|
Archie Lamb
Sir Albert Thomas "Archie" Lamb KBE CMG DFC (23 October 1921 – 19 October 2021) was a British diplomat, writer and RAF fighter pilot. He served as British ambassador to Kuwait from 1974 to 1977, and to Norway from 1978 to 1980. Career Albert Thomas Lamb was born in Britain on 23 October 1921, the son of R. S. Lamb and Violet Lamb (née Haynes). He was educated in Swansea at the Bishop Gore School. He joined the Foreign Office in 1938. On the outbreak of World War II in 1939 he volunteered for the Royal Air Force, but was not called for service until 1941. He did pilot training in Southern Rhodesia; on his way back to Britain in SS ''Oronsay'' his ship was torpedoed and he spent nine days in a lifeboat before being rescued. Commissioned in 1941, he was promoted to flying officer (war-substantive) on 12 March 1943, and to flight lieutenant (war-substantive) on 12 September 1944. He flew combat missions in Hurricanes and Typhoons and was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Ambassador To Norway
The Ambassador of the United Kingdom to Norway is the United Kingdom's foremost diplomatic representative in Norway, and head of the UK's diplomatic mission in Norway. The official title is ''His Britannic Majesty's Ambassador to the Kingdom of Norway''. Norway and the United Kingdom have exchanged diplomats since Norway became independent, when Sir Arthur Herbert was appointed British Minister to Norway on 27 October 1905. England, and later the United Kingdom, has had a diplomatic and/or consular representation in Norway at least since the 17th century. List of heads of mission Ministers to Norway *1905–1910: Sir Arthur Herbert, G.C.V.O. *1911–1923: Sir Mansfeldt Findlay, G.B.E., K.C.M.G. *1923–1929: Rt. Hon. Sir Francis Lindley, G.C.M.G., C.B., C.B.E. *1929–1934: Sir Charles Wingfield, K.C.M.G. *1934–1942: Sir Cecil Dormer, K.C.M.G. Ambassador to the Norwegian Government in Exile *1942–1945: Sir Laurence Collier, K.C.M.G. Ambassadors to Norway *1945–19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to: Government * Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries * Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries ** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government ** Foreign office and foreign minister * United States state law, a legal matter in another state Science and technology * Foreign accent syndrome, a side effect of severe brain injury * Foreign key, a constraint in a relational database Arts and entertainment * Foreign film or world cinema, films and film industries of non-English-speaking countries * Foreign music or world music * Foreign literature or world literature * '' Foreign Policy'', a magazine Music * "Foreign", a song by Jessica Mauboy from her 2010 album '' Get 'Em Girls'' * "Foreign" (Trey Songz song), 2014 * "Foreign", a song by Lil Pump from the album ''Lil Pump'' Other uses * Foreign corporation, a corporation that can do business outside its jurisdiction * Foreign language, a language not spoken by the peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island which makes up around 83 percent of the country's landmass. Bahrain is situated between Qatar and the northeastern coast of Saudi Arabia, to which it is connected by the King Fahd Causeway. According to the 2020 census, the country's population numbers 1,501,635, of which 712,362 are Bahraini nationals. Bahrain spans some , and is the third-smallest nation in Asia after the Maldives and Singapore. The capital and largest city is Manama. Bahrain is the site of the ancient Dilmun civilization.Oman: The Lost Land [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East Centre For Arabic Studies
The Middle East Centre for Arab Studies (MECAS) was an Arabic language college created by the British Army during World War II in Jerusalem, and relocated afterwards as a civilian institution to Lebanon near Beirut where it functioned between 1947–1978. History The Middle East Centre for Arab Studies was established by the British Army during World War II in Jerusalem. Between 1944-1946 it functioned in the requisitioned Austrian Hospice, where it was headed by the English Arabist Bertram Thomas. Its purpose was to teach officers Arabic language and culture. After a short post-war intermezzo in the town of Zarqa in Transjordan, in 1947 it moved to its final location in Shemlan, in the Mount Lebanon Governorate of Lebanon. In Lebanon the college was reopened by the Foreign and Commonwealth Office of the British Government. The college gained notoriety as a "spy school" after it was publicly denounced as such by Kamal Jumblatt speaking in the Lebanese Parliament. Official docume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north of the Danube River and the Bulgarian border. Bucharest was first mentioned in documents in 1459. The city became the capital of Romania in 1862 and is the centre of Romanian media, culture, and art. Its architecture is a mix of historical (mostly Eclectic, but also Neoclassical and Art Nouveau), interbellum ( Bauhaus, Art Deco and Romanian Revival architecture), socialist era, and modern. In the period between the two World Wars, the city's elegant architecture and the sophistication of its elite earned Bucharest the nickname of 'Paris of the East' ( ro, Parisul Estului) or 'Little Paris' ( ro, Micul Paris). Although buildings and districts in the historic city centre were heavily damaged or destroyed by war, earthquakes, and even Nic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of Genoa, which in 2015 became the Metropolitan City of Genoa, had 855,834 resident persons. Over 1.5 million people live in the wider metropolitan area stretching along the Italian Riviera. On the Gulf of Genoa in the Ligurian Sea, Genoa has historically been one of the most important ports on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean: it is currently the busiest in Italy and in the Mediterranean Sea and twelfth-busiest in the European Union. Genoa was the capital of Republic of Genoa, one of the most powerful maritime republics for over seven centuries, from the 11th century to 1797. Particularly from the 12th century to the 15th century, the city played a leading role in the commercial trade in Europe, becoming one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Strong Mayor–Council , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Capitoline Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
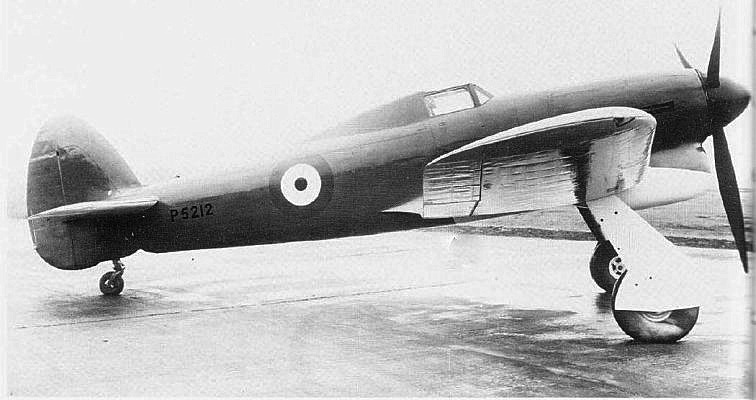
Hawker Typhoon
The Hawker Typhoon is a British single-seat fighter-bomber, produced by Hawker Aircraft. It was intended to be a medium-high altitude interceptor, as a replacement for the Hawker Hurricane, but several design problems were encountered and it never completely satisfied this requirement.Thomas and Shores 1988, p. 16. The Typhoon was originally designed to mount twelve .303 inch (7.7 mm) Browning machine guns and be powered by the latest engines. Its service introduction in mid-1941 was plagued with problems and for several months the aircraft faced a doubtful future. When the ''Luftwaffe'' brought the new Focke-Wulf Fw 190 into service in 1941, the Typhoon was the only RAF fighter capable of catching it at low altitudes; as a result it secured a new role as a low-altitude interceptor. The Typhoon became established in roles such as night-time intruder and long-range fighter. From late 1942 the Typhoon was equipped with bombs and from late 1943 RP-3 rockets were added to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in air forces that use the Royal Air Force (RAF) system of ranks, especially in Commonwealth countries. It has a NATO rank code of OF-2. Flight lieutenant is abbreviated as Flt Lt in the Indian Air Force (IAF) and RAF, and as FLTLT in the Pakistan Air Force (PAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) and Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) and has sometimes also been abbreviated as F/L in many services; it has never been correctly abbreviated as "lieutenant". A flight lieutenant ranks above flying officer and below a squadron leader and is sometimes used as an English language translation of a similar rank in non-English-speaking countries. The rank originated in the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) in 1914. It fell into abeyance when the RNAS merged with the Royal Flying Corps during the First World War but was revived in 1919 in the post-war RAF. An RAF flight lieutenant is the equivalent of a lieutenant in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)