only metropolitan areas in the Southwest that have representatives. While Las Vegas is home to the Las Vegas Raiders NFL football team and the Vegas Golden Knights NHL hockey team, Phoenix is one of only 13 U.S. cities to have representatives in all four: Arizona Diamondbacks in Major League Baseball, Arizona Cardinals in the National Football League, the Phoenix Suns in the National Basketball Association, and the Arizona Coyotes in the National Hockey League. The Greater Phoenix area is home to the Cactus League, one of two spring training leagues for Major League Baseball; fifteen of MLB's thirty teams are now included in the Cactus League. The region has also been the scene of several NFL super bowls. Sun Devil Stadium in Tempe held Super Bowl XXX in 1996, when the Dallas Cowboys defeated the Pittsburgh Steelers. State Farm Stadium in Glendale, Arizona hosted Super Bowl XLII on February 3, 2008, in which the New York Giants defeated the New England Patriots, as well as Super Bowl XLIX, which resulted in the New England Patriots defeating the Seattle Seahawks 28–24. The U.S. Airways Center hosted both the 1995 NBA All-Star Game, 1995 and the 2009 NBA All-Star Games.
In 1997, the Phoenix Mercury were one of the original eight teams to launch the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA). Indoor American football is represented by the Arizona Rattlers located in Phoenix. The region is also host to several major professional golf events: the LPGA's RR Donnelley LPGA Founders Cup, Founder's Cup; the Phoenix Open and the Shriners Hospitals for Children Open (in Las Vegas) of the Professional Golfers' Association of America, PGA; and the Tucson Conquistadores Classic (in Tucson), and the Charles Schwab Cup Championship (in Scottsdale) on the Champions Tour of the PGA.
NASCAR has two venues within the region: The Phoenix International Raceway, was built in 1964 with a one-mile oval, with a one-of-a-kind design, as well as a 2.5-mile road course, and the Las Vegas Motor Speedway, a 1,200-acre (490 ha) complex of multiple tracks for motorsports racing. There are several nationally recognized running events in the region, including The Phoenix Marathon, a qualifier for the Boston Marathon, and the Rock 'n' Roll Marathon Series in both Rock 'n' Roll Arizona Marathon, Phoenix and Rock 'n' Roll Las Vegas Marathon, Las Vegas. Las Vegas is also the end point for the annual Baker to Vegas Challenge Cup Relay, a 120-mile-long foot race by law enforcement teams from around the world, which is the largest law enforcement athletic event in the world. Las Vegas is the premier boxing venue in the country, and is also known for mixed martial arts events.
The Southwest is also home to some of the most prominent rodeos in North America. The Professional Bull Riders association has its headquarters in Pueblo, Colorado. The Professional Bull Riders#World Finals Event Champions, PBR World Finals are held annually in Las Vegas, which also hosts the National Finals Rodeo, which is the nation's premier rodeo event. Other major rodeo events include the week-long Fiesta de los Vaqueros in Tucson, the World's Oldest Rodeo in Prescott, Arizona, the Southwestern International PRCA Rodeo in El Paso, Texas, and the Rodeo de Santa Fe, one of the nation's premier rodeos.
Since the 1950s, Las Vegas has been host to many of professional boxing's largest events, beginning with the Heavyweight non-title bout in 1955 between world light heavyweight champion Archie Moore and perennial contender Niño Valdés. Muhammad Ali fought his last world title bout in Las Vegas against Larry Holmes in 1980, and Floyd Mayweather fought many of his major fights there.
Firenze University Press
(2013) * * * Weber, David J. ''The Mexican Frontier, 1821–1846: The American Southwest Under Mexico'' (1982) * Weber, David J. "The Spanish Borderlands, Historiography Redux." ''The History Teacher'', 39#1 (2005), pp. 43–56. JSTOR
online
American Southwest, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
Water-use Trends in the Desert Southwest, 1950–2000
United States Geological Survey {{Authority control Southwestern United States, Cultural regions of the United States Regions of the Western United States
region of the United States
This is a list of some of the ways ''regions'' is defined in the United States. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the federal government; others by shared culture and history, and others by economic factors.
Interstate regions C ...
that generally includes Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
, and adjacent portions of California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, and Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
. The largest cities by metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
are Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
, Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
, El Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
, Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
, and Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
. Prior to 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
and Coahuila y Tejas
Coahuila y Tejas, officially the Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila y Tejas (), was one of the constituent states of the newly established United Mexican States under its 1824 Constitution.
It had two capitals: first Saltillo (1822–1825) f ...
, settlement was almost non-existent outside of Nuevo México's Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
s and Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
until the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854.
While the region's boundaries are not officially defined, there have been attempts to do so. One such definition is from the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily ...
in California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
in the west (117° west longitude) to Carlsbad, New Mexico
Carlsbad ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Eddy County, New Mexico, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city population was 32,238. Carlsbad is centered at the intersection of U.S. Routes 62/180 and 285, and is the principal city ...
in the east (104° west longitude); another says that it extends from the Mexico–United States border
The Mexico–United States border ( es, frontera Estados Unidos–México) is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border trave ...
in the south to the southern areas of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
in the north (39° north latitude). In another definition, the core Southwestern U.S. includes only the states of Arizona and New Mexico; others focus on the land within the old Spanish and Mexican borders of the ''Nuevo México'' Province or the later American New Mexico Territory.
Distinct elements of the Western lifestyle
Western lifestyle or cowboy culture is the Lifestyle (sociology), lifestyle, or behaviorisms, of, and resulting from the influence of, the (often romanticized) attitudes, ethics and history of the American Western cowboy. In the present day these i ...
thrive in the region, such as Western wear
Western wear is a category of men's and women's clothing which derives its unique style from the clothes worn in the 19th century Wild West. It ranges from accurate historical reproductions of American frontier clothing, to the stylized garment ...
and Southwestern cuisine
The cuisine of the Southwestern United States is food styled after the rustic cooking of the Southwestern United States. It comprises a fusion of recipes for things that might have been eaten by Spanish colonial settlers, cowboys, Native Ame ...
s, including Native American, New Mexican, and Tex-Mex
Tex-Mex cuisine (from the words ''Texan'' and ''Mexican'') is an American cuisine that derives from the culinary creations of the ''Tejano'' people of Texas. It has spread from border states such as Texas and others in the Southwestern United ...
, or various genres of Western music like Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
, and Tejano music styles. Likewise with the sought-after Southwestern architectural styles in the region inspired by blending Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
and Territorial
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
styles, with Mediterranean Revival
Mediterranean Revival is an architectural style introduced in the United States, Canada, and certain other countries in the 19th century. It incorporated references from Spanish Renaissance, Spanish Colonial, Italian Renaissance, French Colonia ...
, Spanish Colonial architecture, Mission Revival architecture
The Mission Revival style was part of an architectural movement, beginning in the late 19th century, for the revival and reinterpretation of American colonial styles. Mission Revival drew inspiration from the late 18th and early 19th century ...
, Pueblo Deco
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
, and Ranch-style houses in the form of the amalgamated Pueblo Revival
The Pueblo Revival style or Santa Fe style is a regional architectural style of the Southwestern United States, which draws its inspiration from Santa Fe de Nuevo México's traditional Pueblo architecture, the Spanish missions, and Territor ...
and Territorial Revival architectures. This is due to the region's influence by the Native American (especially Apache, Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
, and Navajo), Hispano, vaquero, and later American frontier cowboy history.
Regional geography
Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert ( es, Desierto de Chihuahua, ) is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lo ...
s, and the Colorado Plateau; although there are other geographical features as well, such as a portion of the Great Basin Desert
The Great Basin Desert is part of the Great Basin between the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada and the Wasatch Range. The desert is a geographical region that largely overlaps the Great Basin shrub steppe defined by the World Wildlife Fund, a ...
. The deserts dominate the southern and western reaches of the area, while the plateau (which is largely made up of high desert) is the main feature north of the Mogollon Rim
The Mogollon Rim ( or or ) is a topographical and geological feature cutting across the northern half of the U.S. state of Arizona. It extends approximately , starting in northern Yavapai County and running eastward, ending near the border ...
. The two major rivers of the region are the Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of ...
, running in the northern and western areas, and the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
, running in the east, north to south.
 Formed approximately 8000 years ago, the Chihuahuan Desert is a relatively dry desert, although it is slightly wetter than the Sonoran Desert to the west. The Chihuahuan Desert spreads across the southeastern portion of the region, covering from southeastern Arizona, across southern New Mexico, and the portion of western Texas included in the Southwest. While it is the second largest desert in the United States, only a third of the desert is within the United States, with the rest in Mexico. El Paso and Albuquerque are the major US cities in this desert, with other smaller cities being Las Cruces and Roswell in New Mexico and Willcox in Arizona.
The elevation in the Chihuahuan varies from about , as there are several larger mountain ranges, such as the
Formed approximately 8000 years ago, the Chihuahuan Desert is a relatively dry desert, although it is slightly wetter than the Sonoran Desert to the west. The Chihuahuan Desert spreads across the southeastern portion of the region, covering from southeastern Arizona, across southern New Mexico, and the portion of western Texas included in the Southwest. While it is the second largest desert in the United States, only a third of the desert is within the United States, with the rest in Mexico. El Paso and Albuquerque are the major US cities in this desert, with other smaller cities being Las Cruces and Roswell in New Mexico and Willcox in Arizona.
The elevation in the Chihuahuan varies from about , as there are several larger mountain ranges, such as the Organ Mountains
The Organ Mountains (also known as La Sierra de los Órganos) are a rugged mountain range in southern New Mexico in the Southwestern United States. Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks National Monument was declared a national monument on May 21, 2 ...
, the Guadalupe Mountains
The Guadalupe Mountains ( es, Sierra de Guadalupe) are a mountain range located in West Texas and southeastern New Mexico. The range includes the highest summit in Texas, Guadalupe Peak, , and the "signature peak" of West Texas, El Capitan, both ...
, and the Chiracahua Mountains, plus many smaller mountain ranges contained in the area, namely the Animas, San Andres, and Doña Ana Mountains The Doña Ana Mountains are a mountain range in Doña Ana County, New Mexico. The highest elevation in the range is Doña Ana Peak at 5835 feet / 1779 meters, at .
Description
The Doña Ana Mountains are a small, rugged mountain range in the dese ...
in New Mexico; and the Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People
* Franklin (given name)
* Franklin (surname)
* Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class
Places Australia
* Franklin, Tasmania, a township
* Division of Franklin, federal electoral d ...
, Hueco, and Davis Mountains
The Davis Mountains, originally known as Limpia Mountains, are a range of mountains in West Texas, located near Fort Davis, after which they are named. The fort was named for then United States Secretary of War and later Confederate President J ...
in Texas. It also reaches up into the foothills of the higher ranges such as the Black Range and Oscura Mountains
Oscura Mountains, originally known to the Spanish as the ''Sierra Oscura'', are a ridge of mountains, trending north and south, east of the Jornada del Muerto and west of the Tularosa Valley. It is located in Socorro County and Lincoln County, N ...
in New Mexico. High above the desert, these forest-covered and sometimes snow-capped mountains form sky island
Sky islands are isolated mountains surrounded by radically different lowland environments. The term originally referred to those found on the Mexican Plateau, and has extended to similarly isolated high-elevation forests. The isolation has s ...
s, with radically different flora and fauna than the surrounding desert below. The sky islands also supply the surrounding desert foothills with flowing water during the spring runoff and after the summer storms of the New Mexican monsoon season. The Chihuahuan is a "rain shadow" desert, formed between two mountain ranges (the Sierra Madre Occidental on the west and the Sierra Madre Oriental on the east) which block oceanic precipitation from reaching the area. The Chihuahuan Desert is considered the "most biologically diverse desert in the Western Hemisphere and one of the most diverse in the world", and includes more species of cacti than any other desert in the world. The most prolific plants in this region are agave
''Agave'' (; ; ) is a genus of monocots native to the hot and arid regions of the Americas and the Caribbean, although some ''Agave'' species are also native to tropical areas of North America, such as Mexico. The genus is primarily known for ...
, yucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial plant, perennial shrubs and trees in the family (biology), family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their Rosette (botany), rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped Leaf, ...
and creosote bush
''Larrea tridentata'', called creosote bush and greasewood as a plant, chaparral as a medicinal herb, and ''gobernadora'' (Spanish for "governess") in Mexico, due to its ability to secure more water by inhibiting the growth of nearby plants. In S ...
es, in addition to the ubiquitous presence of various cacti species.
 When people think of the desert southwest, the landscape of the Sonoran Desert is what mostly comes to mind. The Sonoran Desert makes up the southwestern portion of the Southwest; most of the desert lies in Mexico, but its United States component lies on the southeastern border of California, and the western 2/3 of southern Arizona. Rainfall averages between per year, and the desert's most widely known inhabitant is the
When people think of the desert southwest, the landscape of the Sonoran Desert is what mostly comes to mind. The Sonoran Desert makes up the southwestern portion of the Southwest; most of the desert lies in Mexico, but its United States component lies on the southeastern border of California, and the western 2/3 of southern Arizona. Rainfall averages between per year, and the desert's most widely known inhabitant is the saguaro cactus
The saguaro (, ) (''Carnegiea gigantea'') is a tree-like cactus species in the monotypic genus ''Carnegiea'' that can grow to be over tall. It is native to the Sonoran Desert in Arizona, the Mexican state of Sonora, and the Whipple Mountains ...
, which is unique to the desert. It is bounded on the northwest by the Mojave Desert, to the north by the Colorado Plateau and to the east by the Arizona Mountains forests
The Arizona Mountains forests are a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of the southwest United States with a rich variety of woodland habitats and wildlife.
Setting
This is a landscape of steep mountains and high stony plateaus with rocky ou ...
and the Chihuahuan Desert. Aside from the trademark saguaro, the desert has the most diverse plant life of any desert in the world, and includes many other species of cacti, including the organ-pipe, senita, prickly pear, barrel, fishhook, hedgehog, cholla, silver dollar, and jojoba. The portion of the Sonora Desert which lies in the Southwestern United States is the most populated area within the region. Six of the top ten major population centers of the region are found within its borders: Phoenix, Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
, Mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by a ...
, Chandler, Glendale Glendale is the anglicised version of the Gaelic Gleann Dail, which means ''valley of fertile, low-lying arable land''.
It may refer to:
Places Australia
* Glendale, New South Wales
** Stockland Glendale, a shopping centre
*Glendale, Queensland, ...
, and Scottsdale, all in Arizona. Also within its borders are Yuma and Prescott Arizona.
The most northwest portion of the American Southwest is covered by the Mojave Desert. Bordered on the south by the Sonoran Desert and the east by the Colorado Plateau, its range within the region makes up the southeast tip of Nevada, the southwestern corner of Utah and the northwestern corner of Arizona. In terms of topography, the Mojave is very similar to the Great Basin Desert, which lies just to its north. Within the region, Las Vegas is the most populous city; other significant population centers include Laughlin and Pahrump in Nevada, St. George and Hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
in Utah, and Lake Havasu City, Kingman, and Bullhead City
Bullhead City is a city located on the Colorado River in Mohave County, Arizona, United States, south of Las Vegas, Nevada, and directly across the Colorado River from Laughlin, Nevada, whose casinos and ancillary services supply much of the em ...
in Arizona. The Mojave is the smallest, driest and hottest desert within the United States. The Mojave gets less than of rain annually, and its elevation ranges from above sea level. The most prolific vegetation is the tall Joshua tree
''Yucca brevifolia'' is a plant species belonging to the genus ''Yucca''. It is tree-like in habit, which is reflected in its common names: Joshua tree, yucca palm, tree yucca, and palm tree yucca.
This monocotyledonous tree is native to the ar ...
, which grow as tall as , and are thought to live almost 1000 years. Other major vegetation includes the Parry saltbush and the Mojave sage, both only found in the Mojave, as well as the creosote bush.
 The Colorado Plateau varies from the large stands of forests in the west, including the largest stand of
The Colorado Plateau varies from the large stands of forests in the west, including the largest stand of ponderosa pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the ...
trees in the world, to the Mesas to the east. Although not called a desert, the Colorado Plateau is mostly made up of high desert. Within the Southwest U.S. region, the Colorado is bordered to the south by the Mogollon Rim and the Sonoran Desert, to the west by the Mojave Desert, and to the east by the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
, the Rio Grande Rift
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihuahu ...
valley, and the Llano Estacado. The Plateau is characterized by a series of plateaus and mesas, interspersed with canyons. The most dramatic example is the Grand Canyon. But that is one of many dramatic vistas included within the Plateau, which includes spectacular lava formations, "painted" deserts, sand dunes, and badlands. One of the most distinctive features of the Plateau is its longevity, having come into existence at least 500 million years ago. The Plateau can be divided into six sections, three of which fall into the Southwest region. Beginning with the Navajo section forming the northern boundary of the Southwestern United States, which has shallower canyons than those in the Canyonlands section just to its north; the Navajo section is bordered to the south by the Grand Canyon section, which of course is dominated by the Grand Canyon; and the southeasternmost portion of the Plateau is the Datil section, consisting of valleys, mesas, and volcanic formations. Albuquerque is the most populous city often considered at the edge of this portion contained in the Southwest region, but Santa Fe, New Mexico and Flagstaff, Arizona, are also significant population centers.

Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
, Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
, and Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
dominate the westernmost metropolitan areas in the Southwest, while Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
, and El Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
dominate the easternmost metropolitan areas.
History
Pre-European contact
 Human history in the Southwest begins with the arrival of the
Human history in the Southwest begins with the arrival of the Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleoamerican culture, named for distinct stone and bone tools found in close association with Pleistocene fauna, particularly two mammoths, at Blackwater Locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, in 1936 a ...
, a Paleo-Indian hunter-gatherer culture which arrived sometime around 9000 BC. This culture remained in the area for several millennia. At some point they were replaced by three great Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
Indian cultures: the Ancestral Pueblo people
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, a ...
, the Hohokam, and the Mogollon, all of which existed among other surrounding cultures including the FremontPatayan
Patayan is a group of prehistoric and historic Native American cultures in parts of modern-day Arizona, west to Lake Cahuilla in California, and in Baja California, from AD 700 to 1550. This included areas along the Gila River, Colorado Riv ...
. Maize began to be cultivated in the region sometime during the early first millennium BC, but it took several hundred years for the native cultures to be dependent on it as a food source. As their dependence on maize grew, Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
Indians began developing irrigation systems around 1500.
 Prior to the arrival of Europeans, the Southwestern United States was inhabited by a very large population of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indian tribes. The area once occupied by the ancestral Puebloans became inhabited by several American Indian tribes, the most populous of which were the Navajo people, Navajo, Ute people, Ute, Southern Paiute, and Hopi. The Navajo, along with the Hopi, were the earliest of the modern Indian tribes to develop in the Southwest. Around AD 1100 their culture began to develop in the Four Corners area of the region. The Navahos Pre-modern human migration, migrated from northwestern Canada and eastern Alaska, where the majority of Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan speakers reside. The Ute were found over most of modern-day Utah and Colorado, as well as northern New Mexico and Arizona. The Paiutes roamed an area which covered over 45,000 square miles of southern Nevada and California, south-central Utah, and northern Arizona. The Hopi settled the lands of the central and western portions of northern Arizona. Their village of Oraibi, Arizona, Oraibi, settled in approximately AD 1100, is, along with Acoma Pueblo, Acoma Sky City in New Mexico, one of the oldest continuously occupied settlements in the United States. The Mogollon area became occupied by the Apaches and the Zuni. The Apache migrated into the American Southwest from the northern areas of North America at some point between 1200 and 1500. They settled throughout New Mexico, eastern Arizona, northern Mexico, parts of western Texas, and southern Colorado. The Zuni count their direct ancestry through the ancestral Puebloans. The modern-day Zuni established a culture along the Zuni River in far-eastern Arizona and western New Mexico. Both major tribes of the O'odham tribe settled in the southern and central Arizona, in the lands once controlled by their ancestors, the Hohokam.
Prior to the arrival of Europeans, the Southwestern United States was inhabited by a very large population of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indian tribes. The area once occupied by the ancestral Puebloans became inhabited by several American Indian tribes, the most populous of which were the Navajo people, Navajo, Ute people, Ute, Southern Paiute, and Hopi. The Navajo, along with the Hopi, were the earliest of the modern Indian tribes to develop in the Southwest. Around AD 1100 their culture began to develop in the Four Corners area of the region. The Navahos Pre-modern human migration, migrated from northwestern Canada and eastern Alaska, where the majority of Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan speakers reside. The Ute were found over most of modern-day Utah and Colorado, as well as northern New Mexico and Arizona. The Paiutes roamed an area which covered over 45,000 square miles of southern Nevada and California, south-central Utah, and northern Arizona. The Hopi settled the lands of the central and western portions of northern Arizona. Their village of Oraibi, Arizona, Oraibi, settled in approximately AD 1100, is, along with Acoma Pueblo, Acoma Sky City in New Mexico, one of the oldest continuously occupied settlements in the United States. The Mogollon area became occupied by the Apaches and the Zuni. The Apache migrated into the American Southwest from the northern areas of North America at some point between 1200 and 1500. They settled throughout New Mexico, eastern Arizona, northern Mexico, parts of western Texas, and southern Colorado. The Zuni count their direct ancestry through the ancestral Puebloans. The modern-day Zuni established a culture along the Zuni River in far-eastern Arizona and western New Mexico. Both major tribes of the O'odham tribe settled in the southern and central Arizona, in the lands once controlled by their ancestors, the Hohokam.
Arrival of Europeans
 The first European intrusion into the region came from the south. In 1539, a Jesuit Franciscan named Marcos de Niza led an expedition from Mexico City which passed through eastern Arizona. The following year Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, based on reports from survivors of the Narváez expedition (1528–36) who had crossed eastern Texas on their way to Mexico City, led an expedition to discover the Seven Golden Cities of Cíbola. The 1582-3 expedition of Antonio de Espejo explored New Mexico and eastern Arizona; and this led to Juan de Oñate's establishment of the Spanish province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in 1598, with a capital founded near Ohkay Owingeh, New Mexico, Ohkay Oweenge Pueblo, which he called San Juan de los Caballeros. Oñate's party also attempted to establish a settlement in Arizona in 1599, but were turned back by inclement weather. In 1610, Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe was founded, making it the oldest capital in United States.
In 1664 Juan Archuleta led an expedition into what is now Colorado, becoming the first European to enter. A second Spanish expedition was led into Colorado by Juan Ulibarrí in 1706, during which he claimed the Colorado territory for Spain.
From 1687 to 1691 the Jesuit priest, Eusebio Kino established several missions in the Santa Cruz River (Arizona), Santa Cruz River valley; and Kino further explored southern and central Arizona in 1694, during which he discovered the ruins of Casa Grande. Beginning in 1732, Spanish settlers began to enter the region, and the Spanish started bestowing land grants in Mexico and the Southwest US. In 1751, the O'odham rebelled against the Spanish incursions, but the revolt was unsuccessful. In fact, it had the exact opposite effect, for the result of the rebellion was the establishment of the Presidio San Ignacio de Tubac, presidio at Tubac, Arizona, Tubac, the first permanent European settlement in Arizona.
In 1768, the Spanish created the Las Californias Province, Provincia de las Californias, which included California and the Southwest US. Over approximately the next 50 years, the Spanish continued to explore the Southwest, and in 1776 the City of Tucson was founded when the Presidio San Augustin del Tucson was created, relocating the presidio from Tubac.
In 1776, two Franciscan priests, Francisco Atanasio Domínguez and Silvestre Vélez de Escalante, led an Dominguez–Escalante Expedition, expedition from Santa Fe heading to California. After passing through Colorado, they became the first Europeans to travel into what is now Utah. Their journey was halted by bad weather in October, and they turned back, heading south into Arizona before turning east back to Santa Fe.
In 1804 Spain divided the Provincia de las Californias, creating the province
The first European intrusion into the region came from the south. In 1539, a Jesuit Franciscan named Marcos de Niza led an expedition from Mexico City which passed through eastern Arizona. The following year Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, based on reports from survivors of the Narváez expedition (1528–36) who had crossed eastern Texas on their way to Mexico City, led an expedition to discover the Seven Golden Cities of Cíbola. The 1582-3 expedition of Antonio de Espejo explored New Mexico and eastern Arizona; and this led to Juan de Oñate's establishment of the Spanish province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in 1598, with a capital founded near Ohkay Owingeh, New Mexico, Ohkay Oweenge Pueblo, which he called San Juan de los Caballeros. Oñate's party also attempted to establish a settlement in Arizona in 1599, but were turned back by inclement weather. In 1610, Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe was founded, making it the oldest capital in United States.
In 1664 Juan Archuleta led an expedition into what is now Colorado, becoming the first European to enter. A second Spanish expedition was led into Colorado by Juan Ulibarrí in 1706, during which he claimed the Colorado territory for Spain.
From 1687 to 1691 the Jesuit priest, Eusebio Kino established several missions in the Santa Cruz River (Arizona), Santa Cruz River valley; and Kino further explored southern and central Arizona in 1694, during which he discovered the ruins of Casa Grande. Beginning in 1732, Spanish settlers began to enter the region, and the Spanish started bestowing land grants in Mexico and the Southwest US. In 1751, the O'odham rebelled against the Spanish incursions, but the revolt was unsuccessful. In fact, it had the exact opposite effect, for the result of the rebellion was the establishment of the Presidio San Ignacio de Tubac, presidio at Tubac, Arizona, Tubac, the first permanent European settlement in Arizona.
In 1768, the Spanish created the Las Californias Province, Provincia de las Californias, which included California and the Southwest US. Over approximately the next 50 years, the Spanish continued to explore the Southwest, and in 1776 the City of Tucson was founded when the Presidio San Augustin del Tucson was created, relocating the presidio from Tubac.
In 1776, two Franciscan priests, Francisco Atanasio Domínguez and Silvestre Vélez de Escalante, led an Dominguez–Escalante Expedition, expedition from Santa Fe heading to California. After passing through Colorado, they became the first Europeans to travel into what is now Utah. Their journey was halted by bad weather in October, and they turned back, heading south into Arizona before turning east back to Santa Fe.
In 1804 Spain divided the Provincia de las Californias, creating the province Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
, which consisted primarily of what would become California, Nevada, Arizona, Colorado, Utah and New Mexico. In 1821 Mexico achieved its independence from Spain and shortly after, in 1824, developed its 1824 Constitution of Mexico, constitution, which established the Alta California territory, which was the same geographic area as the earlier Spanish province.
In 1825, Arizona was visited by its first non-Spanish Europeans, English trappers. In 1836, the Republic of Texas, which contained the easternmost of the Southwest United States, won its independence from Mexico. In 1845 the Republic of Texas was annexed by the United States and immediately became a state, bypassing the usual territory phase. The new state still contained portions of what would eventually become parts of other states. In 1846, the Southwest became embroiled in the Mexican–American War, partly as a result of the United States' annexation of Texas. On August 18, 1846, an American force captured Santa Fe, New Mexico. On December 16 of the same year, American forces captured Tucson, Arizona, marking the end of hostilities in the Southwest United States. When the war ended with the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
on February 2, 1848, the United States gained control of all of present-day California, Nevada and Utah, as well as the majority of Arizona, and parts of New Mexico and Colorado (the rest of present-day Colorado, and most of New Mexico had been gained by the United States in their annexation of the Republic of Texas). The final portion of the Southwestern United States came about through the acquisition of the southernmost parts of Arizona and New Mexico through the Gadsden Purchase in 1853.
In 1851, San Luis, Colorado, San Luis became the first European settlement in what is now Colorado.
Becoming states

 Of the states of which at least a portion make up the Southwest, Texas was the first to achieve statehood. On December 29, 1845, the Republic of Texas was annexed, bypassing the status of becoming a territory, and immediately became a state. Initially, its borders included parts of what would become several other states: almost half of New Mexico, a third of Colorado, and small portions of Kansas, Oklahoma, and Wyoming. Texas current borders were set in the Compromise of 1850, where Texas ceded land to the federal government in exchange for $10 million, which would go to paying off the debt Texas had accumulated in its war with Mexico.
Following the Mexican Cession, the lands of what had been the Mexican territory of Alta California were in flux: portions of what is now New Mexico were claimed, but never controlled, by Texas. With the Compromise of 1850, the states of Texas and California were created (Texas as a slave state, and California as a free state), as well as the Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory. The New Mexico Territory consisted of most of Arizona and New Mexico (excluding a strip along their southern borders), a small section of southern Colorado, and the very southern tip of Nevada; while the Utah Territory consisted of Utah, most of Nevada, and portions of Wyoming and Colorado. The New Mexico Territory was expanded along its southern extent, to its current border, with the signing of the Gadsden Purchase Treaty on December 30, 1853, which was ratified by the U.S. Congress, with some slight alterations, in April 1854.
Of the states of which at least a portion make up the Southwest, Texas was the first to achieve statehood. On December 29, 1845, the Republic of Texas was annexed, bypassing the status of becoming a territory, and immediately became a state. Initially, its borders included parts of what would become several other states: almost half of New Mexico, a third of Colorado, and small portions of Kansas, Oklahoma, and Wyoming. Texas current borders were set in the Compromise of 1850, where Texas ceded land to the federal government in exchange for $10 million, which would go to paying off the debt Texas had accumulated in its war with Mexico.
Following the Mexican Cession, the lands of what had been the Mexican territory of Alta California were in flux: portions of what is now New Mexico were claimed, but never controlled, by Texas. With the Compromise of 1850, the states of Texas and California were created (Texas as a slave state, and California as a free state), as well as the Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory. The New Mexico Territory consisted of most of Arizona and New Mexico (excluding a strip along their southern borders), a small section of southern Colorado, and the very southern tip of Nevada; while the Utah Territory consisted of Utah, most of Nevada, and portions of Wyoming and Colorado. The New Mexico Territory was expanded along its southern extent, to its current border, with the signing of the Gadsden Purchase Treaty on December 30, 1853, which was ratified by the U.S. Congress, with some slight alterations, in April 1854.

 The Colorado Territory was organized on February 28, 1861, created out of lands then currently in the Utah, Kansas, Nebraska, and New Mexico territories. The Nevada Territory was also organized in 1861, on March 2, with land taken from the existing Utah Territory. Initially, only the western 2/3 of what is currently the State of Nevada was included in the territory, with its boundary to the east being the 39th meridian west from Washington, and to the south the 37th parallel north, 37th parallel. In 1862 Nevada's eastern border shifted to the 38th meridian west from Washington, and finally to its current position at the 37th meridian west from Washington in 1866. The boundary modification in 1866 also included adding the southern triangular tip of the present-day state, taken from the Arizona Territory.
From July 24–27, 1861 a Confederate force under the command of Lt. Colonel John Robert Baylor forced the surrender of the small Union garrison stationed at Fort Fillmore, near Mesilla, New Mexico. On August 1, 1861, Baylor declared the creation of the Confederate Arizona, Arizona Territory, and claimed it for the Confederacy, with Mesilla as its capital. The territory, which had been formed by the portion of the existing New Mexico Territory below the 34th parallel, became official on February 14, 1862.
The Colorado Territory was organized on February 28, 1861, created out of lands then currently in the Utah, Kansas, Nebraska, and New Mexico territories. The Nevada Territory was also organized in 1861, on March 2, with land taken from the existing Utah Territory. Initially, only the western 2/3 of what is currently the State of Nevada was included in the territory, with its boundary to the east being the 39th meridian west from Washington, and to the south the 37th parallel north, 37th parallel. In 1862 Nevada's eastern border shifted to the 38th meridian west from Washington, and finally to its current position at the 37th meridian west from Washington in 1866. The boundary modification in 1866 also included adding the southern triangular tip of the present-day state, taken from the Arizona Territory.
From July 24–27, 1861 a Confederate force under the command of Lt. Colonel John Robert Baylor forced the surrender of the small Union garrison stationed at Fort Fillmore, near Mesilla, New Mexico. On August 1, 1861, Baylor declared the creation of the Confederate Arizona, Arizona Territory, and claimed it for the Confederacy, with Mesilla as its capital. The territory, which had been formed by the portion of the existing New Mexico Territory below the 34th parallel, became official on February 14, 1862.
 Nevada was admitted to the Union on October 31, 1864, becoming the 36th state. This was followed by the admittance to the Union of Colorado, which became the 38th state on August 1, 1876. Confederate Arizona was short-lived, however. By May 1862, Confederate forces had been driven out of the region by union troops. That same month a bill was introduced into the U.S. Congress, and on February 24, 1863 Abraham Lincoln signed the Arizona Organic Act, which officially created the U.S. Arizona Territory, Territory of Arizona, splitting the New Mexico Territory at the 107th meridian.
Utah, as shown above, evolved out of the Utah Territory, as pieces of the original territory created in 1850 were carved out: parts were ceded to Nevada, Wyoming, and Colorado in 1861; another section to Nevada in 1862; and the final section to Nevada in 1866. In 1890, the LDS church issued the 1890 Manifesto, which officially banned polygamy for members of the church. It was the last roadblock for Utah entering the Union, and on January 4, 1896, Utah was officially granted statehood, becoming the 45th state.
In 1869, John Wesley Powell led a 3-month expedition which explored the Grand Canyon and the Colorado River. In 1875, he would publish a book describing his explorations, ''Report of the Exploration of the Columbia River of the West and Its Tributaries'', which was later republished as ''The Exploration of the Colorado River and Its Canyons''.
In 1877 silver was discovered in southeastern Arizona. The notorious mining town of Tombstone, Arizona was born to service the miners. The town would become immortalized as the scene of what is considered the greatest gunfight in the history of the Old West, the Gunfight at the O.K. Corral.
Copper was also discovered in 1877, near Bisbee, Arizona, Bisbee and Jerome, Arizona, Jerome in Arizona, which became an important component of the economy of the Southwest. Production began in 1880 and was made more profitable by the expansion of the railroad throughout the territory during the 1880s.
Nevada was admitted to the Union on October 31, 1864, becoming the 36th state. This was followed by the admittance to the Union of Colorado, which became the 38th state on August 1, 1876. Confederate Arizona was short-lived, however. By May 1862, Confederate forces had been driven out of the region by union troops. That same month a bill was introduced into the U.S. Congress, and on February 24, 1863 Abraham Lincoln signed the Arizona Organic Act, which officially created the U.S. Arizona Territory, Territory of Arizona, splitting the New Mexico Territory at the 107th meridian.
Utah, as shown above, evolved out of the Utah Territory, as pieces of the original territory created in 1850 were carved out: parts were ceded to Nevada, Wyoming, and Colorado in 1861; another section to Nevada in 1862; and the final section to Nevada in 1866. In 1890, the LDS church issued the 1890 Manifesto, which officially banned polygamy for members of the church. It was the last roadblock for Utah entering the Union, and on January 4, 1896, Utah was officially granted statehood, becoming the 45th state.
In 1869, John Wesley Powell led a 3-month expedition which explored the Grand Canyon and the Colorado River. In 1875, he would publish a book describing his explorations, ''Report of the Exploration of the Columbia River of the West and Its Tributaries'', which was later republished as ''The Exploration of the Colorado River and Its Canyons''.
In 1877 silver was discovered in southeastern Arizona. The notorious mining town of Tombstone, Arizona was born to service the miners. The town would become immortalized as the scene of what is considered the greatest gunfight in the history of the Old West, the Gunfight at the O.K. Corral.
Copper was also discovered in 1877, near Bisbee, Arizona, Bisbee and Jerome, Arizona, Jerome in Arizona, which became an important component of the economy of the Southwest. Production began in 1880 and was made more profitable by the expansion of the railroad throughout the territory during the 1880s.
 The early 1880s also saw the completion of the second transcontinental railroad, which ran through the heart of the Southwest, called the "Santa Fe Route". It ran from Chicago, down through Topeka, then further south to Albuquerque, before heading almost due west through northern Arizona to Los Angeles.
The repeal of the Sherman Silver Purchase Act in 1893 led to the decline of the silver mining industry in the region.
In 1901, the Santa Fe Railroad reached the South Rim of the Grand Canyon, opening the way for a tourism boom, a trend led by restaurant and hotel entrepreneur Fred Harvey (entrepreneur), Fred Harvey.
The last two territories within the Southwest to achieve statehood were New Mexico and Arizona. By 1863, with the splitting off of the Arizona Territory, New Mexico reached its modern borders. They became states within forty days of one another. On January 6, 1912, New Mexico became the 47th state in the Union. Arizona would shortly follow, becoming the last of the 48 contiguous United States on February 14, 1912.
The early 1880s also saw the completion of the second transcontinental railroad, which ran through the heart of the Southwest, called the "Santa Fe Route". It ran from Chicago, down through Topeka, then further south to Albuquerque, before heading almost due west through northern Arizona to Los Angeles.
The repeal of the Sherman Silver Purchase Act in 1893 led to the decline of the silver mining industry in the region.
In 1901, the Santa Fe Railroad reached the South Rim of the Grand Canyon, opening the way for a tourism boom, a trend led by restaurant and hotel entrepreneur Fred Harvey (entrepreneur), Fred Harvey.
The last two territories within the Southwest to achieve statehood were New Mexico and Arizona. By 1863, with the splitting off of the Arizona Territory, New Mexico reached its modern borders. They became states within forty days of one another. On January 6, 1912, New Mexico became the 47th state in the Union. Arizona would shortly follow, becoming the last of the 48 contiguous United States on February 14, 1912.
Since statehood
Origins of the term and historical/cultural variations
While this article deals with the core definition for the American Southwest, there are many others. The various definitions can be broken down into four main categories: Historical/Archeological; Geological/Topographical; Ecological; and Cultural. In the 1930s and 1940s, many definitions of the Southwest included all or part of Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona, California, Colorado, and Utah. As time has gone on, the definition of the Southwest has become more solidified and more compact. For example, in 1948 the National Geographic Society defined the American Southwest as all of California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico, and the southernmost sections of Oregon, Idaho, and Wyoming, as well as parts of southwest Nebraska, western Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. By 1977, the Society's definition had narrowed to only the four states of Utah, Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico; and by 1982 the portion of the Southwest in the United States, as defined by the Society, had shrunk to Arizona and New Mexico, with the southernmost strip of Utah and Colorado, as well as the Mojave and Colorado deserts in California. Other individuals who focus on Southwest studies who favored a more limited extent of the area to center on Arizona and New Mexico, with small parts of surrounding areas, include Erna Fergusson, Charles Lummis (who claimed to have coined the term, the Southwest), and cultural geographer Raymond Gastil, and ethnologist Miguel León-Portilla. Geographer D. W. Meinig defines the Southwest in a very similar fashion to Reed: the portion of New Mexico west of the Llano Estacado and the portion of Arizona east of the Mojave-Sonoran Desert and south of the "canyon lands" and also including theEl Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
district of western Texas and the southernmost part of Colorado. Meinig breaks the Southwest down into four distinct subregions. He calls the first subregion "Northern New Mexico", and describes it as focused on Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
and Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe. It extends from the San Luis Valley of southern Colorado to south of Socorro, New Mexico, Socorro and including the Manzano Mountains, with an east–west breadth in the north stretching from the upper Canadian River to the upper San Juan River (Colorado River), San Juan River. The area around Albuquerque is sometimes called Central New Mexico.
"Central Arizona" is a vast metropolitan area spread across one contiguous sprawling oasis, essentially equivalent to the Phoenix metropolitan area. The city of Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
is the largest urban center, and located in the approximate center of the area that includes Tempe, Arizona, Tempe, Mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by a ...
, and many others.
Meinig calls the third subregion "El Paso, Tucson, and the Southern Borderlands". While El Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
and Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
are distinctly different cities, they serve as anchor points to the hinterland between them. Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
occupies a large oasis at the western end of the El Paso-Tucson corridor. The region between the two cities is a major transportation trunk with settlements servicing both highway and railway needs. There are also large mining operations, ranches, and agricultural oases. Both El Paso and Tucson have large military installations nearby; Fort Bliss and White Sands Missile Range north of El Paso in New Mexico, and, near Tucson, the Davis-Monthan Air Force Base. About to the southeast are the research facilities at Fort Huachuca. These military installations form a kind of hinterland around the El Paso-Tucson region, and are served by scientific and residential communities such as Sierra Vista, Arizona, Sierra Vista, Las Cruces, and Alamogordo, New Mexico, Alamogordo. El Paso's influence extends north into the Mesilla Valley, and southeast along the Rio Grande into the Trans-Pecos region of Texas.
The fourth subregion Meinig calls the "Northern Corridor and Navajolands", a major highway and railway trunk which connects Albuquerque and Flagstaff, Arizona, Flagstaff. Just north of the transportation trunk are large blocks of American Indian land.
Historical/archeological
As the Territorial evolution of the United States, US expanded westward, the country's American frontier, western border also shifted westward, and consequently, so did the location of the Southwestern and Northwestern United States. In the early years of the United States, Overmountain Men, newly colonized lands lying immediately west of the Appalachian Mountains were State cessions, detached from North Carolina and given the name Southwest Territory. During the decades that followed, the Old Southwest, region known as "the Southwestern United States" covered much of the Deep South east of the Mississippi River. However, as territories and eventual states to the west were added after the Mexican–American War, the geographical "Southwest" expanded, and the relationship of these new acquisitions to the South itself became "increasingly unclear.""Encyclopedia of Southern Culture". Charles Reagan Wilson and William Ferris. University of North Carolina Press 1989 However, archeologist, Erik Reed, gives a description which is the most widely accepted as defining the American Southwest, which runs from Durango, Colorado in the north, to Durango, Mexico, in the south, and from Las Vegas, Nevada in the west to Las Vegas, New Mexico in the East. Reed's definition is roughly equivalent to the western half of the Learning Center of the American Southwest's definition, leaving out any portion of Kansas and Oklahoma, and much of Texas, as well as the eastern half of New Mexico. Since this article is about the Southwestern United States, the areas of Sonora and Chihuahua in Mexico will be excluded. The portion left includes Arizona and western New Mexico, the very southernmost part of Utah, southwestern Colorado, the very tip of west Texas, and triangle formed by the southern tip of Nevada. This will be the defined scope that is used in this article unless otherwise specified in a particular area.Geological/topographical
 Parts of the other states make up the various areas that can be included in the Southwest, depending on the source. The Learning Center of the American Southwest (LCAS) does not rely on current state boundaries, and defines the American Southwest as parts of Arizona, Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah.
From this perspective, almost all of the region's physiographical traits, geological formations, and weather are contained within a box between 26° and 38° northern latitude, and 98° 30' and 124° western longitude.
Parts of the other states make up the various areas that can be included in the Southwest, depending on the source. The Learning Center of the American Southwest (LCAS) does not rely on current state boundaries, and defines the American Southwest as parts of Arizona, Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah.
From this perspective, almost all of the region's physiographical traits, geological formations, and weather are contained within a box between 26° and 38° northern latitude, and 98° 30' and 124° western longitude.
Ecological
When looking at the fauna of the region, there is a broader definition of the American Southwest. The Southwestern Center for Herpetological Research defines the Southwest as being only the states of Arizona, New Mexico, with parts of California, Nevada, Texas, and Utah; although they include all of those six states in their map of the region, solely for ease of defining the border.Cultural

 Lawrence Clark Powell, a major bibliographer whose emphasis is on the Southwest, defined the American Southwest in a 1958 ''Arizona Highways'' article as, "the lands lying west of the Pecos, north of the [Mexican] Border, south of the Mesa Verde and the Grand Canyon, and east of the mountains which wall off Southern California and make it a land in itself."
Texas has long been the focal point of this dichotomy, and is often considered, as such, the ''core area'' of "the South's Southwest." While the Trans-Pecos area is generally acknowledged as part of the ''desert Southwest'', most of Texas and large parts of Oklahoma are often placed into a sub-region of the Southern United States, South, which some consider southwestern in the general framework of the original application, meaning the "Western South". This is an area containing the basic elements of Southern Confederate States of America, history, Culture of the Southern United States, culture, Solid South, politics, Bible Belt, religion, and Southern American English, linguistic and settlement patterns, yet blended with traits of the frontier West. While this particular Southwest is notably different in many ways from the classic "Old South" or Southeastern United States, Southeast, these features are strong enough to give it a separate southwestern identity quite different in nature from that of the interior southwestern states to the west.
One of these distinguishing characteristics in Texas—in addition to having been a Confederate States of America, Confederate state during the Civil War—is that Indigenous and Spanish American culture never played a central role in the development of this area in relative comparison to the others, as the vast majority of settlers were Anglo and blacks from the South.Cultural Regions of the United States. Raymond Gastil. University of Washington Press 1975 Although the present-day state of Oklahoma was Indian Territory until the early 20th century, many of these American Indians were from the southeastern United States and became culturally assimilated early on. The majority of members of these tribes also allied themselves with the Confederacy during the Civil War. Combined with that, once the territory was open for settlement, southeastern pioneers made up a disproportionate number of these newcomers. All this contributed to the new state having a character that differed from other parts of the Southwest with large American Indian populations.
The fact that a majority of residents of Texas and Oklahoma—unlike those in other "southwestern" states—self-identify as living in the South and consider themselves southerners rather than the West and westerners—also lends to treating these two states as a somewhat distinct and separate entity in terms of regional classification.
Lawrence Clark Powell, a major bibliographer whose emphasis is on the Southwest, defined the American Southwest in a 1958 ''Arizona Highways'' article as, "the lands lying west of the Pecos, north of the [Mexican] Border, south of the Mesa Verde and the Grand Canyon, and east of the mountains which wall off Southern California and make it a land in itself."
Texas has long been the focal point of this dichotomy, and is often considered, as such, the ''core area'' of "the South's Southwest." While the Trans-Pecos area is generally acknowledged as part of the ''desert Southwest'', most of Texas and large parts of Oklahoma are often placed into a sub-region of the Southern United States, South, which some consider southwestern in the general framework of the original application, meaning the "Western South". This is an area containing the basic elements of Southern Confederate States of America, history, Culture of the Southern United States, culture, Solid South, politics, Bible Belt, religion, and Southern American English, linguistic and settlement patterns, yet blended with traits of the frontier West. While this particular Southwest is notably different in many ways from the classic "Old South" or Southeastern United States, Southeast, these features are strong enough to give it a separate southwestern identity quite different in nature from that of the interior southwestern states to the west.
One of these distinguishing characteristics in Texas—in addition to having been a Confederate States of America, Confederate state during the Civil War—is that Indigenous and Spanish American culture never played a central role in the development of this area in relative comparison to the others, as the vast majority of settlers were Anglo and blacks from the South.Cultural Regions of the United States. Raymond Gastil. University of Washington Press 1975 Although the present-day state of Oklahoma was Indian Territory until the early 20th century, many of these American Indians were from the southeastern United States and became culturally assimilated early on. The majority of members of these tribes also allied themselves with the Confederacy during the Civil War. Combined with that, once the territory was open for settlement, southeastern pioneers made up a disproportionate number of these newcomers. All this contributed to the new state having a character that differed from other parts of the Southwest with large American Indian populations.
The fact that a majority of residents of Texas and Oklahoma—unlike those in other "southwestern" states—self-identify as living in the South and consider themselves southerners rather than the West and westerners—also lends to treating these two states as a somewhat distinct and separate entity in terms of regional classification.

Vegetation and terrain
Vegetation of the southwest generally includes various types ofyucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial plant, perennial shrubs and trees in the family (biology), family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their Rosette (botany), rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped Leaf, ...
, along with saguaro cactus
The saguaro (, ) (''Carnegiea gigantea'') is a tree-like cactus species in the monotypic genus ''Carnegiea'' that can grow to be over tall. It is native to the Sonoran Desert in Arizona, the Mexican state of Sonora, and the Whipple Mountains ...
, barrel cactus, opuntia, prickly pear cactus, desert spoon, creosote bush
''Larrea tridentata'', called creosote bush and greasewood as a plant, chaparral as a medicinal herb, and ''gobernadora'' (Spanish for "governess") in Mexico, due to its ability to secure more water by inhibiting the growth of nearby plants. In S ...
, sagebrush, and greasewood. Although cacti are thought to only grow in Arizona and New Mexico, many native cacti grow throughout Nevada, Utah, Colorado, and west Texas. Steppe is also located all over the high plains areas in Colorado, New Mexico, and Texas. The mountains of the southwestern states have large tracts of alpine trees.
 Landscape features of the core southwestern areas include mountains, canyons, mesas, buttes, high broad basins, plateaus, desert lands, and some plains, characteristic of the Basin and Range Province. The entire southwestern region features semi-arid to arid terrain. The far eastern part of southwestern Texas, for example, the Texas Hill Country, consists of dry, tall, and rugged rocky hills of limestone and granite. South Texas and the Lower Rio Grande Valley, Rio Grande Valley is mostly flat with many places consisting of scrub and bare topsoil, much like the deserts further west.
Landscape features of the core southwestern areas include mountains, canyons, mesas, buttes, high broad basins, plateaus, desert lands, and some plains, characteristic of the Basin and Range Province. The entire southwestern region features semi-arid to arid terrain. The far eastern part of southwestern Texas, for example, the Texas Hill Country, consists of dry, tall, and rugged rocky hills of limestone and granite. South Texas and the Lower Rio Grande Valley, Rio Grande Valley is mostly flat with many places consisting of scrub and bare topsoil, much like the deserts further west.
Wildlife
The region has an extremely diverse bird population, with hundreds of species being found in the American Southwest. In the Chiricahua Mountains alone, in southeastern Arizona, there can be found more than 400 species. Species include Canada goose, Canadian (''Branta canadensis'') and Snow goose, snow geese, sandhill cranes (''Grus canadensis''), and the Greater roadrunner, roadrunner, the state bird of New Mexico and most famous bird in the region, is found in all states of the Southwest. Birds of prey include the red-tailed hawk (''Buteo jamaicensis''), Cooper's hawk (''Accipiter cooperii''), the osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), golden eagles (''Aquila chrysaetos''), Harris's hawk (''Parabuteo unicinctus''), American kestrel (''Falco sparverius''), peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), the gray hawk (''Buteo plagiatus''), the barn owl (''Tyto alba''), the western screech owl (''Megascops kennicottii''), the great horned owl (''Bubo virginianus''), the elf owl (''Micrathene whitneyi''), and the burrowing owl (''Athene cunicularia'') Other bird species include the turkey vulture (''Cathartes aura''), the black vulture (''Coragyps atratus''), the northern cardinal (''Cardinalis cardinalis''), the blue grosbeak (''Passerina caerulea''), the house finch (''Haemorhous mexicanus''), the lesser goldfinch (''Spinus psaltria''), the broad-billed hummingbird (''Cynanthus latirostris''), the black-chinned hummingbird (''Archilochus alexandri''), Costa's hummingbird (''Calypte costae''), Gambel's quail (''Callipepla gambelii''), the common raven (''Corvus corax''), the Gila woodpecker (''Melanerpes uropygialis''), the gilded flicker (''Colaptes chrysoides''), the cactus wren (''Campylorhynchus brunneicapillus''), and the rock wren (''Salpinctes obsoletus''). Four types of doves call the Southwest home: the white-winged dove (''Zenaida asiatica''), the mourning dove (''Zenaida macroura''), the common ground dove (''Columbina passerina''), and the Inca dove (''Columbina inca'').Climate
 The term "High Desert" is also synonymous with this region. The High Desert is generally defined as the
The term "High Desert" is also synonymous with this region. The High Desert is generally defined as the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily ...
and the Colorado Plateau, which extends from inland southern California into southern Nevada, east to the Rio Grande Rift
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihuahu ...
in New Mexico. The High Desert also extends into parts of the Northwestern United States, Northwest, such as the Red Desert (Wyoming), Red Desert in southwestern Wyoming. The High Desert is very different from the lower desert lands found in Arizona, in the Sonoran Desert. This area of the desert land generally sits at a very high elevation, much higher than the normal desert land, and can receive very cold temperatures at night in the winter (with the exception of California, southern Nevada and southwestern Utah), sometimes near zero degrees on very cold nights. The High Desert also receives a decent amount of snowfall in the winter (with the exception of California, southern Nevada and southwestern Utah) but melts very quickly. Rain falls in this region mainly in the summer, during the North American Monsoon season.
 The desert lands found in Eastern Utah, Northern Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico are usually referred to as the high desert. Colorado has scattered desert lands found in southern, southwestern, western, and northwestern parts of the state. These scattered desert lands are located in and around areas such as, the Roan Plateau, Dinosaur National Monument, Colorado National Monument, Royal Gorge, Cortez, Colorado, Cortez, Dove Creek, Colorado, Dove Creek, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Four Corners Monument, Montrose, Colorado, Montrose, Blue Mesa Reservoir, Pueblo, Colorado, Pueblo, San Luis Valley, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes and Joshua Tree National Park. Besides the
The desert lands found in Eastern Utah, Northern Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico are usually referred to as the high desert. Colorado has scattered desert lands found in southern, southwestern, western, and northwestern parts of the state. These scattered desert lands are located in and around areas such as, the Roan Plateau, Dinosaur National Monument, Colorado National Monument, Royal Gorge, Cortez, Colorado, Cortez, Dove Creek, Colorado, Dove Creek, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Four Corners Monument, Montrose, Colorado, Montrose, Blue Mesa Reservoir, Pueblo, Colorado, Pueblo, San Luis Valley, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes and Joshua Tree National Park. Besides the Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert ( es, Desierto de Chihuahua, ) is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lo ...
, lands in southwestern and southern New Mexico, they also have scattered desert lands in the northwestern and northern portions of their state, which is referred to as the high desert.
During El Niño, winters and springs are generally colder and wetter across southern portions of the region, while the northern portion stays warmer and drier due to a southern jet stream. Under La Niña, the opposite happens, meaning the cool and wet weather tends to stay farther north. The Southwest also experiences multi-year and multi-decade episodes of severe drought, including the ongoing southwestern North American megadrought which emerged starting year 2000.
National parks, monuments and forests
 The southwestern United States contains many well-known national parks including Grand Canyon National Park, Grand Canyon in Arizona, Death Valley National Park, Death Valley in California, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes in Colorado, Arches National Park, Arches in Utah, Big Bend National Park, Big Bend in Texas, Great Basin National Park, Great Basin in Nevada, and White Sands National Park, White Sands in New Mexico.
The southwestern United States contains many well-known national parks including Grand Canyon National Park, Grand Canyon in Arizona, Death Valley National Park, Death Valley in California, Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Great Sand Dunes in Colorado, Arches National Park, Arches in Utah, Big Bend National Park, Big Bend in Texas, Great Basin National Park, Great Basin in Nevada, and White Sands National Park, White Sands in New Mexico.
 Arizona parks and monuments include Grand Canyon, Monument Valley (a Navajo Nation park), Petrified Forest National Park, Petrified Forest, and Saguaro National Park, Saguaro national parks; the national monuments of Agua Fria National Monument, Agua Fria, Canyon de Chelly National Monument, Canyon de Chelly, Casa Grande Ruins National Monument, Casa Grande Ruins, Chiricahua National Monument, Chiricahua, Ironwood Forest National Monument, Ironwood Forest, Montezuma Castle National Monument, Montezuma Castle, Navajo National Monument, Navajo, Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, Organ Pipe Cactus, Pipe Spring National Monument, Pipe Spring, Sonoran Desert National Monument, Sonoran Desert, Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument, Sunset Crater, Tonto National Monument, Tonto, Tuzigoot National Monument, Tuzigoot, Vermilion Cliffs National Monument, Vermilion Cliffs, Walnut Canyon National Monument, Walnut Canyon, and Wupatki National Monument, Wupatki. Other federal areas include the Apache–Sitgreaves National Forests and Tumacacori National Historical Park.
Southern California parks and monuments include Death Valley and Joshua Tree National Park, Joshua Tree national parks; the national monuments of Castle Mountains National Monument, Castle Mountains, Mojave Trails National Monument, Mojave Trails, Sand to Snow National Monument, Sand to Snow, and San Gabriel Mountains National Monument, San Gabriel Mountains; and Mojave National Preserve.
Colorado parks and monuments include Great Sand Dunes, Black Canyon of the Gunnison National Park, Black Canyon of the Gunnison, and Mesa Verde National Park, Mesa Verde national parks; the national monuments of Browns Canyon National Monument, Browns Canyon, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Canyons of the Ancients, Colorado National Monument, Colorado, Hovenweep National Monument, Hovenweep, and Yucca House National Monument, Yucca House. Other federal areas include Curecanti National Recreation Area and Bent's Old Fort National Historic Site; as well as the national forests of San Isabel National Forest, San Isabel, San Juan National Forest, San Juan, and Uncompahgre National Forest, Uncompahgre.
Arizona parks and monuments include Grand Canyon, Monument Valley (a Navajo Nation park), Petrified Forest National Park, Petrified Forest, and Saguaro National Park, Saguaro national parks; the national monuments of Agua Fria National Monument, Agua Fria, Canyon de Chelly National Monument, Canyon de Chelly, Casa Grande Ruins National Monument, Casa Grande Ruins, Chiricahua National Monument, Chiricahua, Ironwood Forest National Monument, Ironwood Forest, Montezuma Castle National Monument, Montezuma Castle, Navajo National Monument, Navajo, Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, Organ Pipe Cactus, Pipe Spring National Monument, Pipe Spring, Sonoran Desert National Monument, Sonoran Desert, Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument, Sunset Crater, Tonto National Monument, Tonto, Tuzigoot National Monument, Tuzigoot, Vermilion Cliffs National Monument, Vermilion Cliffs, Walnut Canyon National Monument, Walnut Canyon, and Wupatki National Monument, Wupatki. Other federal areas include the Apache–Sitgreaves National Forests and Tumacacori National Historical Park.
Southern California parks and monuments include Death Valley and Joshua Tree National Park, Joshua Tree national parks; the national monuments of Castle Mountains National Monument, Castle Mountains, Mojave Trails National Monument, Mojave Trails, Sand to Snow National Monument, Sand to Snow, and San Gabriel Mountains National Monument, San Gabriel Mountains; and Mojave National Preserve.
Colorado parks and monuments include Great Sand Dunes, Black Canyon of the Gunnison National Park, Black Canyon of the Gunnison, and Mesa Verde National Park, Mesa Verde national parks; the national monuments of Browns Canyon National Monument, Browns Canyon, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Canyons of the Ancients, Colorado National Monument, Colorado, Hovenweep National Monument, Hovenweep, and Yucca House National Monument, Yucca House. Other federal areas include Curecanti National Recreation Area and Bent's Old Fort National Historic Site; as well as the national forests of San Isabel National Forest, San Isabel, San Juan National Forest, San Juan, and Uncompahgre National Forest, Uncompahgre.
 Nevada has one national park at Great Basin, and the national monuments of Basin and Range National Monument, Basin and Range, Gold Butte National Monument, Gold Butte, and Tule Springs Fossil Beds National Monument, Tule Springs Fossil Beds. Other federal areas include Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest, Lake Mead National Recreation Area, and Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area.
New Mexico has two national parks, at Carlsbad Caverns National Park, Carlsbad Caverns and White Sands. National monuments include Aztec Ruins National Monument, Aztec Ruins, Bandelier National Monument, Bandelier, El Malpais National Monument, El Malpais, El Morro National Monument, El Morro, Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument, Gila Cliff Dwellings, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks National Monument, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks National Monument, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks, Petroglyph National Monument, Petroglyph, Rio Grande del Norte National Monument, Rio Grande del Norte, and Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument, Salinas Pueblo Missions. Other federal park areas include Chaco Culture National Historical Park, Pecos National Historical Park, Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge, and the national forests of Apache National Forest, Apache, Carson National Forest, Carson, Gila National Forest, Gila, Lincoln National Forest, Lincoln, and Santa Fe National Forest, Santa Fe.
West Texas has two national parks, at Big Bend and Guadalupe Mountains National Park, Guadalupe Mountains. Other federal park areas include Chamizal National Memorial and Fort Davis National Historic Site.
Utah national parks include Arches, Bryce Canyon National Park, Bryce Canyon, Canyonlands National Park, Canyonlands, Capitol Reef National Park, Capitol Reef, and Zion National Park, Zion. National monuments include Bears Ears National Monument, Bears Ears, Cedar Breaks National Monument, Cedar Breaks, Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, Grand Staircase–Escalante, Hovenweep (also in Colorado), Natural Bridges National Monument, Natural Bridges, and Rainbow Bridge National Monument, Rainbow Bridge. Other federal areas include Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, Dixie National Forest, and Manti–La Sal National Forest.
Nevada has one national park at Great Basin, and the national monuments of Basin and Range National Monument, Basin and Range, Gold Butte National Monument, Gold Butte, and Tule Springs Fossil Beds National Monument, Tule Springs Fossil Beds. Other federal areas include Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest, Lake Mead National Recreation Area, and Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area.
New Mexico has two national parks, at Carlsbad Caverns National Park, Carlsbad Caverns and White Sands. National monuments include Aztec Ruins National Monument, Aztec Ruins, Bandelier National Monument, Bandelier, El Malpais National Monument, El Malpais, El Morro National Monument, El Morro, Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument, Gila Cliff Dwellings, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks National Monument, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks National Monument, Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks, Petroglyph National Monument, Petroglyph, Rio Grande del Norte National Monument, Rio Grande del Norte, and Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument, Salinas Pueblo Missions. Other federal park areas include Chaco Culture National Historical Park, Pecos National Historical Park, Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge, and the national forests of Apache National Forest, Apache, Carson National Forest, Carson, Gila National Forest, Gila, Lincoln National Forest, Lincoln, and Santa Fe National Forest, Santa Fe.
West Texas has two national parks, at Big Bend and Guadalupe Mountains National Park, Guadalupe Mountains. Other federal park areas include Chamizal National Memorial and Fort Davis National Historic Site.
Utah national parks include Arches, Bryce Canyon National Park, Bryce Canyon, Canyonlands National Park, Canyonlands, Capitol Reef National Park, Capitol Reef, and Zion National Park, Zion. National monuments include Bears Ears National Monument, Bears Ears, Cedar Breaks National Monument, Cedar Breaks, Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, Grand Staircase–Escalante, Hovenweep (also in Colorado), Natural Bridges National Monument, Natural Bridges, and Rainbow Bridge National Monument, Rainbow Bridge. Other federal areas include Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, Dixie National Forest, and Manti–La Sal National Forest.
Ethnicity
The Southwest is ethnically varied, with significant Anglo-American ethnic group, Anglo American and Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic American populations in addition to more regional African American, Asian American, and Native Americans in the United States, American Indian populations. Hispanic Americans (mostly Mexican Americans, with large populations of Spanish Americans) can be found in large numbers in every major city in the Southwest such asEl Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
(80%), San Antonio, Texas, San Antonio (63%), Los Angeles (48%), Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
(47%), Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
(43%), Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
(41%), Las Vegas, Nevada, Las Vegas (32%), and Mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by a ...
(27%).
Very large Hispanic American populations can also be found in the smaller cities such as Eagle Pass, Texas, Eagle Pass (96%), Las Cruces (56%), Yuma (55%), Blythe, California, Blythe (53%), Pueblo, Colorado, Pueblo (48%), Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe (48%), and Glendale Glendale is the anglicised version of the Gaelic Gleann Dail, which means ''valley of fertile, low-lying arable land''.
It may refer to:
Places Australia
* Glendale, New South Wales
** Stockland Glendale, a shopping centre
*Glendale, Queensland, ...
(36%). Many small towns throughout the southwestern states also have significantly large Latino populations.
The largest African American populations in the Southwest can be found in Las Vegas (10%), San Antonio (7%), and Phoenix (5%).
The largest Asian American populations in the southwest can be found in California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, with some significant Asian population in Phoenix. The most significant American Indian populations can be found in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
and Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
.
Cities and urban areas
The area also contains many of the nation's largest cities and metropolitan areas, despite relatively low population density in rural areas.Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
is the fifth most populous city in the country, and Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
and Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
were some of the fastest-growing cities in the United States. Also, the region as a whole has witnessed some of the highest population growth in the United States, and according to the United States Census Bureau, US Census Bureau, in 2008–2009, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
was the fastest-growing state in America. As of the 2010 Census, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
was the fastest-growing state in the United States, with an increase of 35.1% in the last ten years. Additionally, Arizona (24.6%), Utah (23.8%), Texas (20.6%), and Colorado (16.9%) were all in the top ten fastest-growing states as well.
The largest List of metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan areas are centered around Phoenix metropolitan area, Phoenix (with an estimated population of more than 5 million ), Las Vegas–Paradise, NV MSA, Las Vegas (more than 2.2 million), Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
(more than 1 million), Albuquerque metropolitan area, Albuquerque (more than 900,000), and El Paso metropolitan area, El Paso (more than 840,000). Those five metropolitan areas have an estimated total population of more than 9.6 million , with nearly 60 percent of them living in the two Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
cities—Phoenix and Tucson.
Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
(also the largest Metropolitan statistical area, MSA)
File:Downtown El Paso at sunset.jpeg, 2. El Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
(5th largest MSA)
File:Las Vegas 89.jpg, 3. Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
(2nd largest MSA)
File:Abqdowntown.jpg, 4. Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
(also the 4th largest MSA)
File:Tucson shab1.JPG, 5. Tucson
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
(3rd largest MSA)
Largest cities and metropolitan areas (2020 census)
Sports
Professional

 Of the four Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, major professional sports, Phoenix and Las Vegas are the only metropolitan areas in the Southwest that have representatives. While Las Vegas is home to the Las Vegas Raiders NFL football team and the Vegas Golden Knights NHL hockey team, Phoenix is one of only 13 U.S. cities to have representatives in all four: Arizona Diamondbacks in Major League Baseball, Arizona Cardinals in the National Football League, the Phoenix Suns in the National Basketball Association, and the Arizona Coyotes in the National Hockey League. The Greater Phoenix area is home to the Cactus League, one of two spring training leagues for Major League Baseball; fifteen of MLB's thirty teams are now included in the Cactus League. The region has also been the scene of several NFL super bowls. Sun Devil Stadium in Tempe held Super Bowl XXX in 1996, when the Dallas Cowboys defeated the Pittsburgh Steelers. State Farm Stadium in Glendale, Arizona hosted Super Bowl XLII on February 3, 2008, in which the New York Giants defeated the New England Patriots, as well as Super Bowl XLIX, which resulted in the New England Patriots defeating the Seattle Seahawks 28–24. The U.S. Airways Center hosted both the 1995 NBA All-Star Game, 1995 and the 2009 NBA All-Star Games.
In 1997, the Phoenix Mercury were one of the original eight teams to launch the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA). Indoor American football is represented by the Arizona Rattlers located in Phoenix. The region is also host to several major professional golf events: the LPGA's RR Donnelley LPGA Founders Cup, Founder's Cup; the Phoenix Open and the Shriners Hospitals for Children Open (in Las Vegas) of the Professional Golfers' Association of America, PGA; and the Tucson Conquistadores Classic (in Tucson), and the Charles Schwab Cup Championship (in Scottsdale) on the Champions Tour of the PGA.
NASCAR has two venues within the region: The Phoenix International Raceway, was built in 1964 with a one-mile oval, with a one-of-a-kind design, as well as a 2.5-mile road course, and the Las Vegas Motor Speedway, a 1,200-acre (490 ha) complex of multiple tracks for motorsports racing. There are several nationally recognized running events in the region, including The Phoenix Marathon, a qualifier for the Boston Marathon, and the Rock 'n' Roll Marathon Series in both Rock 'n' Roll Arizona Marathon, Phoenix and Rock 'n' Roll Las Vegas Marathon, Las Vegas. Las Vegas is also the end point for the annual Baker to Vegas Challenge Cup Relay, a 120-mile-long foot race by law enforcement teams from around the world, which is the largest law enforcement athletic event in the world. Las Vegas is the premier boxing venue in the country, and is also known for mixed martial arts events.
The Southwest is also home to some of the most prominent rodeos in North America. The Professional Bull Riders association has its headquarters in Pueblo, Colorado. The Professional Bull Riders#World Finals Event Champions, PBR World Finals are held annually in Las Vegas, which also hosts the National Finals Rodeo, which is the nation's premier rodeo event. Other major rodeo events include the week-long Fiesta de los Vaqueros in Tucson, the World's Oldest Rodeo in Prescott, Arizona, the Southwestern International PRCA Rodeo in El Paso, Texas, and the Rodeo de Santa Fe, one of the nation's premier rodeos.
Since the 1950s, Las Vegas has been host to many of professional boxing's largest events, beginning with the Heavyweight non-title bout in 1955 between world light heavyweight champion Archie Moore and perennial contender Niño Valdés. Muhammad Ali fought his last world title bout in Las Vegas against Larry Holmes in 1980, and Floyd Mayweather fought many of his major fights there.
Of the four Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, major professional sports, Phoenix and Las Vegas are the only metropolitan areas in the Southwest that have representatives. While Las Vegas is home to the Las Vegas Raiders NFL football team and the Vegas Golden Knights NHL hockey team, Phoenix is one of only 13 U.S. cities to have representatives in all four: Arizona Diamondbacks in Major League Baseball, Arizona Cardinals in the National Football League, the Phoenix Suns in the National Basketball Association, and the Arizona Coyotes in the National Hockey League. The Greater Phoenix area is home to the Cactus League, one of two spring training leagues for Major League Baseball; fifteen of MLB's thirty teams are now included in the Cactus League. The region has also been the scene of several NFL super bowls. Sun Devil Stadium in Tempe held Super Bowl XXX in 1996, when the Dallas Cowboys defeated the Pittsburgh Steelers. State Farm Stadium in Glendale, Arizona hosted Super Bowl XLII on February 3, 2008, in which the New York Giants defeated the New England Patriots, as well as Super Bowl XLIX, which resulted in the New England Patriots defeating the Seattle Seahawks 28–24. The U.S. Airways Center hosted both the 1995 NBA All-Star Game, 1995 and the 2009 NBA All-Star Games.
In 1997, the Phoenix Mercury were one of the original eight teams to launch the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA). Indoor American football is represented by the Arizona Rattlers located in Phoenix. The region is also host to several major professional golf events: the LPGA's RR Donnelley LPGA Founders Cup, Founder's Cup; the Phoenix Open and the Shriners Hospitals for Children Open (in Las Vegas) of the Professional Golfers' Association of America, PGA; and the Tucson Conquistadores Classic (in Tucson), and the Charles Schwab Cup Championship (in Scottsdale) on the Champions Tour of the PGA.
NASCAR has two venues within the region: The Phoenix International Raceway, was built in 1964 with a one-mile oval, with a one-of-a-kind design, as well as a 2.5-mile road course, and the Las Vegas Motor Speedway, a 1,200-acre (490 ha) complex of multiple tracks for motorsports racing. There are several nationally recognized running events in the region, including The Phoenix Marathon, a qualifier for the Boston Marathon, and the Rock 'n' Roll Marathon Series in both Rock 'n' Roll Arizona Marathon, Phoenix and Rock 'n' Roll Las Vegas Marathon, Las Vegas. Las Vegas is also the end point for the annual Baker to Vegas Challenge Cup Relay, a 120-mile-long foot race by law enforcement teams from around the world, which is the largest law enforcement athletic event in the world. Las Vegas is the premier boxing venue in the country, and is also known for mixed martial arts events.
The Southwest is also home to some of the most prominent rodeos in North America. The Professional Bull Riders association has its headquarters in Pueblo, Colorado. The Professional Bull Riders#World Finals Event Champions, PBR World Finals are held annually in Las Vegas, which also hosts the National Finals Rodeo, which is the nation's premier rodeo event. Other major rodeo events include the week-long Fiesta de los Vaqueros in Tucson, the World's Oldest Rodeo in Prescott, Arizona, the Southwestern International PRCA Rodeo in El Paso, Texas, and the Rodeo de Santa Fe, one of the nation's premier rodeos.
Since the 1950s, Las Vegas has been host to many of professional boxing's largest events, beginning with the Heavyweight non-title bout in 1955 between world light heavyweight champion Archie Moore and perennial contender Niño Valdés. Muhammad Ali fought his last world title bout in Las Vegas against Larry Holmes in 1980, and Floyd Mayweather fought many of his major fights there.
College
The Southwest is home to a rich tradition of college sports. The Pac-12 Conference has two teams in the region, the Arizona State Sun Devils and the Arizona Wildcats, University of Arizona Wildcats. The Mountain West Conference also has two teams, the UNLV Rebels and the New Mexico Lobos, University of New Mexico Lobos. Conference USA is represented by the UTEP Miners, University of Texas at El Paso Miners. The Big Sky Conference has two teams: the Northern Arizona Lumberjacks, Lumberjacks of Northern Arizona University in Flagstaff, Arizona, and the Southern Utah Thunderbirds, Southern Utah University Thunderbirds in Cedar City, Utah. The Western Athletic Conference also has two representatives, the New Mexico State Aggies, New Mexico State University Aggies in Las Cruces, New Mexico, and the Grand Canyon Antelopes, Grand Canyon University Antelopes in Phoenix. Las Vegas is becoming the nexus for NCAA league basketball tournaments. The Mountain West Conference, the Western Athletic Conference, the West Coast Conference, and the Pac-12 Conference all hold their conference basketball tournaments in Las Vegas. The Southwest is the site of six college football bowl games: the TicketCity Cactus Bowl, formerly known as the Insight Bowl, in Tempe; the Arizona Bowl in Tucson; the Fiesta Bowl, played at the University of Phoenix Stadium; the Las Vegas Bowl; the New Mexico Bowl in Albuquerque; and the Sun Bowl in El Paso, Texas. The erstwhile [20th century] Southwest Conference might seem to have been named after this region, but it had no teams fromArizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
nor New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
. All but one of its teams were from schools in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
."See also" [the article about the] Southwest Conference.
Politics
See also
* Pacific Southwest * Southwest Conference (for a different division of the US for sports) * Water Education Foundation * Western United StatesNotes
References
Further reading
* Bozanic, Andrew D. A., "Preserving Pictures of the Past: The Packaging and Selling of the American Southwest with an Emphasis on the Historic Preservation," ''Nevada Historical Society Quarterly,'' 53 (Fall–Winter 2010), 196–214. * Burke, Flannery. ''A Land Apart: The Southwest and the Nation in the Twentieth Century'' (U of Arizona Press, 2017), x, 413 pp. * * * De León, Arnoldo. ''Mexican Americans in Texas: A Brief History'' (2nd ed. 1999) * Garcia, Richard A. "Changing Chicano Historiography," ''Reviews in American History'' 34.4 (2006) 521–528 in Project MUSE * Griffin-Pierce, Trudy. ''Native Peoples of the Southwest'' (2000) * Lamar, Howard, ed. ''The New Encyclopedia of the American West'' (Yale U.P., 1998) * Meinig, Donald W. ''Southwest: Three Peoples in Geographical Change, 1600–1970,'' (1971), Oxford University Press, * Prampolini, Gaetano, and Annamaria Pinazzi (eds). "The Shade of the Saguaro/La sombra del saguaro," Firenze University PresFirenze University Press
(2013) * * * Weber, David J. ''The Mexican Frontier, 1821–1846: The American Southwest Under Mexico'' (1982) * Weber, David J. "The Spanish Borderlands, Historiography Redux." ''The History Teacher'', 39#1 (2005), pp. 43–56. JSTOR
online
External links
American Southwest, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
Water-use Trends in the Desert Southwest, 1950–2000
United States Geological Survey {{Authority control Southwestern United States, Cultural regions of the United States Regions of the Western United States