|
Ancistrocladaceae
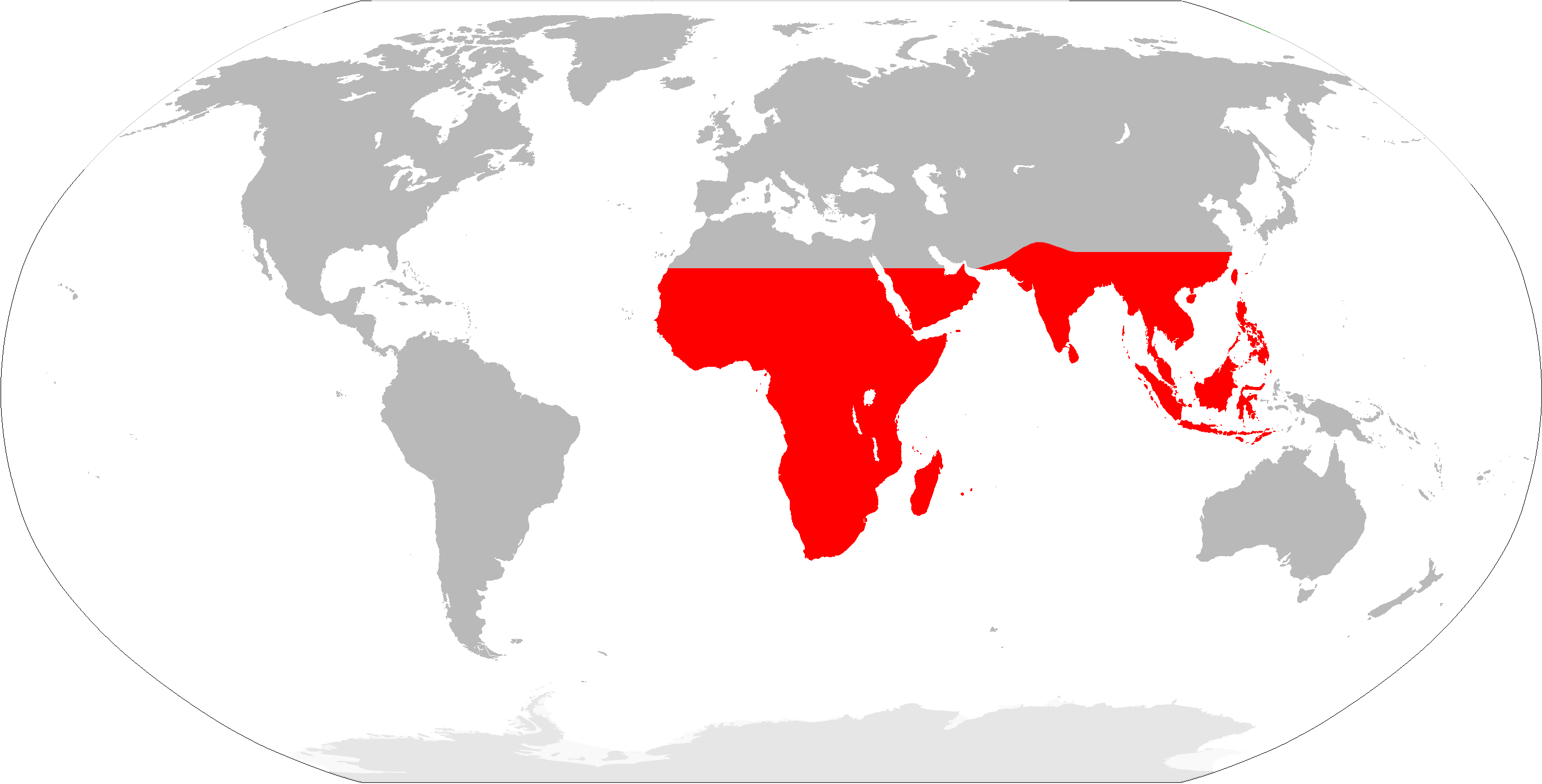
''Ancistrocladus'' is a genus of woody lianas in the monotypic family ''Ancistrocladaceae''. The branches climb by twining other stems or by scrambling with hooked tips. They are found in the tropics of the Old World. Classification The APG II system, of 2003 (unchanged from the APG system, of 1998), also recognizes this family and assigns it to the order Caryophyllales in the clade core eudicots. Recent molecular and biochemical evidence (see thAP-Website suggests the carnivorous taxa in the order Caryophyllales (the families Droseraceae and Nepenthaceae and the species ''Drosophyllum lusitanicum'' and '' Triphyophyllum peltatum'') all belong to the same clade. This family Ancistrocladaceae would belong to this same clade, although the plants in the family are not carnivorous. A close relationship between this family and the family Dioncophyllaceae (containing the carnivorous species ''T. peltatum'') is supported by similar pollen and petiole structure. The Cronquist system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caryophyllales
Caryophyllales ( ) is a diverse and heterogeneous order of flowering plants that includes the cacti, carnations, amaranths, ice plants, beets, and many carnivorous plants. Many members are succulent, having fleshy stems or leaves. The betalain pigments are unique in plants of this order and occur in all its families with the exception of Caryophyllaceae and Molluginaceae. Description The members of Caryophyllales include about 6% of eudicot species. This order is part of the core eudicots. Currently, the Caryophyllales contains 37 families, 749 genera, and 11,620 species The monophyly of the Caryophyllales has been supported by DNA sequences, cytochrome c sequence data and heritable characters such as anther wall development and vessel-elements with simple perforations. Circumscription As with all taxa, the circumscription of Caryophyllales has changed within various classification systems. All systems recognize a core of families with centrospermous ovules and seeds. Mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophyllum Lusitanicum
''Drosophyllum'' ( , rarely ) is a genus of carnivorous plants containing the single species ''Drosophyllum lusitanicum'', commonly known as Portuguese sundew or dewy pine. In appearance, it is similar to the related genus ''Drosera'' (the sundews), and to the much more distantly related ''Byblis'' (the rainbow plants). Description ''Drosophyllum lusitanicum'' is a perennial carnivorous plant with woody stems at the base, short, simple or rarely branched, tortuous or erect. Leaves are basal in a dense rosette, sessile, linear, sheathed, circinate, covered with sessile and pedunculated glands. The caulines are sessile, alternate, the upper bracteiform. Flowers are on top, racemiform or corymbiform and bear five yellow petals. The flower calyx has five lobes and is late deciduous. The plant has ten stamens and introrsal anthers. Gynoecium has five carpels. It has five styles, simple; capitate stigma. Fruit is in a unilocular capsule, and is partially divided into five locules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancistrocladus Heyneanus
''Ancistrocladus heyneanus'' or Kardal is a liana endemic to the Western Ghats of southwestern India India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so .... Leaves are alternate, oblong in shape, 10-25 cm long, margins are entire. References External links About Medicinal researchAbout Medicinal researchDetails about the plant* https://www.lap-publishing.com/catalog/details/store/gb/book/978-3-8473-0181-3/betulinic-acid-from-ancistrocladus-heyneanus-wall-ex-grah Ancistrocladaceae Endemic flora of India (region) Plants described in 1839 {{Caryophyllales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lianas
A liana is a long- stemmed, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and uses trees, as well as other means of vertical support, to climb up to the canopy in search of direct sunlight. The word ''liana'' does not refer to a taxonomic grouping, but rather a habit of plant growth – much like ''tree'' or ''shrub''. It comes from standard French ''liane'', itself from an Antilles French dialect word meaning to sheave. Ecology Lianas are characteristic of tropical moist broadleaf forests (especially seasonal forests), but may be found in temperate rainforests and temperate deciduous forests. There are also temperate lianas, for example the members of the ''Clematis'' or ''Vitis'' (wild grape) genera. Lianas can form bridges amidst the forest canopy, providing arboreal animals with paths across the forest. These bridges can protect weaker trees from strong winds. Lianas compete with forest trees for sunlight, water and nutrients from the soil. Forests without lian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeotropical
The Paleotropical Kingdom (Paleotropis) is a floristic kingdom comprising tropical areas of Africa, Asia and Oceania (excluding Australia and New Zealand), as proposed by Ronald Good and Armen Takhtajan. Part of its flora, inherited from the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana or exchanged later (e.g. Piperaceae with pantropical distribution and but few warm temperate representatives), is shared with the Neotropical Kingdom, comprising tropical areas of Central and South America. Moreover, the Paleotropical flora influenced the tropical flora of the Australian Kingdom. The Paleotropical Kingdom is subdivided into five floristic subkingdoms according to Takhtajan (or three, according to Good) and about 13 floristic regions. In this article the floristic subkingdoms and regions are given as delineated by Takhtajan. Origin A distinct community of vascular plants evolved millions of years ago, and are now found on several separate areas. Millions of years ago, the warmer and wetter areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violales
Violales is a botanical name of an order of flowering plants and takes its name from the included family Violaceae; it was proposed by Lindley (1853). The name has been used in several systems, although some systems used the name Parietales for similar groupings. In the 1981 version of the influential Cronquist system, order Violales was placed in subclass Dilleniidae with a circumscription consisting of the families listed below. Some classifications such as that of Dahlgren placed the Violales in the superorder Violiflorae (also called Violanae). The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) system does not recognize order Violales; Violaceae is placed in order Malpighiales and the other families are reassigned to various orders as indicated. * order Violales Perleb 1826 *: family Achariaceae → order Malpighiales *: family Ancistrocladaceae → order Caryophyllales *: family Begoniaceae → order Cucurbitales *: family Bixaceae → order Malvales *: family Caricaceae → orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cronquist System
The Cronquist system is a taxonomic classification system of flowering plants. It was developed by Arthur Cronquist in a series of monographs and texts, including ''The Evolution and Classification of Flowering Plants'' (1968; 2nd edition, 1988) and ''An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants'' (1981) (''see'' Bibliography). Cronquist's system places flowering plants into two broad classes, Magnoliopsida ( dicotyledons) and Liliopsida (monocotyledons). Within these classes, related orders are grouped into subclasses. While the scheme was widely used, in either the original form or in adapted versions, many botanists now use the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants, first developed in 1998. The system as laid out in Cronquist's ''An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants'' (1981) counts 64 orders and 321 families in class Magnoliopsida and 19 orders and 65 families in class Liliopsida. ''The Evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioncophyllaceae
The Dioncophyllaceae are a family of flowering plants consisting of three species of lianas native to the rainforests of western Africa. Their closest relatives are Ancistrocladaceae. Both families lie within a clade of mostly carnivorous plants which, since 1998 or so, have been moved to the order Caryophyllales. This clade also includes the families Droseraceae (sundews and Venus' flytrap) and Nepenthaceae (an Old World genus of pitcher plants), as well as Drosophyllaceae. All species in the family are lianas at some point in their lifecycles, and climb by the use of pairs of hooks or tendrils formed by the end of the leaf midribs. The best-known member is the carnivorous '' Triphyophyllum peltatum'', although the family contains two other species: ''Habropetalum dawei'' and ''Dioncophyllum thollonii''. History of classification The Cronquist system (1981) had placed the family in order Violales. The APG II system, of 2003 (unchanged from the APG system, of 1998), does rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APG System
The APG system (Angiosperm Phylogeny Group system) of plant classification is the first version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy. Published in 1998 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, it was replaced by the improved APG II in 2003, APG III system in 2009 and APG IV system in 2016. History The original APG system is unusual in being based, not on total evidence, but on the cladistic analysis of the DNA sequences of three genes, two chloroplast genes and one gene coding for ribosomes. Although based on molecular evidence only, its constituent groups prove to be supported by other evidence as well, for example pollen morphology supports the split between the eudicots and the rest of the former dicotyledons. The system is rather controversial in its decisions at the family level, splitting a number of long-established families and submerging some other families. It also is unusual in not using botanical names above the level of order, that is, an orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droseraceae
Droseraceae is a family (biology), family of carnivorous flowering plants, also known as the sundew family. It consists of approximately 180 species in three Extant taxon, extant genera. Representatives of the Droseraceae are found on all continents except Antarctica. Description Droseraceae are carnivorous plant, carnivorous herbaceous plants that may be annuals or perennials. Their leaves are alternate and Glossary of botanical terms#adaxial, adaxially Glossary of botanical terms#circinate, circinate, with at least one leaf surface containing hairs with mucilage-producing glands at the tip. Their flowers are bisexual, usually with three carpels and five sepals, petals and stamens. Their pollen grains are Glossary of botanical terms#triporate, triporate or multiporate and released in Glossary of botanical terms#tetrad, tetrads. Despite being carnivorous, their flowers are insect-pollinated, typically with white to purple flowers that close at night. They produce small see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)