|
Asinius Pollio
Gaius Asinius Pollio (75 BC – AD 4) was a Roman soldier, politician, orator, poet, playwright, literary critic, and historian, whose lost contemporaneous history provided much of the material used by the historians Appian and Plutarch. Pollio was most famously a patron of Virgil and a friend of Horace and poems to him were dedicated by both men. Early life Asinius Pollio was born in ''Teate Marrucinorum'', the modern current Chieti in Abruzzi, central Italy. According to an inscription, his father was called Gnaeus Asinius Pollio. He had a brother named Asinius Marrucinus, whom Catullus calls out for his tasteless practical joke, whose name suggests a family origin among the Marrucini. Pollio may therefore have been the grandson of Herius Asinius, a plebeian and a general of the Marrucini who fought on the Italian side in the Social War. Pollio moved in the literary circle of Catullus and entered public life in 56 BC by supporting Lentulus Spinther. In 54, he unsuccessful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerome
Jerome (; ; ; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome. He is best known for his translation of the Bible into Latin (the translation that became known as the Vulgate) and his commentaries on the whole Bible. Jerome attempted to create a translation of the Old Testament based on a Hebrew version, rather than the Septuagint, as Vetus Latina, prior Latin Bible translations had done. His list of writings is extensive. In addition to his biblical works, he wrote polemical and historical essays, always from a theologian's perspective. Jerome was known for his teachings on Christian moral life, especially those in cosmopolitan centers such as Rome. He often focused on women's lives and identified how a woman devoted to Jesus should live her life. This focus stemmed from his close patron relationships with several pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plebs
In ancient Rome, the plebeians or plebs were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary. Etymology The precise origins of the group and the term are unclear, but may be related to the Greek, ''plēthos'', meaning masses. In Latin, the word is a singular collective noun, and its genitive is . Plebeians were not a monolithic social class. In ancient Rome In the annalistic tradition of Livy and Dionysius, the distinction between patricians and plebeians was as old as Rome itself, instituted by Romulus' appointment of the first hundred senators, whose descendants became the patriciate. Modern hypotheses date the distinction "anywhere from the regal period to the late fifth century" BC. The 19th-century historian Barthold Georg Niebuhr believed plebeians were possibly foreigners immigrating from other parts of Italy. This hypothesis, that plebeians were raci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Scribonius Curio (tribune 50 BC)
Gaius Scribonius Curio ( – 49 BC) was the son of Gaius Scribonius Curio and consul in 76 BC. His political allegiances changed over the course of the 50s BC until his tribunate, when he sided with Julius Caesar after possibly receiving a massive bribe. During the civil war, he sided with Caesar and led Caesarian troops to Sicily and then to Africa, where he was killed in battle. Biography Early life Curio was the son of his homonymous father and his wife Memmia, born around 84 BC. Curio and Mark Antony had a close friendship, which was denounced by their political enemies as immoral or possibly an affair. In a defamatory speech against Anthony, Cicero accused Antony of being Curio's lover, claiming that after the two youths had been banned from seeing each other by Curio's father, Curio smuggled Antony in through his father's roof. Opponent of Caesar His first recorded political activity was, with his father, to support Publius Clodius Pulcher in the senat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubicon
The Rubicon (; ; ) is a shallow river in northeastern Italy, just south of Cesena and north of Rimini. It was known as ''Fiumicino'' until 1933, when it was identified with the ancient river Rubicon, crossed by Julius Caesar in 49 BC. The river flows for around from the Apennine Mountains to the Adriatic Sea through the south of the Emilia-Romagna region, between the towns of Rimini and Cesena. Etymology The Latin word comes from the adjective , meaning "red". The river was so named because its waters are colored red by iron deposits in the riverbed. History During the Roman Republic, the Rubicon marked the boundary between the Roman province of Cisalpine Gaul and the areas directly controlled by Rome and its (allies), to the south. On the north-western side, the border was marked by the river Arno, a much wider and more important waterway, which flows westward from the Apennine Mountains (the Arno and the Rubicon rise not far from each other) into the Tyrrhenian Sea. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
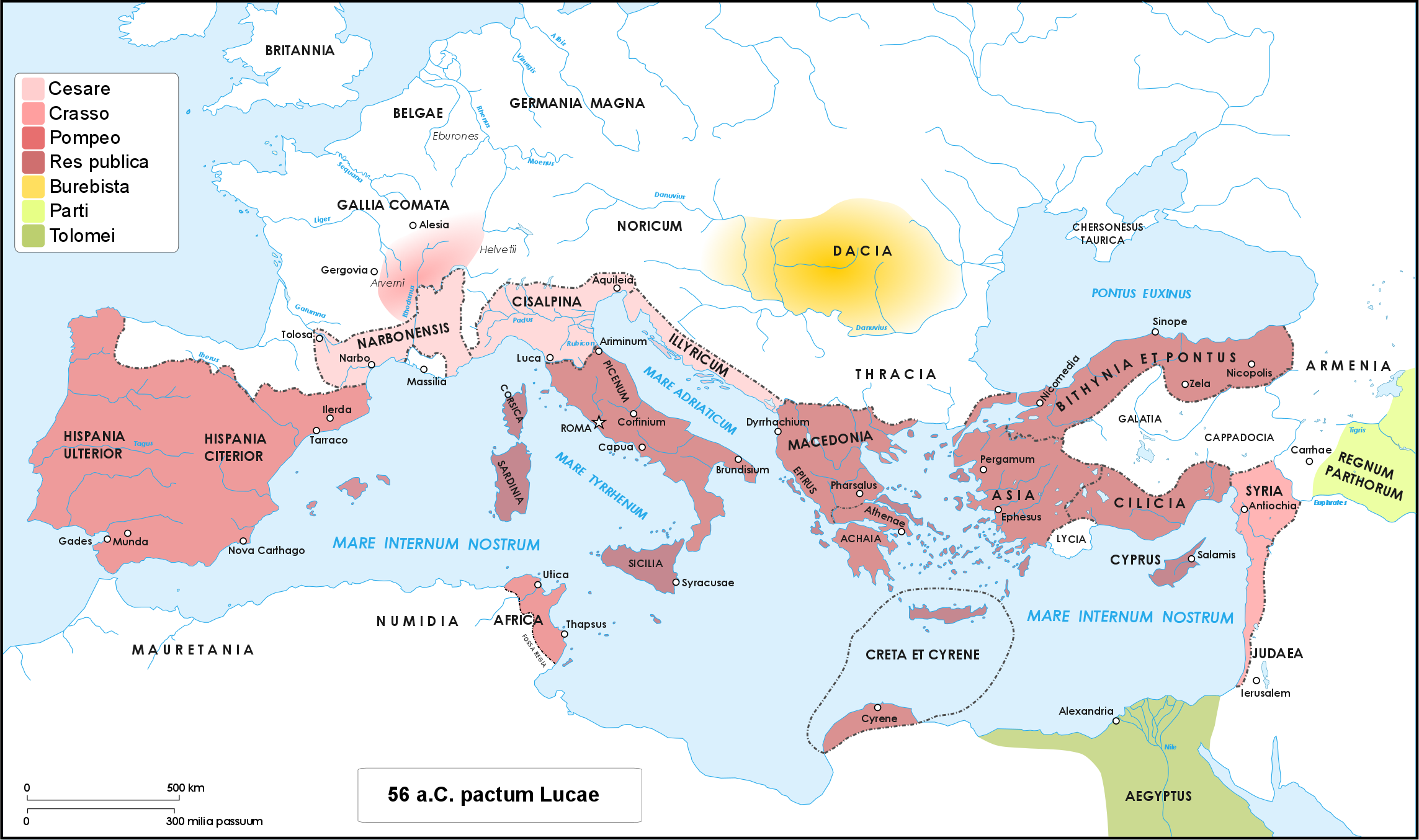
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected return to Rome on the expiration of his Lex Vatinia, governorship in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Before the war, Caesar had led an Gallic Wars, invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 50 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down, led to the outbreak of civil war. Pompey and his allies induced the Roman Senate, Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies in the opening days of 49 BC. Caesar refused and instead Crossing the Rubicon, marched on Rome. The war was fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece in the Roman era, Greece, Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt, Africa (Roman province), Africa, and Hispania. The decisive events occurred in Greece in 48 BC: Pompey defeated Caesar at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome". Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, Irving.Richest People in History Ancient Roman Crassus. Trivia-Library. '' The People's Almanac''. 1975–1981. Web. 23 December 2009."Often named as the richest man ever, a more accurate conversion of sesterce would put his modern figure between $200 million and $20 billion." Peter L. BernsteinThe 20 Richest People Of All Time/ref> Crassus began his public career as a military commander under Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his civil war. Following Sulla's assumption of the dictatorship, Crassus amassed an enormous fortune through property speculation. Crassus rose to political prominence following his victory over the slave revolt led by Spartacus, sharing the consulship with his rival Pompey the Great. A political and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. As a young man, he was a partisan and protégé of the dictator Sulla, after whose death he achieved much military and political success himself. He was an ally and a rival of Julius Caesar, and died in civil war with him. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–81 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first consulship without following the traditional '' cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated three triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Triumvirate
The First Triumvirate was an informal political alliance among three prominent politicians in the late Roman Republic: Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, Marcus Licinius Crassus, and Gaius Julius Caesar. The republican constitution had many veto points. In order to bypass constitutional obstacles and force through the political goals of the three men, they forged an alliance in secret where they promised to use their respective influence to support each other. The "triumvirate" was not a formal magistracy, nor did it achieve a lasting domination over state affairs. It was formed among the three men due to their mutual need to overcome opposition in the senate against their proposals in the previous years. Initially secret, it emerged publicly during Caesar's first consulship in 59 BC to push through legislation for the three allies. Caesar secured passage of an agrarian law which helped resettle Pompey's veterans, a law ratifying Pompey's settlements after the Third Mithridatic War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Porcius Cato (tribune 56 BC)
Gaius Porcius Cato (1st century BC) was a distant relative, probably a second cousin, of the more famous Marcus Porcius Cato, called Cato the Younger. This Cato was probably the son of Gaius Porcius Cato, the homonymous consul of 114 BC, being then the grandson of Marcus Porcius Cato Licinianus and thereby the great-grandson of the famous Cato the Censor, often called Cato the Elder. Gaius Porcius Cato was a client (an adherent) of triumvir Marcus Licinius Crassus and was an ally of Clodius (Publius Clodius Pulcher) the infamous Patrician tribune of the plebs, in his street gang war against Milo (Titus Annius Milo). He attacked Publius Cornelius Lentulus Spinther and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus ( Pompey the Great) in 59 BC by prosecuting a follower, Gabinius, for '' ambitus'' (political corruption) but was thwarted by a Pompeian praetor and was chased from the rostra by an angry crowd. In 57 BC he spoke against delaying the aedelician elections (Clodius was standing and Milo wanted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impeach
Impeachment is a process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements. In Europe and Latin America, impeachment tends to be confined to ministerial officials as the unique nature of their positions may place ministers beyond the reach of the law to prosecute, or their misconduct is not codified into law as an offense except through the unique expectations of their high office. Both " peers and commoners" have been subject to the process, however. From 1990 to 2020, there have been at least 272 impeachment charges against 132 different heads of state in 63 countries. Most democracies (with the notable exception of the United States) involve the courts (often a national constitutional court) in some way. In Latin America, which includes almost 40% of the world's presidential systems, ten presidents from seven countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |