|
Amompharetus
Amompharetus, son of Poliadas, was a Spartan company commander at the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC. The name means "of irreproachable valor". Before the battle, both the Greek and Persian armies camped in front of each other for 10 days on the plain of Plateaea, with only small raids on each side. However, the Persians diverted the Greek water supply and cut off their supply of food, so the Greeks were forced to find a new camp. The plan was for the main contingent of Greeks to set out first during the night, with the Spartans guarding the rear. After the main contingent of Greeks had left the encampment, and it was time for the Spartans to set off to take up the rear, Amompharetus refused to leave the field without a fight, insisting that the unalterable law of Sparta forbade retreat from the battlefield. It took some convincing and rank-pulling on behalf of the Spartan regent, Pausanias, and a not inconsiderable amount of time, to compel Amompharetus and his unit to follow the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
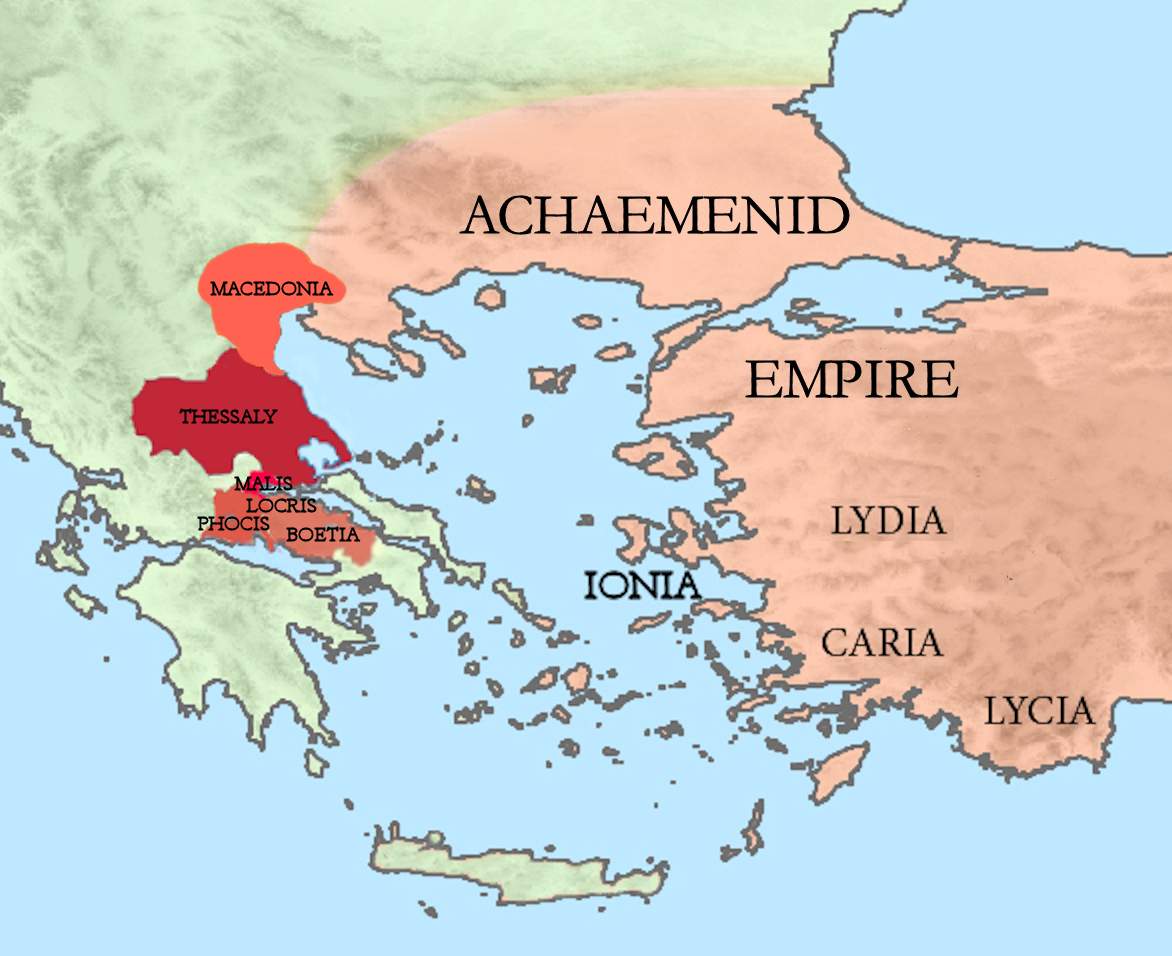
Battle Of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states (including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and Megara), and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I (allied with Greece's Boeotians, Thessalians, and Macedonians). The previous year the Persian invasion force, led by the Persian king in person, had scored victories at the battles of Thermopylae and Artemisium and conquered Thessaly, Phocis, Boeotia, Euboea and Attica. However, at the ensuing Battle of Salamis, the allied Greek navy had won an unlikely but decisive victory, preventing the conquest of the Peloponnesus. Xerxes then retreated with much of his army, leaving his general Mardonius to finish off the Greeks the following year. In the summer of 479 BC the Greeks assembled a huge (by ancient standards) army and marched out of the Peloponnesus. The Persians retreated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (general)
Pausanias ( grc-gre, Παυσανίας; died c. 477 BC) was a Spartan regent and a general. In 479 BC, as a leader of the Hellenic League's combined land forces, Pausanias won a pivotal victory in the Battle of Plataea ending the Second Persian invasion of Greece. One year after the victories over the Persians and the Persians' allies, Pausanias fell under suspicion of conspiring with the Persian king, Xerxes I to betray Greeks and died in 477 BC in Sparta starved to death by fellow citizens. What is known of his life is largely according to Thucydides' ''History of the Peloponnesian War'', Diodorus' ''Bibliotheca historica'' and a handful of other classical sources. Early life Pausanias like all Spartan citizens (Spartiate), would have gone through intense training from the age of seven and was required to be a regular soldier until the age of thirty. Pausanias was from the royal house of the Agiads. Yet this did not exempt him from going through the same training as every o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mardonius (general)
Mardonius ( peo, 𐎶𐎼𐎯𐎢𐎴𐎡𐎹 ; grc-gre, Μαρδόνιος ; died 479 BC) was a leading Persian military commander during the Persian Wars with Greece in the early 5th century BC who died at the Battle of Plataea. Early years Mardonius was the son of Gobryas, a Persian nobleman who had assisted the Achaemenid prince Darius when he claimed the throne. The alliance between the new king and his friend was cemented by diplomatic marriages: Darius married Gobryas' daughter, and Gobryas married Darius' sister. Furthermore, Mardonius married Darius' daughter Artozostra. Thus, Darius the Great was simultaneously Mardonius' uncle, father-in-law, and half-brother-in-law. Persian Wars with the Greeks First Persian invasion of Greece Darius appointed Mardonius as one of his generals and, after the Ionian Revolt, sent him in 492 BC to punish the Greek city-state of Athens for assisting the Ionians. On his way to Athens, he used his army in the Ionian cities to depose th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solon
Solon ( grc-gre, Σόλων; BC) was an Athenian statesman, constitutional lawmaker and poet. He is remembered particularly for his efforts to legislate against political, economic and moral decline in Archaic Athens.Aristotle ''Politics'' 1273b 35–1274a 21 His reforms failed in the short term, yet Solon is credited with having laid the foundations for Athenian democracy.Stanton, G. R. ''Athenian Politics c. 800–500 BC: A Sourcebook'', Routledge, London (1990), p. 76.E. Harris, ''A New Solution to the Riddle of the Seisachtheia'', in ''The Development of the Polis in Archaic Greece'', eds. L. Mitchell and P. Rhodes (Routledge 1997) 103 His constitutional reform also succeeded in overturning most laws established by Draco. Modern knowledge of Solon is limited by the fact that his works only survive in fragments and appear to feature interpolations by later authors and by the general paucity of documentary and archaeological evidence covering Athens in the early 6th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamis Island
Salamis ( ; el, Σαλαμίνα, Salamína; grc, label=Ancient and Katharevousa, Σαλαμίς, Salamís) is the largest Greek island in the Saronic Gulf, about off-coast from Piraeus and about west of central Athens. The chief city, Salamina, lies in the west-facing core of the crescent on Salamis Bay, which opens into the Saronic Gulf. On the eastern side of the island is its main port, Paloukia, in size second in Greece only to the port of Piraeus. Name The traditional etymology of Salamis derives it from the eponymous nymph Salamis, the mother of Cychreus, the legendary first king of the island. A more modern theory considers "Salamis" to come from the root ''sal'' 'salt' and ''-amis'' 'middle'; thus ''Salamis'' would be the place amid salt water. Other fringe theories have attempted to connect the name to the Semitic root Š-L-M 'health, safety, peace', because of the well-sheltered harbor, but have been for the most part rejected by the academic community. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megara
Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, before being taken by Athens. Megara was one of the four districts of Attica, embodied in the four mythic sons of King Pandion II, of whom Nisos was the ruler of Megara. Megara was also a trade port, its people using their ships and wealth as a way to gain leverage on armies of neighboring poleis. Megara specialized in the exportation of wool and other animal products including livestock such as horses. It possessed two harbors, Pagae to the west on the Corinthian Gulf, and Nisaea to the east on the Saronic Gulf of the Aegean Sea. It is part of Athens metropolitan area. Early history According to Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias, the Megarians said that their town owed its origin to Car (Greek mythology), Car, the son of Phoroneus, who bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verdict
In law, a verdict is the formal trier of fact, finding of fact made by a jury on matters or questions submitted to the jury by a judge. In a bench trial, the judge's decision near the end of the trial is simply referred to as a finding. In England and Wales, a coroner's findings used to be called verdicts but are, since 2009, called conclusions (see ). Etymology The term "verdict", from the Latin ''veredictum'', literally means "to say the truth" and is derived from Middle English ''verdit'', from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman: a compound of ''ver'' ("true", from the Latin ''vērus'') and ''dit'' ("speech", from the Latin ''dictum'', the Grammatical gender, neuter past participle of ''dīcere'', to say). Criminal law In a Criminal law, criminal case, the verdict, which may be either "not guilty" or "guilty"—except in Scotland where the verdict of "not proven" is also available—is handed down by the jury. Different counts in the same case may have different verdicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |