|
Attack On Šabac
The attack on Šabac was attack of the united rebel forces of the Chetniks, Yugoslav Partisans, forces of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia and Pećanac Chetniks against German forces garrisoned in Šabac in Axis-occupied Yugoslavia (modern-day Serbia) in period between 21 and 26 September 1941, during the Uprising in Serbia (1941), Uprising in Serbia. The commander of all forces was Chetnik Captain Dragoslav Račić, commander of the Chetnik ''Cer Detachment'' composed of five companies with about 1,500 soldiers. Račić participated in the battle contrary to instructions of his superior commander Draža Mihailović who refused to allow Chetniks to attack much stronger and well prepared German garrison in Šabac. The Partisan forces of the communist party composed of three detachments with about 1,100 soldiers were commanded by Nebojša Jerković while forces of 500 Pećanac Chetniks were commanded by Bogdan Ilić – Cerski. The Axis forces were under supreme command of General F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uprising In Serbia (1941)
The uprising in Serbia was initiated in July 1941 by the Communist Party of Yugoslavia against the German occupation forces and their Serbian quisling auxiliaries in the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia. At first the Yugoslav Partisans had mounted diversions and conducted sabotage and had attacked representatives of Aćimović's quisling administration. In late August some Chetniks joined the uprising and liberated Loznica. The uprising soon reached mass proportions. Partisans and Chetniks captured towns that weak German garrisons had abandoned. The armed uprising soon engulfed great parts of the occupied territory. The largest liberated territory in occupied Europe was created by the Partisans in western Serbia, and was known as the Republic of Užice. Rebels shared power on the liberated territory; the center of the Partisan liberated territory was in Užice, and Chetniks had their headquarters on Ravna Gora. As the uprising progressed, the ideological rift b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosta Pećanac
Konstantin "Kosta" Milovanović Pećanac ( sr-cyrl, Константин Коста Миловановић Пећанац; 1879–1944) was a Serbian and Yugoslav Chetnik commander ('' vojvoda'') during the Balkan Wars, World War I and World War II. Pećanac fought on the Serbian side in both Balkan Wars and World War I, joining the forces of Kosta Vojinović during the Toplica uprising of 1917. Between the wars he was an important leader of Chetnik veteran associations, and was known for his strong hostility to the Yugoslav Communist Party, which made him popular in conservative circles. As president of the Chetnik Association during the 1930s, he transformed it into an aggressively partisan Serb political organisation with over half a million members. During World War II, Pećanac collaborated with both the German military administration and their puppet government in the German-occupied territory of Serbia. Just before the Axis invasion of Yugoslavia in April 1941, the Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1922–1952) and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (1941–1953). Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, he consolidated power to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically adhering to the Leninist interpretation of Marxism, he formalised these ideas as Marxism–Leninism, while his own policies are called Stalinism. Born to a poor family in Gori in the Russian Empire (now Georgia), Stalin attended the Tbilisi Spiritual Seminary before joining the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. He edited the party's newspaper, ''Pravda'', and raised funds for Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction via robberies, kidnappings and protection rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comintern
The Communist International (Comintern), also known as the Third International, was a Soviet Union, Soviet-controlled international organization founded in 1919 that advocated world communism. The Comintern resolved at its Second Congress to "struggle by all available means, including armed force, for the overthrow of the international bourgeoisie and the creation of an international Soviet republic (system of government), Soviet republic as a transition stage to the complete abolition of the state". The Comintern was preceded by the 1916 dissolution of the Second International. The Comintern held seven World Congresses in Moscow between 1919 and 1935. During that period, it also conducted thirteen Enlarged Plenums of its governing Executive Committee of the Communist International, Executive Committee, which had much the same function as the somewhat larger and more grandiose Congresses. Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union, dissolved the Comintern in 1943 to avoid antag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslav Communists
Yugoslav or Yugoslavian may refer to: * Yugoslavia, or any of the three historic states carrying that name: ** Kingdom of Yugoslavia, a European monarchy which existed 1918–1945 (officially called "Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes" 1918–1929) ** Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia or SFR Yugoslavia, a federal republic which succeeded the monarchy and existed 1945–1992 ** Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, or FR Yugoslavia, a new federal state formed by two successor republics of SFR Yugoslavia established in 1992 and renamed "Serbia and Montenegro" in 2003 before its dissolution in 2006 * Yugoslav government-in-exile, an official government of Yugoslavia, headed by King Peter II * Yugoslav Counter-Intelligence Service * Yugoslav Inter-Republic League * Yugoslav Social-Democratic Party, a political party in Slovenia and Istria during the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Kingdom of Yugoslavia * Serbo-Croatian language, proposed in 1861 and rejected as the legal name of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Occupied Yugoslavia
World War II in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia began on 6 April 1941, when the country was swiftly conquered by Axis forces and partitioned between Germany, Italy, Hungary, Bulgaria and their client regimes. Shortly after Germany attacked the USSR on 22 June 1941, the communist-led republican Yugoslav Partisans, on orders from Moscow, launched a guerrilla liberation war fighting against the Axis forces and their locally established puppet regimes, including the Axis-allied Independent State of Croatia (NDH) and the Government of National Salvation in the German-occupied territory of Serbia. This was dubbed the National Liberation War and Socialist Revolution in post-war Yugoslav communist historiography. Simultaneously, a multi-side civil war was waged between the Yugoslav communist Partisans, the Serbian royalist Chetniks, the Axis-allied Croatian Ustaše and Home Guard, Serbian Volunteer Corps and State Guard, Slovene Home Guard, as well as Nazi-allied Russian Protective Corp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslav Royal Army
The Yugoslav Army ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Jugoslovenska vojska, JV, Југословенска војска, ЈВ), commonly the Royal Yugoslav Army, was the land warfare military service branch of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia (originally Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes). It existed from the Kingdom's formation in December 1918, until its surrender to the Axis powers on 17 April 1941. Aside from fighting along the Austrian border in 1919–20 related to territorial disputes, and some border skirmishes on its southern borders in the 1920s, the JV was not involved in fighting until April 1941 when it was quickly overcome by the German-led invasion of Yugoslavia. Shortly before the Axis invasion of Yugoslavia, Serbian officers of the Yugoslav General Staff, encouraged by the British SOE in Belgrade, led a military coup against Prince Paul and the Cvetković government for adhering to the Tripartite Pact. Beyond the problems of inadequate equipment and incomplete mobilization, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chetnik
The Chetniks ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, Четници, Četnici, ; sl, Četniki), formally the Chetnik Detachments of the Yugoslav Army, and also the Yugoslav Army in the Homeland and the Ravna Gora Movement, was a Yugoslav royalist and Serbian nationalist movement and guerrilla force in Axis-occupied Yugoslavia. Although it was not a homogeneous movement, it was led by Draža Mihailović. While it was anti-Axis in its long-term goals and engaged in marginal resistance activities for limited periods, it also engaged in tactical or selective collaboration with the occupying forces for almost all of the war. The Chetnik movement adopted a policy of collaboration with regard to the Axis, and engaged in cooperation to one degree or another by establishing '' modus vivendi'' or operating as "legalised" auxiliary forces under Axis control. Over a period of time, and in different parts of the country, the movement was progressively drawn into collaboration agreements: first with the puppet Gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravna Gora (highland)
Ravna Gora ( sr-Cyrl, Равна Гора) is a highland in central Serbia, at the mountain of Suvobor. It is renowned as the birthplace of the modern Chetnik movement under the leadership of Dragoljub Mihailović in 1941. Ravna Gora was the site of a celebration marking the 50th anniversary of VE Day in 1995. Among others, the celebration was attended by Major Richard Felman of the United States Air Force, one of more than 400 US airmen rescued by the Chetniks during World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin .... According to statistics compiled by the US Air Force Air Crew Rescue Unit, between 1 January and 15 October 1944, a total of 1,152 American airmen were airlifted from Yugoslavia, 795 with the assistance of the Yugoslav Partisans and 356 with the help of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Invasion Of Yugoslavia
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to: Mathematics * Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis *Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinate dimension * Axis, a line generated by basis vector in a linear algebra Politics *Axis powers of World War II, 1936–1945. *Axis of evil (first used in 2002), U.S. President George W. Bush's description of Iran, Iraq, and North Korea *Axis of Resistance (first used in 2002), the Shia alliance of Iran, Syria, and Hezbollah *Political spectrum, sometimes called an axis Science *Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis *Axis (anatomy), the second cervical vertebra of the spine * ''Axis'' (genus), a genus of deer *Axis, an anatomical term of orientation *Axis, a botanical term meaning the line through the centre of a plant *Optical axis, a line of rotational symmetry * ''Axis'' (journal), online journal published by The Mineralo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Purges In Serbia In 1944–45
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered around common ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange which allocates products to everyone in the society.: "One widespread distinction was that socialism socialised production only while communism socialised production and consumption." Communist society also involves the absence of private property, social classes, money, and the state. Communists often seek a voluntary state of self-governance, but disagree on the means to this end. This reflects a distinction between a more libertarian approach of communization, revolutionary spontaneity, and workers' self-management, and a more vanguardist or communist party-driven approach through the development of a constitutional socialist state f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
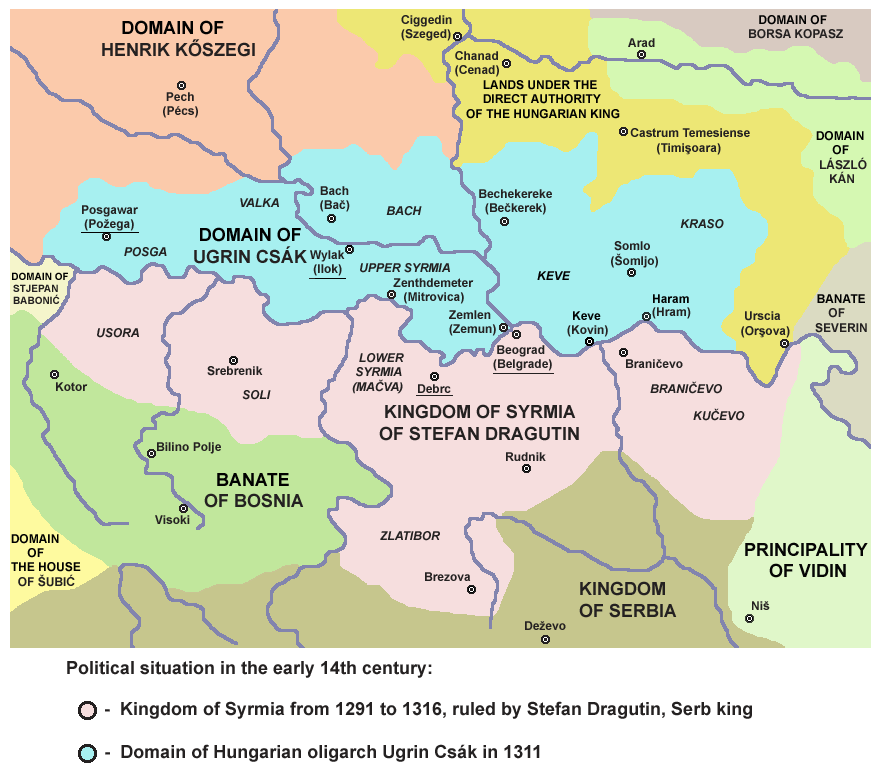
Mačva
Mačva ( sr-Cyrl, Мачва, ; hu, Macsó) is a geographical and historical region in the northwest of Central Serbia, on a fertile plain between the Sava and Drina rivers. The chief town is Šabac. The modern Mačva District of Serbia is named after the region, although the region of Mačva includes only the northern part of this district. A small northern part of Mačva region is in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, in the Syrmia District. Name The region is named after a town of Mačva, which existed in the Medieval Ages near the river Sava. In the past, the region was also known as ''Lower Srem'', while the neighbouring region on the northern bank of the river Sava (present-day Srem) was known as ''Upper Srem''. In Serbian Cyrillic, the region is known as Мачва, in Serbian Latin, Bosnian and Croatian as ''Mačva'', in Hungarian as ''Macsó'' or ''Macsóság'', in Turkish as ''Maçva'', and in German as ''Matschva''. History Throughout history, the region of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |