|
Agua Puerca
Agua Puerca is a small village in the Mexican state of San Luis Potosí, in the municipality of Tamasopo. It is located in the mountains of the La Huasteca/ Pame-Chichimeca region, about west of Ciudad Valles and west of the port of Tampico, Tamaulipas Tamaulipas (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas), is a state in the northeast region of Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entiti .... Agua Puerca has a population of about 500 people. Its name means "Dirty water," because the water used to be so poor in quality. The town only got electricity in March 2005, and has yet to get running water. When the well in the town is full, people are able to get all of their water from there. When it is dry, however, they must walk over an hour away to get water. The NGO Tools for Development has been assisting the people of the town in many ways, organizing Humanitarian Briga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican State
The states of Mexico are first-level administrative territorial entities of the country of Mexico, which is officially named Mexico, United Mexican States. There are 32 federal entities in Mexico (31 states and the capital, Mexico City, as a separate entity that is not formally a state). States are further divided into municipalities of Mexico, municipalities. Mexico City is divided in boroughs of Mexico City, boroughs, officially designated as or , similar to other state's municipalities but with different administrative powers. List ''Mexico's post agency, Correos de México, does not offer an official list of state name abbreviations, and as such, they are not included below. A list of Mexican states and several versions of their abbreviations can be found Template:Mexico State-Abbreviation Codes, here.'' } , style="text-align: center;" , ''Coahuila de Zaragoza'' , , style="text-align: center;" colspan=2 , Saltillo , style="text-align: right;" , , style="text-align ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí), is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is San Luis Potosí City. Located in Central Mexico, San Luis Potosí is bordered by seven other Mexican states: Nuevo León to the north; Tamaulipas to the north-east; Veracruz to the east; Hidalgo, Querétaro and Guanajuato to the south; and Zacatecas to north-west. In addition to the capital city, other major cities in the state include Ciudad Valles, Matehuala, Rioverde, and Tamazunchale. History In pre-Columbian times, the territory now occupied by the state of San Luis Potosí contained parts of the cultural areas of Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica. Its northern and western-central areas were inhabited by the Otomi and Chichimeca tribes. These indigenous groups were nomadic hunter-gatherers. Although many indigenou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
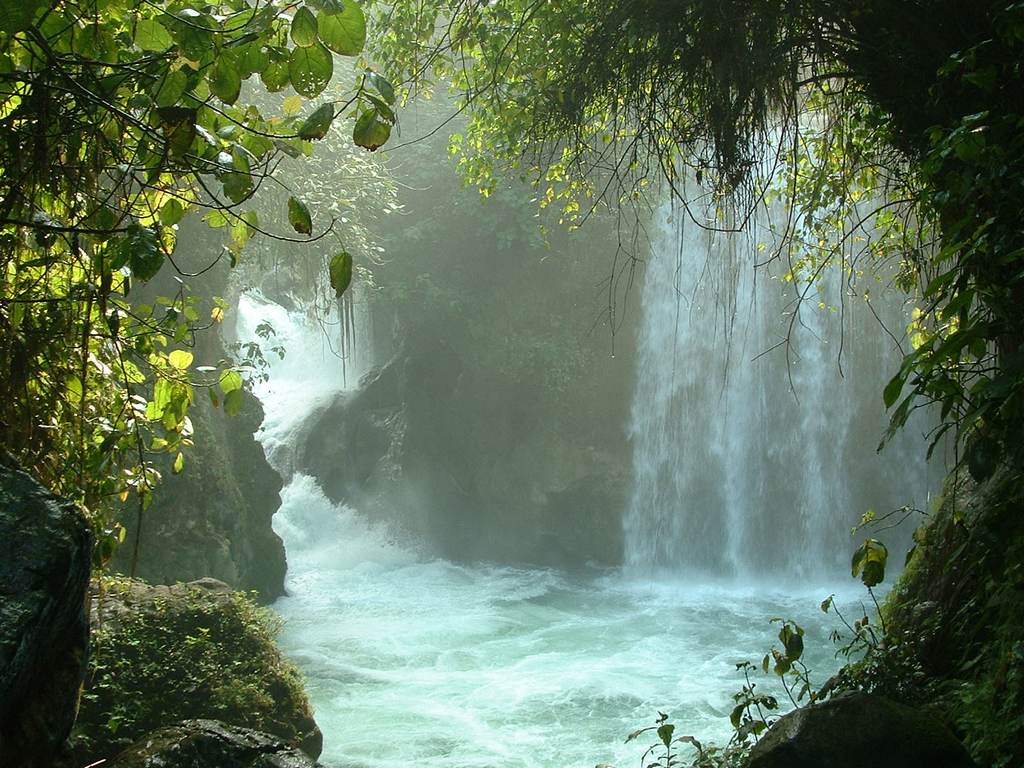
Tamasopo
Tamasopo is a municipality and town in the Mexican state of San Luis Potosí. The town is located at . The municipality had an area of and a population of 28,848 in 2010, including the population of the town of Tamasopo with 4,326 people. Geography Tamasopo is located in the foothills of the Sierra Madre Oriental. The town of Tamosopo has an elevation of . The surrounding mountains rise to about 5,000 feet (1,500 m) above sea level. Tamasopo is famous for its enchanting waterfalls in a lush rain forest El Puente de Dios is two miles (3 km) northwest of Tamasopo town. It consists of waterfalls into a narrow gorge and cavern beneath an arch through which the Gallinas river runs rapidly. Blue and clear water pools for swimming are at the top and bottom of the cavern. The Cascada de Tamasopo is two miles (3 km) north of the town. It features three cascades tumbling about into pools divided by travertine ledges and shelves. The character of the waterfalls rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Huasteca
La Huasteca is a geographical and cultural region located partially along the Gulf of Mexico and including parts of the states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Puebla, Hidalgo, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro and Guanajuato. It is roughly defined as the area in which the Huastec people had influence when their civilization was at its height during the Mesoamerican period. Today, the Huastecs occupy only a fraction of this region with the Nahua people now the most numerous indigenous group. However, those who live in the region share a number of cultural traits such as a style of music and dance, along with religious festivals such as Xantolo. Geography and environment Historically and ethnically, the Huasteca region is defined by the area dominated by the Huastecs at their height. The actual extension of the region is somewhat disputed as well as how it should be sub-divided. Geographically it has been defined as from the Sierra Madre Oriental to the Gulf of Mexico with the Sierra de Tamau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
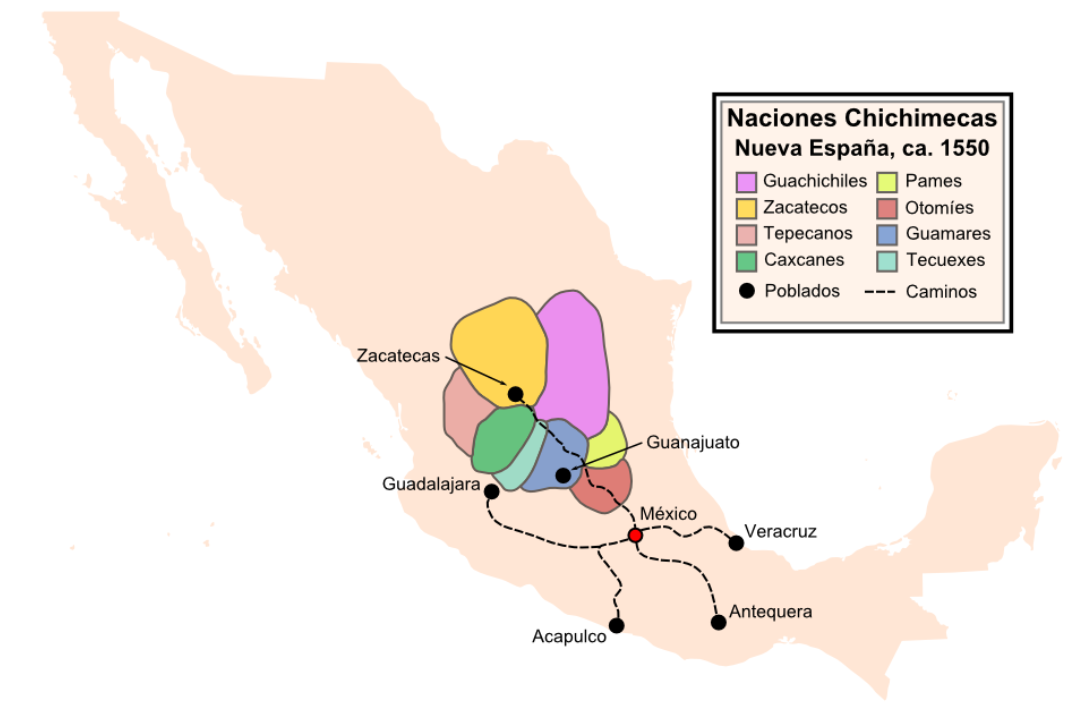
Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajio region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that described Germanic tribes. The name, with its pejorative sense, was adopted by the Spanish Empire. For the Spanish, in the words of scholar Charlotte M. Gradie, "the Chichimecas were a wild, nomadic people who lived north of the Valley of Mexico. They had no fixed dwelling places, lived by hunting, wore little clothes and fiercely resisted foreign intrusion into their territory, which happened to contain silver mines the Spanish wished to exploit." In spite of not having temples or idols, they practiced animal sacrifice, and they were feared for their expertise and brutality in war. The Spanish invasion resulted in a "drastic population decline of all the peoples known collectively as Chichimecas, and to the eventual disappearance as peoples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciudad Valles
Ciudad Valles is the second-largest city in the Mexican state of San Luis Potosí. It is located in the eastern part of the state (), in the cultural region of Huasteca. The city is also the municipal seat of the surrounding municipality of the same name. The city had a 2014 census population of 176,935. Government Ciudad Valles is a municipality governed by a democratically elected Presidente Municipal (Municipal President) or Mayor for a period of three years. Climate Ciudad Valles has a humid tropical climate. During the summer from April to October, Ciudad Valles experiences high temperatures. The all-time high temperature is along with a consistent humidity. In the winter Ciudad Valles has mild temperatures; a few times a year the thermometer registers less than The all-time low is . Transportation The Pan-American Highway or Interamerican Highway built in the 1930s represents Ciudad Valles' most vital corridor. The Highway leads north to Nuevo Laredo via Monterrey, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tampico
Tampico is a city and port in the southeastern part of the state of Tamaulipas, Mexico. It is located on the north bank of the Pánuco River, about inland from the Gulf of Mexico, and directly north of the state of Veracruz. Tampico is the fifth-largest city in Tamaulipas, with a population of 314,418 in the city proper and 929,174 in the metropolitan area. During the period of Mexico's first oil boom in the early 20th century, the city was the "chief oil-exporting port of the Americas" and the second-busiest in the world, yielding great profits that were invested in the city's famous architecture, often compared to that of Venice and New Orleans.Dave Graham, "Crime-ridden state poses acid test for Mexican oil reform" ''Reuters,'' 25 June 2014, accesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas), is a state in the northeast region of Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 43 municipalities. Tamaulipas is bordered by the states of Nuevo León to the west, San Luis Potosí to the southwest, and Veracruz to the southeast. To the north, it has a stretch of the U.S.–Mexico border with the state of Texas, and to the east it is bordered by the Gulf of Mexico. In addition to the capital city, Ciudad Victoria, the state's largest cities include Reynosa, Matamoros, Nuevo Laredo, Tampico, and Mante. Etymology The name Tamaulipas is derived from ''Tamaholipa'', a Huastec term in which the ''tam-'' prefix signifies "place (where)". No scholarly agreement exists on the meaning of ''holipa'', but "high hills" is a common interpretation. Another explanation of the state name is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tools For Development
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates back hundreds of millennia, have been observed using tools to make other tools. Early human tools, made of such materials as stone, bone, and wood, were used for preparation of food, hunting, manufacture of weapons, and working of materials to produce clothing and useful artifacts. The development of metalworking made additional types of tools possible. Harnessing energy sources, such as animal power, wind, or steam, allowed increasingly complex tools to produce an even larger range of items, with the Industrial Revolution marking an inflection point in the use of tools. The introduction of widespread automation in the 19th and 20th centuries allowed tools to operate with minimal human supervision, further increasing the productivity of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_8.33.27.png)