Cervical Vertebra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In

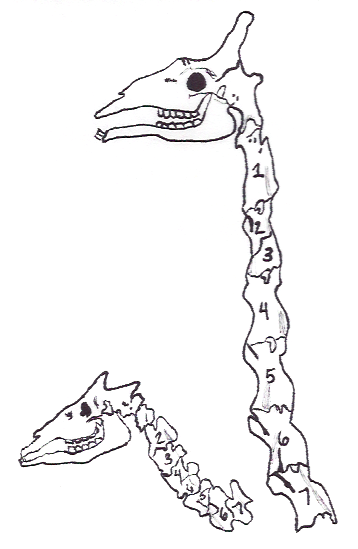 By convention, the cervical
By convention, the cervical
 The vertebra prominens, or C7, has a distinctive long and prominent spinous process, which is palpable from the skin surface. Sometimes, the seventh cervical vertebra is associated with an abnormal extra rib, known as a cervical rib, which develops from the anterior root of the transverse process. These ribs are usually small, but may occasionally compress blood vessels (such as the subclavian artery or subclavian vein) or nerves in the brachial plexus, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the upper limb, a condition known as thoracic outlet syndrome. Very rarely, this rib occurs in a pair.
The long spinous process of C7 is thick and nearly horizontal in direction. It is not bifurcated, and ends in a tubercle that the ligamentum nuchae attaches to. This process is not always the most prominent of the spinous processes, being found only about 70% of the time, C6 or T1 can sometimes be the most prominent.
The transverse processes are of considerable size; their posterior roots are large and prominent, while the anterior are small and faintly marked. The upper surface of each usually has a shallow sulcus for the eighth spinal nerve, and its extremity seldom presents more than a trace of bifurcation.
The transverse foramen may be as large as that in the other cervical vertebrae, but it is generally smaller on one or both sides; occasionally, it is double, and sometimes it is absent.
On the left side, it occasionally gives passage to the vertebral artery; more frequently, the vertebral vein traverses it on both sides, but the usual arrangement is for both artery and vein to pass in front of the transverse process, not through the foramen.
The vertebra prominens, or C7, has a distinctive long and prominent spinous process, which is palpable from the skin surface. Sometimes, the seventh cervical vertebra is associated with an abnormal extra rib, known as a cervical rib, which develops from the anterior root of the transverse process. These ribs are usually small, but may occasionally compress blood vessels (such as the subclavian artery or subclavian vein) or nerves in the brachial plexus, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the upper limb, a condition known as thoracic outlet syndrome. Very rarely, this rib occurs in a pair.
The long spinous process of C7 is thick and nearly horizontal in direction. It is not bifurcated, and ends in a tubercle that the ligamentum nuchae attaches to. This process is not always the most prominent of the spinous processes, being found only about 70% of the time, C6 or T1 can sometimes be the most prominent.
The transverse processes are of considerable size; their posterior roots are large and prominent, while the anterior are small and faintly marked. The upper surface of each usually has a shallow sulcus for the eighth spinal nerve, and its extremity seldom presents more than a trace of bifurcation.
The transverse foramen may be as large as that in the other cervical vertebrae, but it is generally smaller on one or both sides; occasionally, it is double, and sometimes it is absent.
On the left side, it occasionally gives passage to the vertebral artery; more frequently, the vertebral vein traverses it on both sides, but the usual arrangement is for both artery and vein to pass in front of the transverse process, not through the foramen.
File:Computed tomographs of normal cervical vertebrae (thumbnail).jpg, Scrollable computed tomography images of normal cervical vertebrae
File:Cervical vertebrae animation small.gif, Position of cervical vertebrae (shown in red). Animation.
File:Blausen 0222 CervicalSpine.png, Illustration of cervical vertebrae
File:Cervical vertebrae - close-up - animation2.gif, Shape of cervical vertebrae (shown in blue and yellow). Animation.
File:Human cervical vertebra.stl, 3D image
File:Cervical vertebrae lateral3.png, Cervical vertebrae, lateral view (shown in blue and yellow)
File:Illu vertebral column.svg, Vertebral column
File:Gray 111 - Vertebral column-coloured.png, Vertebral column
File:HWS seitlich Annotation.jpg, X-ray of cervical vertebrae
File:Cervical XRayFlexionExtension.jpg, X-ray of cervical spine in flexion and extension
File:Gray86.png, First cervical vertebra, or atlas
File:Gray87.png, Second cervical vertebra, or epistropheus, from above
File:Gray88.png, Second cervical vertebra, epistropheus, or axis, from the side
File:Gray89.png, Seventh cervical vertebra
File:Gray305.png, Posterior atlanto-occipital membrane and atlantoaxial ligament
File:Gray308.png, Median sagittal section through the occipital bone and first three cervical vertebrae
File:Gray384.png, Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra
File:Cervical Spine Anterior View.png, Anterior view of cervical spine showing the vertebral arteries along with the spinal nerves. See this in 3
here.
Diagram
at kenyon.edu
Mnemonic for Landmarks
Cervical vertebra quiz
Cervical vertebrae
- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School {{DEFAULTSORT:Cervical Vertebrae Bones of the head and neck Bones of the thorax Bones of the vertebral column
tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p ...
s, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characterist ...
e of the neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In ...
, immediately below the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, t ...
. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid
Sauropsida ("lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the class Reptilia. Sauropsida is the sister taxon to Synapsida, the other clade of amniotes which includes mammals as its only modern representatives. Although early s ...
species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
s and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living speci ...
with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.
In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
(hole) in each transverse process, through which the in
vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline ...
, vertebral veins, and inferior cervical ganglion pass. The remainder of this article focuses upon human anatomy.
Structure

 By convention, the cervical
By convention, the cervical vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characterist ...
e are numbered, with the first one (C1) closest to the skull and higher numbered vertebrae (C2–C7) proceeding away from the skull and down the spine.
The general characteristics of the third through sixth cervical vertebrae are described here. The first, second, and seventh vertebrae are extraordinary, and are detailed later.
* The bodies of these four vertebrae are small, and broader from side to side than from front to back.
** The ''anterior'' and ''posterior surfaces'' are flattened and of equal depth; the former is placed on a lower level than the latter, and its inferior border is prolonged downward, so as to overlap the upper and forepart of the vertebra below.
** The ''upper surface'' is concave transversely, and presents a projecting lip on either side.
** The ''lower surface'' is concave from front to back, convex from side to side, and presents laterally shallow concavities that receive the corresponding projecting lips of the underlying vertebra.
* The pedicles are directed laterally and backward, and attach to the body midway between its upper and lower borders, so that the superior vertebral notch is as deep as the inferior, but it is, at the same time, narrower.
* The laminae are narrow and thinner above than below; the vertebral foramen
In a typical vertebra, the vertebral foramen is the foramen (opening) formed by the anterior segment (the body), and the posterior part, the vertebral arch.
The vertebral foramen begins at cervical vertebra #1 (C1 or atlas) and continues infer ...
is large and of a triangular form.
* The spinous process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
is short and bifid, the two divisions being often of unequal size. Because the spinous processes are so short, certain superficial muscles (the trapezius and splenius capitis) attach to the nuchal ligament rather than directly to the vertebrae; the nuchal ligament itself attaching to the spinous processes of C2–C7 and to the posterior tubercle of the atlas.
* The superior and inferior articular processes of cervical vertebrae have fused on either or both sides to form articular pillars, columns of bone that project laterally from the junction of the pedicle and lamina.
* The articular facets
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
are flat and of an oval form:
** the ''superior'' face backward, upward, and slightly medially.
** the ''inferior'' face forward, downward, and slightly laterally.
* The transverse processes are each pierced by the foramen transversarium, which, in the upper six vertebrae, gives passage to the vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline ...
and vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
, as well as a plexus of sympathetic nerves
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the ...
. Each process consists of an anterior and a posterior part. These two parts are joined, outside the foramen, by a bar of bone that exhibits a deep sulcus on its upper surface for the passage of the corresponding spinal nerve.
** The anterior portion is the homologue of the rib in the thoracic region, and is therefore named the ''costal process'' or ''costal element''. It arises from the side of the body, is directed laterally in front of the foramen, and ends in a tubercle, the anterior tubercle.
** The posterior part, the true transverse process, springs from the vertebral arch behind the foramen and is directed forward and laterally; it ends in a flattened vertical tubercle, the posterior tubercle.
The anterior tubercle of the sixth cervical vertebra is known as the carotid tubercle or Chassaignac tubercle (for Édouard Chassaignac). This separates the carotid artery from the vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline ...
and the carotid artery can be massaged against this tubercle to relieve the symptoms of supraventricular tachycardia. The carotid tubercle is also used as a landmark for anaesthesia of the brachial plexus and cervical plexus.
The cervical spinal nerves emerge from above the cervical vertebrae. For example, the cervical spinal nerve 3 (C3) passes above C3.
Atlas and axis
Theatlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
(C1) and axis (C2) are the two topmost vertebrae.
The atlas (C1) is the topmost vertebra, and along with the axis forms the joint connecting the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, t ...
and spine. It lacks a vertebral body, spinous process, and discs either superior or inferior to it. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior arch, posterior arch, and two lateral masses.
The axis (C2) forms the pivot on which the atlas rotates. The most distinctive characteristic of this bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
is the strong odontoid process (dens) that rises perpendicularly from the upper surface of the body and articulates with C1. The body is deeper in front than behind, and prolonged downward anteriorly so as to overlap the upper and front part of the third vertebra.
Vertebra prominens
 The vertebra prominens, or C7, has a distinctive long and prominent spinous process, which is palpable from the skin surface. Sometimes, the seventh cervical vertebra is associated with an abnormal extra rib, known as a cervical rib, which develops from the anterior root of the transverse process. These ribs are usually small, but may occasionally compress blood vessels (such as the subclavian artery or subclavian vein) or nerves in the brachial plexus, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the upper limb, a condition known as thoracic outlet syndrome. Very rarely, this rib occurs in a pair.
The long spinous process of C7 is thick and nearly horizontal in direction. It is not bifurcated, and ends in a tubercle that the ligamentum nuchae attaches to. This process is not always the most prominent of the spinous processes, being found only about 70% of the time, C6 or T1 can sometimes be the most prominent.
The transverse processes are of considerable size; their posterior roots are large and prominent, while the anterior are small and faintly marked. The upper surface of each usually has a shallow sulcus for the eighth spinal nerve, and its extremity seldom presents more than a trace of bifurcation.
The transverse foramen may be as large as that in the other cervical vertebrae, but it is generally smaller on one or both sides; occasionally, it is double, and sometimes it is absent.
On the left side, it occasionally gives passage to the vertebral artery; more frequently, the vertebral vein traverses it on both sides, but the usual arrangement is for both artery and vein to pass in front of the transverse process, not through the foramen.
The vertebra prominens, or C7, has a distinctive long and prominent spinous process, which is palpable from the skin surface. Sometimes, the seventh cervical vertebra is associated with an abnormal extra rib, known as a cervical rib, which develops from the anterior root of the transverse process. These ribs are usually small, but may occasionally compress blood vessels (such as the subclavian artery or subclavian vein) or nerves in the brachial plexus, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the upper limb, a condition known as thoracic outlet syndrome. Very rarely, this rib occurs in a pair.
The long spinous process of C7 is thick and nearly horizontal in direction. It is not bifurcated, and ends in a tubercle that the ligamentum nuchae attaches to. This process is not always the most prominent of the spinous processes, being found only about 70% of the time, C6 or T1 can sometimes be the most prominent.
The transverse processes are of considerable size; their posterior roots are large and prominent, while the anterior are small and faintly marked. The upper surface of each usually has a shallow sulcus for the eighth spinal nerve, and its extremity seldom presents more than a trace of bifurcation.
The transverse foramen may be as large as that in the other cervical vertebrae, but it is generally smaller on one or both sides; occasionally, it is double, and sometimes it is absent.
On the left side, it occasionally gives passage to the vertebral artery; more frequently, the vertebral vein traverses it on both sides, but the usual arrangement is for both artery and vein to pass in front of the transverse process, not through the foramen.
Function
The movement of nodding the head takes place predominantly through flexion and extension at the atlanto-occipital joint between the atlas and theoccipital bone
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the c ...
. However, the cervical spine is comparatively mobile, and some component of this movement is due to flexion and extension of the vertebral column itself. This movement between the atlas and occipital bone is often referred to as the "yes joint", owing to its nature of being able to move the head in an up-and-down fashion.
The movement of shaking or rotating the head left and right happens almost entirely at the joint between the atlas and the axis, the atlanto-axial joint
The atlanto-axial joint is a joint in the upper part of the neck between the atlas bone and the axis bone, which are the first and second cervical vertebrae. It is a pivot joint.
Structure
The atlanto-axial joint is a joint between the atlas b ...
. A small amount of rotation of the vertebral column itself contributes to the movement. This movement between the atlas and axis is often referred to as the "no joint", owing to its nature of being able to rotate the head in a side-to-side fashion.
Clinical significance
Cervical degenerative changes arise from conditions such as spondylosis,stenosis
A stenosis (from Ancient Greek στενός, "narrow") is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture' ...
of intervertebral discs, and the formation of osteophytes. The changes are seen on radiographs, which are used in a grading system from 0–4 ranging from no changes (0) to early with minimal development of osteophytes (1) to mild with definite osteophytes (2) to moderate with additional disc space stenosis
A stenosis (from Ancient Greek στενός, "narrow") is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture' ...
or narrowing (3) to the stage of many large osteophytes, severe narrowing of the disc space, and more severe vertebral end plate sclerosis (4).
Injuries to the cervical spine are common at the level of the second cervical vertebrae, but neurological injury is uncommon. C4 and C5 are the areas that see the highest amount of cervical spine trauma.
If it does occur, however, it may cause death or profound disability, including paralysis of the arms, legs, and diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
, which leads to respiratory failure.
Common patterns of injury include the odontoid fracture and the hangman's fracture
Hangman's fracture is the colloquial name given to a fracture of both pedicles, or '' partes interarticulares'', of the ''axis vertebra'' ( C2).
Causes
The injury mainly occurs from falls, usually in elderly adults, and motor accidents mainly d ...
, both of which are often treated with immobilization in a cervical collar
A cervical collar, also known as a neck brace, is a medical device used to support and immobilize a person's neck. It is also applied by emergency personnel to those who have had traumatic head or neck injuries, and can be used to treat chronic m ...
or Halo brace.
A common practice is to immobilize a patient's cervical spine to prevent further damage during transport to hospital. This practice has come under review recently as incidence rates of unstable spinal trauma can be as low as 2% in immobilized patients. In clearing the cervical spine, Canadian studies have developed the Canadian C-Spine Rule (CCR) for physicians to decide who should receive radiological imaging.
Landmarks
Thevertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordate ...
is often used as a marker of human anatomy. This includes:
* At C1, base of the nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next pass ...
and the hard palate
* At C2, the teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, te ...
of a closed mouth
* At C3, the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bon ...
and hyoid bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical verteb ...
* At C4, the common carotid artery bifurcates.
* From C4–5, the thyroid cartilage
* From C6–7, the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
* At C6, the oesophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an Organ (anatomy), organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by Peristalsis, peristaltic contracti ...
becomes continuous with the laryngopharynx and also where the larynx becomes continuous with the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from th ...
. It is also the level where the carotid pulse can be palpated against the transverse process of the C6 vertebrae.
Additional images
here.
See also
*Vertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordate ...
* Cervical fracture
References
External links
Diagram
at kenyon.edu
Mnemonic for Landmarks
Cervical vertebra quiz
Cervical vertebrae
- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School {{DEFAULTSORT:Cervical Vertebrae Bones of the head and neck Bones of the thorax Bones of the vertebral column