|
Articular Process
The articular process or zygapophysis ( + apophysis) of a vertebra is a projection of the vertebra that serves the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the ''articular facet''.Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 Articular processes spring from the junctions of the pedicles and laminæ, and there are two right and left, and two superior and inferior. These stick out of an end of a vertebra to lock with a zygapophysis on the next vertebra, to make the backbone more stable. * The superior processes or prezygapophysis project upward from a lower vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less backward (oblique coronal plane). * The inferior processes or postzygapophysis project downward from a higher vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less forward and outward. The articular surfaces are coated with hyaline cartilage Hyaline cartilage is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebra
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae. They are distinguished by the presence of Zygapophysial joint, facets on the sides of the bodies for Articulation (anatomy), articulation with the head of rib, heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercle (rib), tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoke
A yoke is a wooden beam used between a pair of oxen or other animals to enable them to pull together on a load when working in pairs, as oxen usually do; some yokes are fitted to individual animals. There are several types of yoke, used in different cultures, and for different types of oxen. A pair of oxen may be called a ''yoke of oxen'', and yoke is also a verb, as in "to ''yoke'' a pair of oxen". Other animals that may be yoked include horses, mules, donkeys, and water buffalo. Etymology The word "yoke" is believed to derive from Proto-Indo-European *yugóm (yoke), from root *''yewg''- (join, unite), and is thus cognate with '' yoga''. This root has descendants in almost all known Indo-European languages including German ''Joch'', Latin ''iugum'', Ancient Greek ζυγόν (''zygon''), Persian یوغ (''yuğ''), Sanskrit युग (''yugá''), Hittite 𒄿𒌑𒃷 (iúkan), Old Church Slavonic иго (''igo''), Lithuanian ''jungas'', Old Irish ''cuing'', and Armenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubercle (bone)
In the skeleton of humans and other animals, a tubercle, tuberosity or apophysis is a Tubercle, protrusion or eminence that serves as an attachment for skeletal muscles. The muscles attach by tendons, where the enthesis is the connective tissue between the tendon and bone. A ''tuberosity'' is generally a larger tubercle (bone), tubercle. Main tubercles Humerus The humerus has two tubercles, the greater tubercle and the lesser tubercle. These are situated at the Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, proximal end of the bone, that is the end that connects with the scapula. The greater/lesser tubercule is located from the top of the acromion laterally and inferiorly. Radius The radius has two, the radial tuberosity and Lister's tubercle. Ribs On a rib cage, rib, tubercle is an eminence on the back surface, at the junction between the neck and the body of the rib. It consists of an articular and a non-articular area. The lower and more medial articular area is a small o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedicle Of Vertebral Arch
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamina Of The Vertebral Arch
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmented column of vertebrae that surrounds and protects the spinal cord. The vertebrae are separated by intervertebral discs in a series of cartilaginous joints. The dorsal portion of the spinal column houses the spinal canal, an elongated body cavity, cavity formed by the alignment of the vertebral neural arches that encloses and protects the spinal cord, with spinal nerves exiting via the intervertebral foramina to innervate each body segment. There are around 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human spine is one of the most-studied examples, as the general structure of human vertebrae is fairly homology (biology), typical of that found in other mammals, reptiles, and birds. The shape of the vertebral body does, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has a considerable amount of collagen. It contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is relatively simple. Structure Hyaline cartilage is the most common kind of cartilage in the human body. It is primarily composed of type II collagen and proteoglycans. Hyaline cartilage is located in the trachea, nose, epiphyseal plate, sternum, and ribs. Hyaline cartilage is covered externally by a fibrous membrane known as the perichondrium. The primary cells of cartilage are chondrocytes, which are in a matrix of fibrous tissue, proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. As cartilage does not have lymph glands or blood vessels, the movements of solutes, including nutrients, occur via diffusion within the fluid compartments contiguous with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Pillar
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pars Interarticularis
The pars interarticularis, or pars for short, is the part of a vertebra located between the inferior and superior articular processes of the facet joint. In the transverse plane, it lies between the lamina and pedicle. In other words, in the axial view, it is the bony mass between the facets that is anterior to the lamina and posterior to the pedicle. It is abnormal in spondylolysis, either due to fracture or congenitally. Bilateral C2 pars fractures are known as a variant of the hangman's fracture. On an anterior oblique radiograph of the lumbar spine, the pars is the neck of the imaginary Scottie dog; the Scottie dog's eye is the pedicle, its hindlegs the spinous process, its nose the transverse process, its ear the superior articular facet and its forelegs the inferior articular facet. Stress fractures of the pars interarticularis are known to be associated with playing sports such as volleyball, although the mechanism is somewhat unclear. Patients with spina bifida occulta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
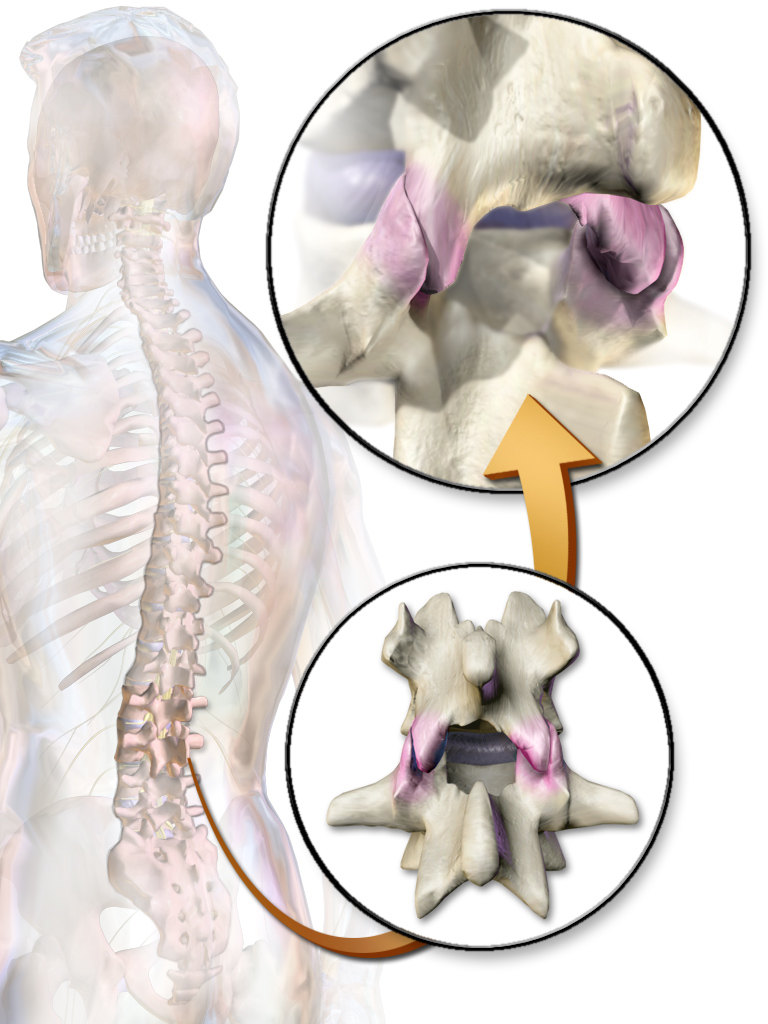
Zygapophyseal Joint
The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each spinal motion segment and each facet joint is innervated by the recurrent meningeal nerves. Innervation Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature. Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the dorsal rami) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions: # The facet joint between C2 and C3 is innervated by the third occipital ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |