|
Augusta Trajana
Stara Zagora ( bg, Стара Загора, ) is the sixth-largest city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of the homonymous Stara Zagora Province. Name The name comes from the Slavic root ''star'' ("old") and the name of the medieval region of Zagore ("beyond the alkanmountains" in Slavic) The original name was Beroe, which was changed to Ulpia Augusta Traiana by the Romans. From the 6th century the city was called Vereja and, from 784, Irenopolis ( Greek: Ειρηνούπολις) in honour of the Byzantine empress Irene of Athens. In the Middle Ages it was called Boruj by the Bulgarians and later, Železnik. The Turks called it Eski Hisar (old fort) and Eski Zagra, from which its current name derives, assigned in 1871. History The original Thracian settlement dates from the 5-4th century BC when it was called Beroe or Beroia. The city was founded by Philip II of Macedon in 342 BC. Under the Roman Empire, the city was renamed ''Ulpia Augusta Traiana'' in ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
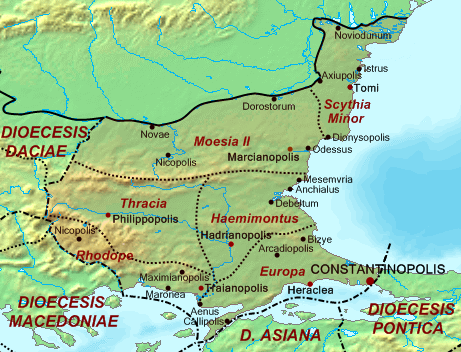
Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD. Confines From the perspective of classical Greece, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia and Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Thracian kingdom as it stood during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. With the annexation of the Thracian kingdom by the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922). Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, but they take their Turkish name, ''Osmanlı'' ("Osman" became altered in some European languages as "Ottoman"), from the house of Osman I (reigned 1299–1326), the founder of the House of Osman, the ruling dynasty of the Ottoman Empire for its entire 624 years. Expanding from its base in Söğüt, the Ottoman principality began incorporating other Turkish-speaking Muslims and non-Turkish Christians. Crossing into Europe from the 1350s, coming to dominate the Mediterranean Sea and, in 1453, invading Constantinople (the capital city of the Byzantine Empire), the Ottoman Turks blocked all major land routes between Asia and Europe. Western Europeans had to find other ways to trade with the East. Brief history The "Ottomans" first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Boruy
The battle of Beroia ( bg, Битка при Боруй) took place in June 1208 near the city of Stara Zagora, Bulgaria between the Bulgarians and the Latin Empire. It resulted in a Bulgarian victory. Origins of the conflict In the summer of 1208 the new Emperor of Bulgaria Boril who continued the war of his predecessor Kaloyan against the Latin Empire invaded Eastern Thrace. The Latin Emperor Henry gathered an army in Selymbria (''Silivri'') and headed to Adrianople (''Odrin''). The battle Upon the news of the Crusaders' march, the Bulgarians retreated to better positions in the area of Beroia (Stara Zagora). At night, they sent the Byzantine captives and the spoil to the north of the Balkan Mountains The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border betw ... and moved in a battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors. The Fourth Crusade had originally been called to retake the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem but a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army sacking the city of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. Originally, the plan had been to restore the deposed Byzantine Emperor Isaac II Angelos, who had been usurped by Alexios III Angelos, to the throne. The crusaders had been promised financial and military aid by Isaac's son Alexios IV, with which they had planned to continue to Jerusalem. When the crusaders reached Constantinople the situation quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms or barbarian tribes to which the empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the empire, for groups of "barbarian" mercenaries of various sizes who were typically allowed to settle within the empire. Roman Republic In the early Roman Republic, ''foederati'' were tribes that were bound by a treaty (''foedus'' ) to come to the defence of Rome but were neither Roman colonies nor beneficiaries of Roman citizenship (''civitas''). Members of the Latini tribe were considered blood allies, but the rest were federates or ''socii''. The friction between the treaty obligations without the corresponding benefits of Romanity led to the Social War between the Romans, with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565. His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals conquered the Ostrogothic kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million ''solidi''. During his reign, Justinian also subdued the ''Tz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic War (376–382)
Between 376 and 382 the Gothic War against the Eastern Roman Empire, and in particular the Battle of Adrianople, is commonly seen as a major turning point in the history of the Roman Empire, the first of a series of events over the next century that would see the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, although its ultimate importance to the Empire's eventual fall is still debated. It was one of the many Gothic Wars with the Roman Empire. Background In the summer of 376, a massive number of Goths arrived on the Danube River, the border of the Roman Empire, requesting asylum from the Huns. There were two groups: the Thervings led by Fritigern and Alavivus and the Greuthungi led by Alatheus and Saphrax. Eunapius states their number as 200,000 including civilians but Peter Heather estimates that the Thervings may have had only 10,000 warriors and 50,000 people in total, with the Greuthungi about the same size. The Cambridge Ancient History places modern estimates at around 90,000 pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serdica
Serdika or Serdica (Bulgarian: ) is the historical Roman name of Sofia, now the capital of Bulgaria. Currently, Serdika is the name of a district located in the city. It includes four neighbourhoods: "Fondovi zhilishta"; "Banishora", "Orlandovtsi" and "Malashevtsi" as well as the central parts of "Draz mahala". It has an area of 17.53 km² that counts for 1.3% of the total Capital Municipality area and 8.8% of the city proper. Serdica has a population of 52,918. There are 6 kindergartens, 13 schools and 6 chitalishta in the territory of the district. Healthcare infrastructure includes II and V City Hospitals; Institute of Transport Medicine and two polyclinics. The Sofia Central Railway Station; Central Bus Station Sofia and the Lavov Most are also located in Serdica. See also *Edict of Serdica (AD 311), through which Emperor Galerius decreed a policy of tolerance towards Christianity *History of Sofia The history of Sofia, Bulgaria's capital and largest city, spans th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocletianopolis (Thrace)
Diocletianopolis ( el, Διοκλητιανούπολις, bg, Диоклецианопол, "Town of Diocletian") was a magnificent ancient Roman town in the region of Thrace, nowadays the town of Hisarya in Bulgaria. Its impressive remains include the enormous defensive walls which still stand close to their original height for the majority of their circuit. There is an on-site museum for the many objects discovered. The site The Roman city was situated on a terrace with valleys on three sides and centred on hot mineral springs. Today the city's interior lies mostly buried under a green park. Excavations are still uncovering more unknown and impressive parts of the city. History Archaeological discoveries show that the site was inhabited from 6,000 years BC probably due to the many hot mineral springs nearby. Later, a Thracian settlement developed there and in the 5th and 4th centuries BC it became a major market town trading with Greek cities on the northern Aegean as evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Beroe
The Battle of Beroe was a conflict near Stara Zagora, ancient ''Ulpia Augusta Traiana'', between the Romans and Goths The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ... in 250 AD which resulted in a Gothic victory. References Beroe Beroe Beroe Beroe Military history of Bulgaria History of Stara Zagora Province Beroe {{AncientRome-battle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia. Diocles rose through the ranks of the military early in his career, eventually becoming a cavalry commander for the army of Emperor Carus. After the deaths of Carus and his son Numerian on a campaign in Persia, Diocles was proclaimed emperor by the troops, taking the name Diocletianus. The title was also claimed by Carus's surviving son, Carinus, but Diocletian defeated him in the Battle of the Margus. Diocletian's reign stabilized the empire and ended the Crisis of the Third Century. He appointed fellow officer Maximian as ''Augustus'', co-emperor, in 286. Diocletian reigned in the Eastern Empire, and Maximian reigned in the Western Empire. Diocletian delegated further on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |