|
Advanced Packaging (semiconductors)
Advanced packaging is the aggregation and interconnection of components before traditional integrated circuit packaging. Advanced packaging allows multiple devices (electrical, mechanical, or semiconductor) to be merged and packaged as a single electronic device. Unlike traditional integrated circuit packaging, advanced packaging employs processes and techniques that are performed at semiconductor fabrication facilities. Advanced packaging thus sits between fabrication and traditional packaging -- or, in other terminology, between BEoL and post-fab. Advanced packaging includes multi-chip modules, 3D ICs, 2.5D ICs, heterogeneous integration, fan-out wafer-level packaging, system-in-package, quilt packaging, combining logic (processors) and memory in a single package, die stacking, several chiplet A chiplet is a tiny integrated circuit (IC) that contains a well-defined subset of functionality. It is designed to be combined with other chiplets on an interposer in a single pack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit Packaging
In electronics manufacturing, integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of semiconductor device fabrication, in which the block of semiconductor material is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. The case, known as a " package", supports the electrical contacts which connect the device to a circuit board. In the integrated circuit industry, the process is often referred to as packaging. Other names include semiconductor device assembly, assembly, encapsulation or sealing. The packaging stage is followed by testing of the integrated circuit. The term is sometimes confused with electronic packaging, which is the mounting and interconnecting of integrated circuits (and other components) onto printed-circuit boards. Design considerations Electrical The current-carrying traces that run out of the die, through the package, and into the printed circuit board (PCB) have very different electrical properties compared to on-chip signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Fabrication Plant
In the microelectronics industry, a semiconductor fabrication plant (commonly called a fab; sometimes foundry) is a factory where devices such as integrated circuits are manufactured. Fabs require many expensive devices to function. Estimates put the cost of building a new fab over one billion U.S. dollars with values as high as $3–4 billion not being uncommon. TSMC invested $9.3 billion in its ''Fab15'' 300 mm wafer manufacturing facility in Taiwan. The same company estimations suggest that their future fab might cost $20 billion. A foundry model emerged in the 1990s: Foundries that produced their own designs were known as integrated device manufacturers (IDMs). Companies that farmed out manufacturing of their designs to foundries were termed fabless semiconductor companies. Those foundries, which did not create their own designs, were called pure-play semiconductor foundries. The central part of a fab is the clean room, an area where the environment is controlled to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronics, electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of Photolithography, photolithographic and chemical processing steps (such as surface passivation, thermal oxidation, planar process, planar diffusion and p–n junction isolation, junction isolation) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer (electronics), wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. The entire manufacturing process takes time, from start to packaged chips ready for shipment, at least six to eight weeks (tape-out only, not including the circuit design) and is performed in highly specialized semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back End Of Line
The back end of line (BEOL) is the second portion of IC fabrication where the individual devices (transistors, capacitors, resistors, etc.) get interconnected with wiring on the wafer, the metalization layer. Common metals are copper and aluminum. BEOL generally begins when the first layer of metal is deposited on the wafer. BEOL includes contacts, insulating layers (dielectrics), metal levels, and bonding sites for chip-to-package connections. After the last FEOL step, there is a wafer with isolated transistors (without any wires). In BEOL part of fabrication stage contacts (pads), interconnect wires, vias and dielectric structures are formed. For modern IC process, more than 10 metal layers can be added in the BEOL. Steps of the BEOL: # Silicidation of source and drain regions and the polysilicon region. # Adding a dielectric (first, lower layer is pre-metal dielectric (PMD) – to isolate metal from silicon and polysilicon), CMP processing it # Make holes in PMD, make a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-chip Module
A multi-chip module (MCM) is generically an electronic assembly (such as a package with a number of conductor terminals or "pins") where multiple integrated circuits (ICs or "chips"), semiconductor dies and/or other discrete components are integrated, usually onto a unifying substrate, so that in use it can be treated as if it were a larger IC. Other terms for MCM packaging include "heterogeneous integration" or "hybrid integrated circuit". The advantage of using MCM packaging is it allows a manufacturer to use multiple components for modularity and/or to improve yields over a conventional monolithic IC approach. Overview Multi-chip modules come in a variety of forms depending on the complexity and development philosophies of their designers. These can range from using pre-packaged ICs on a small printed circuit board (PCB) meant to mimic the package footprint of an existing chip package to fully custom chip packages integrating many chip dies on a high density interconnection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-dimensional Integrated Circuit
A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D IC) is a MOSFET, MOS (metal-oxide semiconductor) integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by stacking as many as 16 or more ICs and interconnecting them vertically using, for instance, through-silicon vias (TSVs) or Cu-Cu connections, so that they behave as a single device to achieve performance improvements at reduced power and smaller footprint than conventional two dimensional processes. The 3D IC is one of several 3D integration schemes that exploit the z-direction to achieve electrical performance benefits in microelectronics and nanoelectronics. 3D integrated circuits can be classified by their level of interconnect hierarchy at the global (Integrated circuit packaging, package), intermediate (bond pad) and local (transistor) level. In general, 3D integration is a broad term that includes such technologies as 3D wafer-level packaging (3DWLP); 2.5D and 3D interposer-based integration; 3D stacked ICs (3D-SICs); monolithic 3D ICs; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Integration
A multi-chip module (MCM) is generically an electronic assembly (such as a package with a number of conductor terminals or "pins") where multiple integrated circuits (ICs or "chips"), semiconductor dies and/or other discrete components are integrated, usually onto a unifying substrate, so that in use it can be treated as if it were a larger IC. Other terms for MCM packaging include "heterogeneous integration" or "hybrid integrated circuit". The advantage of using MCM packaging is it allows a manufacturer to use multiple components for modularity and/or to improve yields over a conventional monolithic IC approach. Overview Multi-chip modules come in a variety of forms depending on the complexity and development philosophies of their designers. These can range from using pre-packaged ICs on a small printed circuit board (PCB) meant to mimic the package footprint of an existing chip package to fully custom chip packages integrating many chip dies on a high density interconnectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
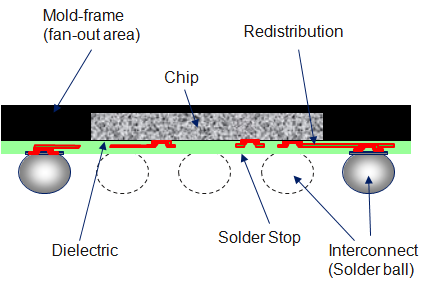
Fan-out Wafer-level Packaging
Fan-out wafer-level packaging (also known as wafer-level fan-out packaging, fan-out WLP, FOWL packaging, FO-WLP, FOWLP, etc.) is an integrated circuit packaging technology, and an enhancement of standard wafer-level packaging (WLP) solutions. In conventional technologies, a wafer is diced first, and then individual dies are packaged; package size is usually considerably larger than the die size. By contrast, in standard WLP flows integrated circuits are packaged while still part of the wafer, and the wafer (with outer layers of packaging already attached) is diced afterwards; the resulting package is practically of the same size as the die itself. However, the advantage of having a small package comes with a downside of limiting the number of external contacts that can be accommodated in the limited package footprint; this may become a significant limitation when complex semiconductor devices requiring a large number of contacts are considered. Fan-out WLP was developed to relax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System In A Package
A system in a package (SiP) or system-in-package is a number of integrated circuits enclosed in one or more chip carrier packages that may be stacked using package on package. The SiP performs all or most of the functions of an electronic system, and is typically used inside a mobile phone, digital music player, etc. Dies containing integrated circuits may be stacked vertically on a substrate. They are internally connected by fine wires that are bonded to the package. Alternatively, with a flip chip technology, solder bumps are used to join stacked chips together. A SiP is like a system on a chip (SoC) but less tightly integrated and not on a single semiconductor die. SiP dies can be stacked vertically or tiled horizontally, unlike less dense multi-chip modules, which place dies horizontally on a carrier. SiP connects the dies with standard off-chip wire bonds or solder bumps, unlike slightly denser three-dimensional integrated circuits which connect stacked silicon dies with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quilt Packaging
Quilt Packaging (QP) is an integrated circuit packaging and chip-to-chip interconnect packaging technology that utilizes “ nodule” structures that extend out horizontally from the edges of microchips to make electrically and mechanically robust chip-to-chip interconnections. QP nodules are created as an integral part of the microchip using standard back end of the line semiconductor device fabrication techniques. Solder is then electroplated on top of the nodules to enable the chip to chip interconnection with sub-micron alignment accuracy. Small high yielding “chiplets” made from any semiconductor material (Silicon, Gallium Arsenide, Silicon Carbide, Gallium Nitride, etc.), can be “quilted” together to create larger multi-function meta-chip. Thus, QP technology can integrate multiple chips with dissimilar technologies or substrate materials in planar, 2.5D and 3D configurations. RF Analog Performance Multiple measured insertion loss on QP interconnec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiplet
A chiplet is a tiny integrated circuit (IC) that contains a well-defined subset of functionality. It is designed to be combined with other chiplets on an interposer in a single package. A set of chiplets can be implemented in a mix-and-match "LEGO-like" assembly. This provides several advantages over a traditional system on chip (SoC): * Reusable IP (Intellectual Property): the same chiplet can be used in many different devices * Heterogeneous integration: chiplets can be fabricated with different processes, materials, and nodes, each optimized for its particular function * Known good die: chiplets can be tested before assembly, improving the yield of the final device Multiple chiplets working together in a single integrated circuit may be called a multi-chip module (MCM), hybrid IC, 2.5D IC, or an advanced package. Chiplets may be connected with standards such as UCIe, Bunch of Wires (BoW), OpenHBI, and OIF XSR. See also * UCIe Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |