|
Avatar (spacecraft)
Avatar ( sa, अवतार, ; from "Aerobic Vehicle for Transatmospheric Hypersonic Aerospace TrAnspoRtation") is a concept study for a robotic single-stage reusable spaceplane capable of horizontal takeoff and landing, by India's Defence Research and Development Organisation. The mission concept is for low cost military and commercial satellite space launches. This spaceplane concept is unrelated to India's RLV Technology Demonstration Programme (RLV-TD). Concept The idea is to develop a spaceplane vehicle that can take off from conventional airfields. Its liquid air cycle engine would collect air in the atmosphere on the way up, liquefy it, separate oxygen and store it on board for subsequent flight beyond the atmosphere. The Avatar, a reusable launch vehicle, was first announced in May 1998 at the Aero India 98 exhibition held at Bangalore. Avatar is projected to weigh 25 tons, of which 60% of that mass would be liquid hydrogen fuel. The oxygen required by the vehicle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes to date have been rocket-powered but then landed as unpowered gliders. Four types of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran, U.S. X-37, and the Chinese CSSHQ. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2019 all past, current, and planned orbital vehicles launch vertically on a separate rocket. Orbital spaceflight takes place at high velocities, with orbital kinetic energies typically at least 50 times greater than suborbital trajectories. Consequently, heavy heat shielding is required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The current comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
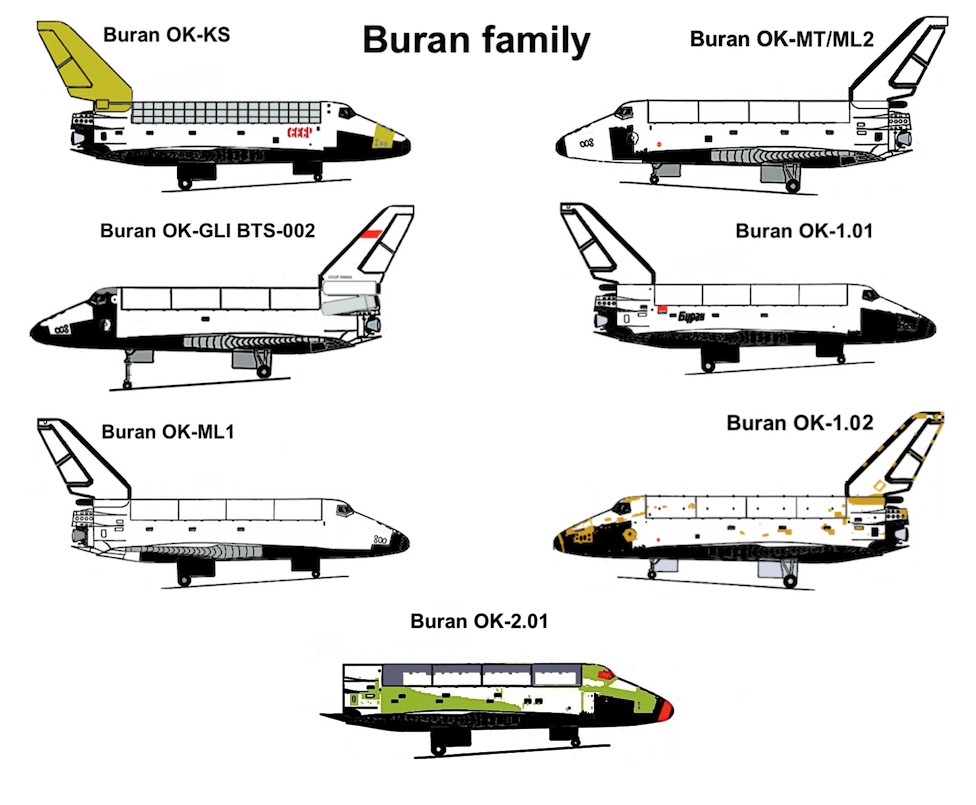
Buran (spacecraft)
''Buran'' (russian: Буран, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing X-37
The Boeing X-37, also known as the Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV), is a reusable robotic spacecraft. It is boosted into space by a launch vehicle, then re-enters Earth's atmosphere and lands as a spaceplane. The X-37 is operated by the United States Space Force for orbital spaceflight missions intended to demonstrate reusable space technologies. It is a 120-percent-scaled derivative of the earlier Boeing X-40. The X-37 began as a NASA project in 1999, before being transferred to the United States Department of Defense in 2004. Until 2019, the program was managed by Air Force Space Command. An X-37 first flew during a drop test in 2006; its first orbital mission was launched in April 2010 on an Atlas V rocket, and returned to Earth in December 2010. Subsequent flights gradually extended the mission duration, reaching in orbit for the fifth mission, the first to launch on a Falcon 9 rocket. The latest mission, the sixth, launched on an Atlas V on 17 May 2020 and concluded on 12 Nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Utah, most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the county seat, seat of Salt Lake County, Utah, Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, the city is the core of the Salt Lake City metropolitan area, which had a population of 1,257,936 at the 2020 census. Salt Lake City is further situated within a larger metropolis known as the Salt Lake City–Provo–Orem Combined Statistical Area, Salt Lake City–Ogden–Provo Combined Statistical Area, a corridor of contiguous urban and suburban development stretched along a segment of the Wasatch Front, comprising a population of 2,746,164 (as of 2021 estimates), making it the 22nd largest in the nation. It is also the central core of the larger of only two major urban areas located within the Great Basin (the other being Reno, Nevada). Salt Lake C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ISRO acts as the executive of DOS as well. ISRO is India's primary agency for performing tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and the development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extraterrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites. The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai, recognising the need in space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within DAE. In 1972, the government of India set up a Space Commissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Entry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides; and ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft capable of being navigated or following a predetermined course. Technologies and procedures allowing the controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass (ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Crewed space vehicles must be slowed to subsonic speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTHL
Aircraft can have different ways to take off and land. Conventional airplanes accelerate along the ground until sufficient lift is generated for takeoff, and reverse the process to land. Some airplanes can take off at low speed, this being a short takeoff. Some aircraft such as helicopters and Harrier jump jets can take off and land vertically. Rockets also usually take off vertically, but some designs can land horizontally. Horizontal takeoff and landing Aircraft Conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) =Takeoff= Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aircraft goes through a transition from moving along the ground (taxiing) to flying in the air, usually starting on a runway. For balloons, helicopters and some specialized fixed-wing aircraft (VTOL aircraft such as the Harrier), no runway is needed. Takeoff is the opposite of landing. =Landing= Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying aircraft or spacecraft (or animals) returns to the ground. When the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Takeoff Weight
The maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) or maximum gross takeoff weight (MGTOW) or maximum takeoff mass (MTOM) of an aircraft is the maximum weight at which the pilot is allowed to attempt to take off, due to structural or other limits. The analogous term for rockets is gross lift-off mass, or GLOW. MTOW is usually specified in units of kilograms or pounds. MTOW is the heaviest weight at which the aircraft has been shown to meet all the airworthiness requirements applicable to it. MTOW of an aircraft is fixed and does not vary with altitude, air temperature, or the length of the runway to be used for takeoff or landing. Maximum permissible takeoff weight or "regulated takeoff weight", varies according to flap setting, altitude, air temperature, length of runway and other factors. It is different from one takeoff to the next, but can never be higher than the MTOW. Certification standards Certification standards applicable to the airworthiness of an aircraft contain many requirements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form. To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully liquid state at atmospheric pressure, H2 needs to be cooled to .IPTS-1968 iupac.org, accessed 2020-01-01 A common method of obtaining liquid hydrogen involves a compressor resembling a jet engine in both appearance and principle. Liquid hydrogen is typically used as a concentrated form of . Storing it as liquid takes less space than storing it as a gas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aero India
Aero India is a biennial air show and aviation exhibition held in Bengaluru, India at the Yelahanka Air Force Station. It is organised by the Defence Exhibition Organisation, Ministry of Defence. Organisers The Defence Ministry of India, Indian Air Force, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Department of Space, the Union Civil Aviation Ministry and other such organisations join hands to organise the Aero India show, making it the largest air show in Asia. Air shows The first edition of the air show was held in 1996. During this Aero India Show, many manufacturers and service providers from the Indian aerospace and aviation industry meet the potential buyers of their products. After 1996, the 4th edition of the air show took place in 2003. About 176 exhibitors from 22 countries all over the world came to grace the show. In the year 2005, more than 380 participants came to the Aero India show's 5th edition. In this show, many military and civil aircraft as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |