|
Aschenstein
{{Infobox mountain , name = Aschenstein , photo = , photo_size = 282px , photo_alt = , photo_caption = , elevation = {{Höhe, 945, , link=false ({{convert, 945, m, ft, disp=output only, abbr=on) , elevation_ref = , isolation = , isolation_ref = , prominence = , prominence_ref = , listing = , range = Bavarian Forest , parent_peak = , location = Bavaria, Germany , map = Germany Bavaria , map_image = , map_alt = , map_caption = , map_relief = , map_size = , label = , label_position = , coordinates = {{coord, 48.8184, 13.2567, type:mountain_region:DE-BY, format=dms, display=inline,title , topo = , type = , geology = Gneiss , volcanic_arc/belt = , age = , last_eruption = , first_ascent = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian Forest
The village of Zell in the Bavarian Forest The Bavarian Forest (German: ' or ''Bayerwald''; bar, Boarischa Woid) is a wooded, low-mountain region in Bavaria, Germany that is about 100 kilometres long. It runs along the Czech border and is continued on the Czech side by the Bohemian Forest (Czech: ''Šumava''). Most of the Bavarian Forest lies within the province of Lower Bavaria, but the northern part lies within Upper Palatinate. In the south it reaches the border with Upper Austria. Geologically and geomorphologically, the Bavarian Forest is part of the Bohemian Forest - the highest of the truncated highlands of the Bohemian Massif. The area along the Czech border has been designated as the Bavarian Forest National Park (240 km2), established in 1970 as the first national park in Germany. Another 3,008 km2 has been designated as the Bavarian Forest Nature Park, established 1967, and another 1,738 km2 as the Upper Bavarian Forest Nature Park, established in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenting
Zenting is a municipality in the district of Freyung-Grafenau in Bavaria in Germany. Location The municipality lies in the region of Danube Forest (''Donau-Wald'') in the middle of the Bavarian Forest. The village nestles in a sunny, south-facing bowl, above which the Brotjacklriegel (1,016 m) and Aschenstein (945 m) tower to the north. Zenting is located around 35 km NW of Passau, 13 km from Tittling, 18 km SW of Grafenau, 26 km N of Vilshofen an der Donau and 15 km from the A 3 (Iggensbach Iggensbach is a municipality in the district of Deggendorf in Bavaria in Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, a ... exit). References Freyung-Grafenau {{FreyungGrafenau-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geißlstein
The Geißlstein, at 906 metres, is one of the smaller mountains in the Bavarian Forest. It lies east of the Brotjacklriegel and next to the Aschenstein {{Infobox mountain , name = Aschenstein , photo = , photo_size = 282px , photo_alt = , photo_caption = , elevation = {{Höhe, 945, , link=false ({{convert, 945, m, ft, disp=output only .... Its summit has no views. It may only be reached through trackless terrain. Mountains under 1000 metres Mountains of Bavaria Mountains of the Bavarian Forest Regen (district) {{Bavaria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
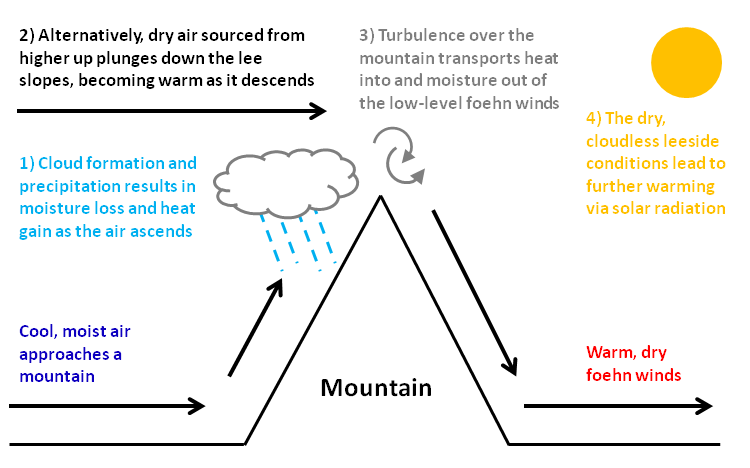
Föhn
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the leeward, lee (downwind side) of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as 14 °C (25 °F) in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (german: Föhn, ) arose in the Alps, Alpine region. Originating from Latin ''(ventus) favonius'', a mild west wind of which Anemoi, Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by rm, favuogn or just ''fuogn'', the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Bavaria
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Under 1000 Metres
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zugspitze
The Zugspitze (), at above Normalhöhennull, sea level, is the highest peak of the Wetterstein Mountains as well as the highest mountain in Germany. It lies south of the town of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, and the Austria–Germany border runs over its western summit. South of the mountain is the ''Zugspitzplatt'', a high karst plateau with numerous caves. On the flanks of the Zugspitze are three glaciers, including the two largest in Germany: the Schneeferner#Northern Schneeferner, Northern Schneeferner with an area of 30.7 hectares and the Höllentalferner with an area of 24.7 hectares. The third is the Schneeferner#Southern Schneeferner, Southern Schneeferner which covers 8.4 hectares. The Zugspitze was first climbed on 27 August 1820 by Josef Naus, his survey assistant, Maier, and mountain guide, Johann Georg Tauschl. Today there are three normal routes to the summit: one from the Höllental (Wetterstein), Höllental valley to the northeast; another out of the Reintal (Wetterste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dachstein (mountain)
Hoher Dachstein () is a strongly karstic mountain in central Austria and the second-highest mountain in the Northern Limestone Alps. It is situated at the border of Upper Austria and Styria, and is the highest point in each of those states. Parts of the massif also lie in the state of Salzburg, leading to the mountain being referred to as the ''Drei-Länder-Berg'' ("three-state mountain"). The Dachstein massif covers an area of around with dozens of peaks above 2,500 m, the highest of which are in the southern and southwestern areas. The main summit of the Hoher Dachstein is at an elevation of . Seen from the north, the Dachstein massif is dominated by glaciers with rocky summits rising beyond them. By contrast, to the south, the mountain drops almost vertically to the valley floor. Geology The geology of the Dachstein massif is dominated by the ''Dachstein-Kalk'' Formation ("Dachstein limestone"), dating from Triassic times. In common with other karstic areas, the Dach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Limestone Alps
The Northern Limestone Alps (german: Nördliche Kalkalpen), also called the Northern Calcareous Alps, are the ranges of the Eastern Alps north of the Central Eastern Alps located in Austria and the adjacent Bavarian lands of southeastern Germany. The distinction from the latter group, where the higher peaks are located, is based on differences in geological composition. Geography If viewed on a west–east axis, the Northern Limestone Alps extend from the Rhine valley and the Bregenz Forest in Vorarlberg, Austria in the west extending along the border between the German federal-state of Bavaria and Austrian Tyrol, through Salzburg, Upper Austria, Styria and Lower Austria and finally ending at the Wienerwald at the city-limits of Vienna in the east. The highest peaks in the Northern Limestone Alps are the Parseierspitze () in the Lechtal Alps,Reynolds, Kev (2010). ''Walking in the Alps'', Cicerone, . and the Hoher Dachstein (). Other notable peaks in this range include the Zugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurmansbang
Thurmansbang is a municipality in the district of Freyung-Grafenau in Bavaria in Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References Freyung-Grafenau {{FreyungGrafenau-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |