Mačva on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mačva ( sr-Cyrl, Мачва, ; hu, Macsó) is a geographical and historical region in the northwest of


 The region was then included into
The region was then included into
Beginning in 1918, the region was part of the
 List of largest inhabited places in Mačva (with population figures):
*
List of largest inhabited places in Mačva (with population figures):
*
www.macva.com
{{DEFAULTSORT:Macva Mačva, Geographical regions of Serbia Historical regions in Serbia Geography of Šumadija and Western Serbia Geography of Vojvodina
Central Serbia
Central Serbia ( sr, централна Србија / centralna Srbija), also referred to as Serbia proper ( sr, link=no, ужа Србија / uža Srbija), is the region of Serbia lying outside the autonomous province of Vojvodina to the nort ...
, on a fertile plain between the Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
and Drina
The Drina ( sr-Cyrl, Дрина, ) is a long Balkans river, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps wh ...
rivers. The chief town is Šabac
Šabac (Serbian Cyrillic: Шабац, ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Mačva District in western Serbia. The traditional centre of the fertile Mačva region, Šabac is located on the right banks of the river Sava. , the city p ...
. The modern Mačva District
The Mačva District ( sr, / , ) is one of eight administrative districts of Šumadija and Western Serbia. It expands in the western parts of Serbia, in the geographical regions of Mačva, Podrinje, Posavina, and Pocerina. According to the ...
of Serbia is named after the region, although the region of Mačva includes only the northern part of this district. A small northern part of Mačva region is in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
, in the Syrmia District.
Name
The region is named after a town of Mačva, which existed in the Medieval Ages near the riverSava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
. In the past, the region was also known as ''Lower Srem'', while the neighbouring region on the northern bank of the river Sava (present-day Srem) was known as ''Upper Srem''.
In Serbian Cyrillic
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, th ...
, the region is known as Мачва, in Serbian Latin, Bosnian and Croatian
Croatian may refer to:
* Croatia
*Croatian language
*Croatian people
*Croatians (demonym)
See also
*
*
* Croatan (disambiguation)
* Croatia (disambiguation)
* Croatoan (disambiguation)
* Hrvatski (disambiguation)
* Hrvatsko (disambiguation)
* S ...
as ''Mačva'', in Hungarian as ''Macsó'' or ''Macsóság'', in Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
as ''Maçva'', and in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
as ''Matschva''.
History
Throughout history, the region of Mačva has successively been a part of theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
(1st-4th century); the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
(4th-5th century; 5th-7th century; and 11th-12th century), the Hun Empire (5th century), Avar Khaganate
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars ...
(7th century), the Slavic-controlled territories (7th-9th century), the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
(9th-11th century), the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephe ...
(12th-13th century; 14th century; 15th century; 16th century), the State of Serb king Stefan Dragutin (13th-14th century), the Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
(14th century), the State of Nikola Altomanović (14th century), the Moravian Serbia
Moravian Serbia (), the Principality of Moravian Serbia ( sr, Кнежевина Моравска Србија, translit=Kneževina Moravska Srbija) or the Realm of Prince Lazar are the names used in historiography for the largest and most power ...
(14th century), the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire ...
(15th century), the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
(15th century; 16th-18th century; 18th-19th century), the Kingdom of Serbia under the Habsburg Monarchy (1718–1739), Karađorđe's Serbia
Revolutionary Serbia ( sr, Устаничка Србија / Ustanička Srbija), or Karađorđe's Serbia ( sr, Карађорђева Србија / Karađorđeva Srbija), refers to the state established by the Serbian revolutionaries in Ottoman ...
(1804–1813), the vassal Principality of Serbia
The Principality of Serbia ( sr-Cyrl, Књажество Србија, Knjažestvo Srbija) was an autonomous state in the Balkans that came into existence as a result of the Serbian Revolution, which lasted between 1804 and 1817. Its creation was ...
(1815–1878), the independent Principality of Serbia
The Principality of Serbia ( sr-Cyrl, Књажество Србија, Knjažestvo Srbija) was an autonomous state in the Balkans that came into existence as a result of the Serbian Revolution, which lasted between 1804 and 1817. Its creation was ...
(1878–1882), the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Prin ...
(1882–1918), the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama ...
(1918–1929), the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
(1929–1941), the area governed by the Military Administration in Serbia
The Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia (german: Gebiet des Militärbefehlshabers in Serbien; sr, Подручје Војног заповедника у Србији, Područje vojnog zapovednika u Srbiji) was the area of the Kin ...
(1941–1944), the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Y ...
(1944–1992), the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, Cрбија и Црна Гора, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Y ...
(1992–2003), and Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, Cрбија и Црна Гора, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yu ...
(2003–2006). Since 2006, the region is part of an independent Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hung ...
.
Mačva was inhabited since the Stone Age. Before the Roman conquest, the region was inhabited by Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, a ...
and Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
ic Scordisces. In the first century BC, the region was conquered by the Romans, and Scordisces were pushed to the northern side of the Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
river. During the Roman rule, the region was part of the provinces of Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
and Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
.
Roman rule lasted until the 5th century, and the region was conquered by the Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th ...
, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
, Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
, Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
and Avars. In the 6th century, Slavic tribes settled in the region.



 The region was then included into
The region was then included into Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, Frankish Kingdom
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks duri ...
, and Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
. In the 11th century, the Byzantine province known as the Theme of Sirmium
The Theme of Sirmium ( el, θέμα Σιρμίου) was a Byzantine administrative unit (theme), which existed in present-day Serbia, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina in the 11th century. Its capital was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica).
Backgr ...
included both, the present-day region of Srem and Mačva, thus Srem became the designation for both regions.
In the 13th century, the region was included into the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephe ...
and Banovina of Mačva Banovina may refer to:
* Banovinas of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia from 1929 to 1941
* Banovina (region) in central Croatia, also known as Banija
* ''Radio Banovina'', radio station in the city of Glina, Croatia
* Palace ''Banovina'', governmental b ...
was formed in 1247. Banovina was named after a town called Mačva, but the location of this settlement has not been clearly established in modern times. It is suspected that the town of Mačva existed a few kilometers down the river from modern Šabac
Šabac (Serbian Cyrillic: Шабац, ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Mačva District in western Serbia. The traditional centre of the fertile Mačva region, Šabac is located on the right banks of the river Sava. , the city p ...
.
During the Hungarian administration the region was ruled by several powerful bans. Hungarian king Béla IV granted authority over Mačva to Rostislav Mikhailovich, a refugee Russian prince. In the 13th century, Béla of Macsó (grandson of Béla IV) ruled Mačva as well as Usora and Soli (areas across Drina
The Drina ( sr-Cyrl, Дрина, ) is a long Balkans river, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps wh ...
river in today's northeastern Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
).
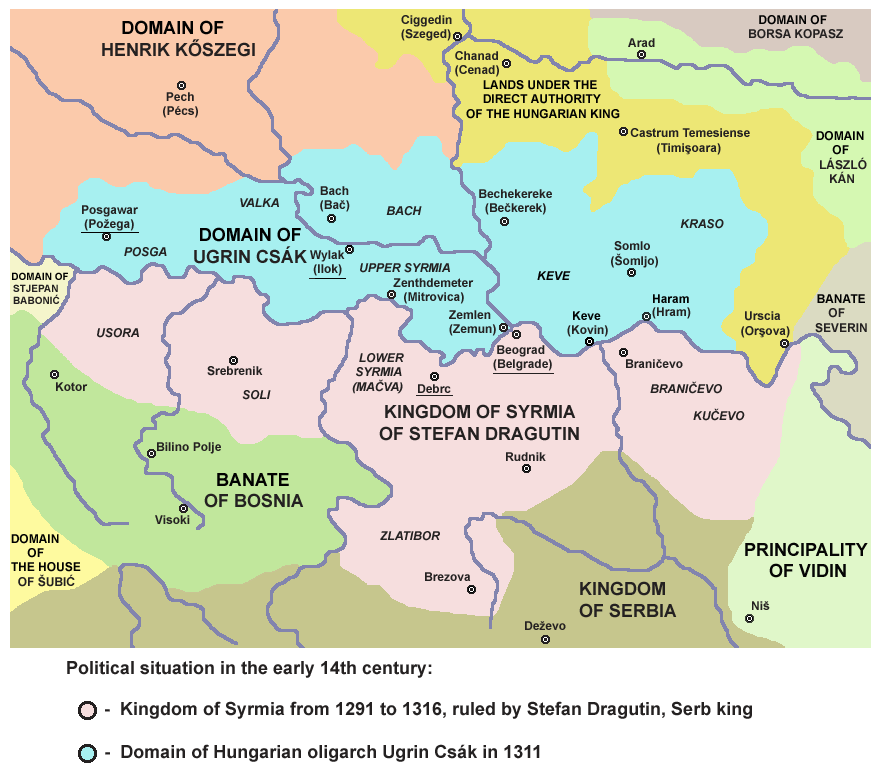
Between 1282 and 1316 the Serb King Stefan Dragutin
Stefan Dragutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Драгутин, hu, Dragutin István; 1244 – 12 March 1316) was King of Serbia from 1276 to 1282. From 1282, he ruled a separate kingdom which included northern Serbia, and (from 1284) the neig ...
ruled the ''Kingdom of Srem'', which consisted of Mačva, Usora, Soli and some adjacent territories. His capital cities were Debrc (between Belgrade and Šabac
Šabac (Serbian Cyrillic: Шабац, ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Mačva District in western Serbia. The traditional centre of the fertile Mačva region, Šabac is located on the right banks of the river Sava. , the city p ...
) and Belgrade. In that time the name ''Srem'' was designation for two territories: ''Upper Srem'' (present day Srem) and ''Lower Srem'' (present day Mačva). Kingdom of Srem under the rule of Stefan Dragutin was located in Lower Srem. According to some sources, Stefan Dragutin also ruled over Upper Srem, but other sources are mentioning another local ruler, Ugrin Csák, who ruled over Upper Srem and Slavonija.
At first, Stefan Dragutin was a vassal of the Hungarian king, but since the central power in the Kingdom of Hungary collapsed, both, Stefan Dragutin and Ugrin Csák were de facto independent rulers. Stephen Dragutin died in 1316, and was succeeded by his son, King Vladislaus II (1316–1324). Vladislaus II was defeated by the king of Serbia, Stefan Dečanski
Stefan Uroš III ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош III, ), known as Stefan Dečanski ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Дечански, ; 1276 – 11 November 1331), was the King of Serbia from 6 January 1322 to 8 September 1331. Dečanski was the son o ...
, in 1324, and after this, Mačva became a subject of dispute between the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Hungary.
In the 14th century, the bans of the Garay family ( Paul Garay, Nicholas I Garay
Nicholas I Garai ( hu, Garai I Miklós, hr, Nikola I Gorjanski) (''c.'' 132525 July 1386) was a most influential officeholder under king Louis I and queen Mary of Hungary. He was ban of Macsó between 1359 and 1375, and palatine from 1375 until h ...
and his son Nicholas II Garay) which were under the Hungarian suzerainty expanded their rule not only to Bosnia but to Srem and the last one also became the ban of Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja, ...
and Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, which was also part of the Kingdom of Hungary at the time. Mačva was part of the Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
of Stefan Dušan
Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан, ), known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr, / ; circa 1308 – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Tsar (or Emperor) and autocrat of the Serbs, Gre ...
and part of the state of the Serbian prince Lazar Hrebeljanović
Lazar Hrebeljanović ( sr-cyr, Лазар Хребељановић; ca. 1329 – 15 June 1389) was a medieval Serbian ruler who created the largest and most powerful state on the territory of the disintegrated Serbian Empire. Lazar's state, ...
.
In the 15th century, Mačva was part of Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire ...
, and since 1459, it was part of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. In the 16th-17th century, Mačva was part of the Ottoman Sanjak of Zvornik
Zvornik ( sr-cyrl, Зворник, ) is a city in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located in Republika Srpska, on the left bank of the Drina river. In 2013, it had a population of 58,856 inhabitants.
The town of Mali Zvornik ("Little Zvornik") li ...
, which was part of the Pashaluk of Bosnia
Eyalets ( Ottoman Turkish: ایالت, , English: State), also known as beylerbeyliks or pashaliks, were a primary administrative division of the Ottoman Empire.
From 1453 to the beginning of the nineteenth century the Ottoman local government ...
. It was under Ottoman administration until 1718, when it was captured by the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. Between 1718 and 1739, Mačva was part of the Habsburg-administered Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Prin ...
, and since 1739, it was again part of the Ottoman Empire. In this time, the region was part of the Ottoman Sanjak of Smederevo. In 1788, the "Mačvanska knežina" ("Princedom of Mačva" - a local administrative unit) had 25 villages with 845 houses. The name of the local administrator ("oberknez") was Uroš Drmanović. Between 1804 and 1815, Mačva was part of Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hung ...
ruled by Karađorđe
Đorđe Petrović ( sr-Cyrl, Ђорђе Петровић, ), better known by the sobriquet Karađorđe ( sr-Cyrl, Карађорђе, lit=Black George, ; – ), was a Serbian revolutionary who led the struggle for his country's indepen ...
. Since 1817, it was part of the autonomous Principality of Serbia
The Principality of Serbia ( sr-Cyrl, Књажество Србија, Knjažestvo Srbija) was an autonomous state in the Balkans that came into existence as a result of the Serbian Revolution, which lasted between 1804 and 1817. Its creation was ...
, and since 1882, part of the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Prin ...
.
During World War I, the Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
army occupied the region and committed war crimes against innocent Serb civilians in Mačva and Podrinje
Podrinje (Serbian Cyrillic: Подриње) is the Slavic name of the Drina river basin, known in English as the Drina Valley. The Drina basin is shared between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia, with majority of its territory being located in ...
Beginning in 1918, the region was part of the
Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama ...
(later renamed Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
). Between 1918 and 1922 the region was part of Podrinjski okrug, between 1922 and 1929 part of Podrinjska oblast, while between 1929 and 1941 it was part of Drina Banovina
The Drina Banovina or Drina Banate ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Drinska banovina, Дринска бановина), was a province ( banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. Its capital was Sarajevo and it included porti ...
. Between 1941 and 1944, Mačva was part of the area governed by the Military Administration in Serbia
The Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia (german: Gebiet des Militärbefehlshabers in Serbien; sr, Подручје Војног заповедника у Србији, Područje vojnog zapovednika u Srbiji) was the area of the Kin ...
, and since 1945, it has been part of the Socialist Republic of Serbia
, life_span = 1944–1992
, status = Constituent state of Yugoslavia
, p1 = Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia
, flag_p1 = Flag of German Reich (1935–1945).svg
, p2 ...
and new socialist Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
. After the breakup of Yugoslavia and Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
, Mačva became part of an independent Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hung ...
.
Geography
Mačva is located in the southern edge ofPannonian basin
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only the ...
, between the Cer and Fruška Gora Mountains. Territory of Mačva is divided among 3 municipalities: Šabac
Šabac (Serbian Cyrillic: Шабац, ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Mačva District in western Serbia. The traditional centre of the fertile Mačva region, Šabac is located on the right banks of the river Sava. , the city p ...
(including 18 settlements of Mačva), Bogatić (including 14 settlements of Mačva), and Sremska Mitrovica
Sremska Mitrovica (; sr-Cyrl, Сремска Митровица, hu, Szávaszentdemeter, la, Sirmium) is a city and the administrative center of the Srem District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the left ban ...
(including 7 settlements of Mačva). Total number of settlements in Mačva is 39, of which 37 are rural, and 2 (Šabac
Šabac (Serbian Cyrillic: Шабац, ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Mačva District in western Serbia. The traditional centre of the fertile Mačva region, Šabac is located on the right banks of the river Sava. , the city p ...
and Mačvanska Mitrovica) are urban.
Inhabited places
 List of largest inhabited places in Mačva (with population figures):
*
List of largest inhabited places in Mačva (with population figures):
* Šabac
Šabac (Serbian Cyrillic: Шабац, ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Mačva District in western Serbia. The traditional centre of the fertile Mačva region, Šabac is located on the right banks of the river Sava. , the city p ...
(55,163)
* Bogatić (7,350)
* Majur (6,854)
* Pocerski Pričinović
Pocerski Pričinović ( sr-cyr, Поцерски Причиновић, ) is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Šabac municipality, in the Mačva District. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 5,992 peopl ...
(5,992)
* Badovinci
Badovinci ( sr-cyr, Бадовинци, ) is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Bogatić municipality, in the Mačva District. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 5,406 people (2002 census).
Name
The name o ...
(5,406)
* Prnjavor Prnjavor is a common South Slavic placename, meaning "village on a monastery's property". It can refer to the following places:
Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Prnjavor, Bosnia and Herzegovina, a town and municipality in northern Bosnia and Herzegovina
* ...
(4,464)
* Mačvanska Mitrovica (3,896)
Note: Mačvanska Mitrovica is geographically located in Mačva, but it is part of Syrmia District (in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
).
Education
Several teachers' associations exist in Mačva.http://www.macvanski.page.tl/ English Language Teachers` Association, Mačva countyFamous people from Mačva
* Rostislav Mikhailovich, a Rus' prince, first Duke of Mačva (after 1248–1262) *Stefan Dragutin
Stefan Dragutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Драгутин, hu, Dragutin István; 1244 – 12 March 1316) was King of Serbia from 1276 to 1282. From 1282, he ruled a separate kingdom which included northern Serbia, and (from 1284) the neig ...
, king of Lower Srem (Mačva) between 1282 and 1316.
* Stefan Vladislav II, king of Lower Srem (1316–1325).
* Uroš Drmanović, oberknez of "Mačvanska knežina" in 1788.
* Stojan Čupić (1765–1815), also known as "Zmaj od Noćaja", was a Serbian voivod in the First Serbian Uprising
The First Serbian Uprising ( sr, Prvi srpski ustanak, italics=yes, sr-Cyrl, Први српски устанак; tr, Birinci Sırp Ayaklanması) was an uprising of Serbs in the Sanjak of Smederevo against the Ottoman Empire from 14 February 1 ...
.
* Milorad Ruvidić (1863 - 1914), Serbian architect.
* Laza Lazarević (1851–1891), Serbian writer and psychiatrist.
* Janko Veselinović (writer), Janko Veselinović (1862–1905), Serbian literate.
* Bora Simić - Joja (born in 1929), poet.
* Milić Stanković (1934–2000), a controversial painter who became known as Milić od Mačve (meaning "Milić of Mačva").
* Dušan Kovačević (born in 1948), literate, dramaturgist.
* Dragan Martinović (born in 1957), painter.
* Nenad Stanković (born in 1965), painter.
* Miloš Blagojević (born in 1989), sculptor.
See also
*Mačva District
The Mačva District ( sr, / , ) is one of eight administrative districts of Šumadija and Western Serbia. It expands in the western parts of Serbia, in the geographical regions of Mačva, Podrinje, Posavina, and Pocerina. According to the ...
* Banate of Mačva
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
www.macva.com
{{DEFAULTSORT:Macva Mačva, Geographical regions of Serbia Historical regions in Serbia Geography of Šumadija and Western Serbia Geography of Vojvodina