|
Bad Kleinkirchheim
Bad Kleinkirchheim is a municipality and spa town in the district of Spittal an der Drau, in Carinthia, Austria. Until the middle of the 20th century, agriculture was the dominant focus, but it is now a renowned spa and ski resort. Although records show people appreciating the area as a recreation area as early as the 11th century, and the first bathing guests arriving in the 17th century, it was only in the last few decades that Bad Kleinkirchheim began to move away from agriculture and focus on its potential for tourism. Geography Location Bad Kleinkirchheim is at an average elevation of in a stretch of a glacial trough valley in the Gurktal Alps (Nock Mountains), between the Millstätter See and the upper Gurk River. The populated section lies between and , and the highest point in the area is the peak of the Klomnock, at . North of Kleinkirchheim and St. Oswald, part of the Nockberge National Park is within the area’s boundaries. To the north and south of the valley, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spittal An Der Drau (district)
Bezirk Spittal an der Drau is an administrative district (''Bezirk'') in the state of Carinthia, Austria. Geography With an area of the district is 2,763.99 km², it is Austria's second largest district by area (after Liezen), even larger than the Austrian state of Vorarlberg, and by far the largest district in Carinthia. The administrative centre is Spittal an der Drau, other major settlements are Gmünd, Greifenburg, Millstatt, Obervellach, Radenthein, Seeboden, Steinfeld, and Winklern. Together with the neighbouring districts of Hermagor and Feldkirchen, Spittal forms the Upper Carinthia (''Oberkärnten'') region according to the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS). It borders on East Tyrol (Lienz District) in the west and the Austrian state of Salzburg in the north. The mountainous area comprises the southern ranges of the High Tauern and the Möll valley, the western Gurktal Alps (Nock Mountains), as well as the broad Drava Valley and the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurktal Alps
The Gurktal Alps (german: Gurktaler Alpen, sl, Krške Alpe) is a mountain range located in the Central Eastern Alps in Austria, named after the valley of the Gurk river. The range stretches west to Lake Millstatt and east to Neumarkter Sattel (north-northwest of Neumarkt in der Steiermark). The highest peak is the Styrian Eisenhut (2441m). Geography Location The range is located between the Mur Valley in the north, separating it from the Niedere Tauern, and the Drava in the south, where it borders on the Gailtal Alps and Karavanke ranges of the Southern Limestone Alps. In the west, the Gurktal Alps reach up to the Katschberg Pass and the Ankogel Group of the Hohe Tauern range. In the east, the Neumarkt Pass in Upper Styria separates it from the adjacent Lavanttal Alps. Subdivisions The Gurktal Alps may be divided into five subgroups: * The ''Nock Mountains'' lie between the Liesertal and Flattnitzer Höhe. Their highest peak is the Eisenhut (2,441 m). * The ''Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
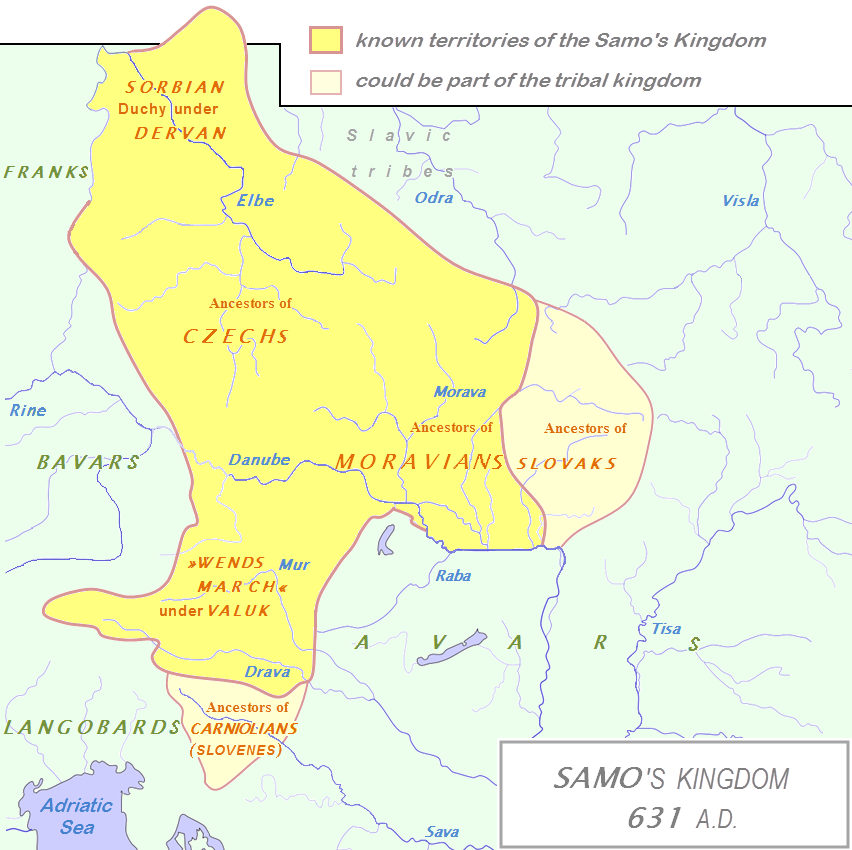
Duchy Of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria (German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire. During internal struggles of the ruling Ottonian dynasty, the Bavarian territory was considerably diminished by the separation of the newly established Duchy of Carinthia in 976. Between 1070 and 1180 the Holy Roman Emperors were again strongly opposed by Bavaria, especially by the ducal House of Welf. In the final conflict between the Welf and Hohenstaufen dynasties, Duke Henry the Lion was banned and deprived of his Bavarian and Saxon fiefs by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drava
The Drava or Drave''Utrata Fachwörterbuch: Geographie - Englisch-Deutsch/Deutsch-Englisch'' by Jürgen Utrata (2014). Retrieved 10 Apr 2014. (german: Drau, ; sl, Drava ; hr, Drava ; hu, Dráva ; it, Drava ) is a river in southern Central Europe. With a length of ,Joint Drava River Corridor Analysis Report 27 November 2014 including the Sextner Bach source, it is the fifth or sixth longest tributary of the Danube, after the Tisza, Sava, Prut, Mureș (river), Mureș and perhaps Siret (river), Siret. The Drava drains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Settlement Of The Eastern Alps
The settlement of the Eastern Alps region by early Slavs took place during the 6th to 8th centuries. It is part of the southward expansion of the early Slavs which would result in the characterization of the South Slavic group, and would ultimately result in the ethnogenesis of present-day Slovenes. The Eastern Alpine territories concerned comprise modern-day Slovenia, Eastern Friuli and large parts of modern-day Austria (Carinthia, Styria, East Tyrol, Lower Austria and Upper Austria). Historical background The migration of Slavic peoples from their homeland began in roughly the late 4th to early 5th century, as Germanic peoples started moving into the territory of the Roman Empire. The migrations were stimulated by the arrival of Huns into Eastern Europe. The Germanic peoples subsequently fought for control over territories in the eastern part of the disintegrating Roman Empire. Slavic tribes were part of various tribal alliances with the Germanic (Lombards, Gepids) and Euras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celts, Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, Raetia and Vindelici to the west, Pannonia to the east and south-east, and Roman Italy, Italia (Triveneto, Venetia et Histria) to the south. The kingdom was founded around 400 BC, and had its capital at the royal residence at Virunum on the Magdalensberg. Area and population Around 800 BC, the region was inhabited mostly by the people of the local Celtic Hallstatt culture. Around 450 BC, they merged with the people of the other core Celtic areas in the south-western regions of Germany and La Tène culture, eastern France. The country is mountainous and rich in iron and salt. It supplied material for the manufacturing of arms in Pannonia, Moesia, and northern Italy. The famous Noric steel was largely used in the maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Kleinkirchheim Pfarrkirche Heiliger Ulrich 20072007 51
Bad or BAD may refer to: Common meanings *Evil, the opposite of moral good * Erroneous, inaccurate or incorrect *Unhealthy, or counter to well-being *Antagonist, the threat or obstacle of moral good Acronyms * BAD-2, a Soviet armored trolley car * Bank account debits tax, an Australian tax * Bcl-2-associated death promoter, a pro-apoptotic protein * Team B.A.D., a professional wrestling tag team Films * ''Andy Warhol's Bad'', a 1977 film * ''Bad'', an unfinished film by Theo van Gogh Music Performers * B. A. D., the Taiwanese boy band, who formed in 1998 * Big Audio Dynamite, Mick Jones' post-Clash band, from London * Royce da 5'9", the American rapper known as Bad, in the group Bad Meets Evil Albums * ''Bad'' (album), a 1987 album by Michael Jackson * ''BAD'', or ''Bigger and Deffer'', the second album by LL Cool J, 1987 Songs * "Bad" (U2 song), 1984 * "Bad" (Michael Jackson song), 1987 * "Bad", from the 2011 album ''Symphony Soldier'' by The Cab * "Bad" (Wale song), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krems, Carinthia
Krems in Kärnten is a municipality in the district of Spittal an der Drau in Carinthia in Austria. Geography The municipal area is located in the Krems Valley of northern Carinthia, at the border with the Austrian states of Salzburg (Lungau) and Styria (Upper Styria). It stretches down from the Lieser River, a tributary of the Drava, up to the Nock Mountains, part of the Gurktal Alps range. The village of Innerkrems is the starting point of the scenic Nockalm Road to Reichenau, in the north the Schönfeldsattel Pass leads to Thomatal (Bundschuh) in Salzburg. To the west, the Katschberg Pass road and the parallel Tauern Autobahn are significant transport routes. The mountainous region is a popular winter sport destination, including several ski slopes and platter lifts. The Krems municipality is subdivided into seven cadastral communities: Eisentratten, Kremsbrücke, Leoben, Nöring, Puchreit, Reitern, and Sankt Nikolai. History In 1197, Rauchenkatsch Castle was first docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichenau, Carinthia
Reichenau ( sl, Rajnava) is a municipality in the district of Feldkirchen in the Austrian state of Carinthia. Geography The municipal area is situated in the upper valley of the Gurk River within the Nock Mountains range (part of the Gurktal Alps). In the north, the road from Feldkirchen leads up to Turracher Höhe Pass and Turracher See at a height of AA on the border with Predlitz-Turrach in Styria and further down into the Mur Valley. Another small mountain lake is Falkertsee at in the west. Reichenau is the eastern terminus of the ''Nockalmstraße'' scenic route through the Nock Mountains to Krems. Reichenau consists of the cadastral communities Ebene Reichenau, Sankt Lorenzen, Sankt Margarethen, Wiedweg, and Winkl. Neighboring municipalities History The remote and densely forested area of the upper Gurk Valley was settled by Celtic colonists when the region was part of the Noricum kingdom, which in 15 BC was incorporated as a province of the Roman Empire. From a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radenthein
Radenthein ( sl, Radenče ) is a town in Spittal an der Drau District, in the Austrian state of Carinthia. Geography The town is situated in the Gegend valley (''Gegendtal'') of the Nock Mountains range (part of the Gurktal Alps), stretching to the eastern shore of Lake Millstatt. Radenthein borders on the municipalities of Millstatt in the west and Bad Kleinkirchheim in the east. The municipal area comprises the cadastral communities of Döbriach, Kaning, Laufenberg, Radenthein proper, Sankt Peter, and Tweng. History The remote, densely forested valley was not colonized until about 1000. A chapel at ''villam Ratehtim'' was first mentioned in an 1177 deed, then part of the Millstatt Abbey estates within the Duchy of Carinthia; it was raised to a parish in 1262. Since the Middle Ages Radenthein had been an iron ore and garnet mining area and the site of a finery forge, even the use of reverberatory furnaces is documented since the late 18th century. When about 1908 an extensive o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |